|
Coffin Corner (aerodynamics)
Coffin corner (also known as the aerodynamic ceiling or Q corner) is the region of flight where a fast but subsonic fixed-wing aircraft's Stall (flight), stall speed is near the critical Mach number, at a given gross weight and G-force, G-force loading. In this region of flight, it is very difficult to keep an airplane in stable flight. Because the stall speed is the minimum speed required to maintain level flight, any reduction in speed will cause the airplane to stall and lose altitude. Because the critical Mach number is the maximum speed at which air can travel over the wings without losing lift due to flow separation and shock waves, any increase in speed will cause the airplane to lose lift, or to pitch heavily nose-down, and lose altitude. The "corner" refers to the triangular shape at the top of a flight envelope chart where the stall speed and critical Mach number are within a few knots of each other. The "coffin" refers to the possible death in these kinds of stalls. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. Vertical distance measurements in the "down" direction are commonly referred to as depth. In aviation In aviation, the term altitude can have several meanings, and is always qualified by explicitly adding a modifier (e.g. "true altitude"), or implicitly through the context of the communication. Parties exchanging altitude information must be clear which definition is being used. Aviation altitude is measured using either mean sea level (MSL) or local ground level (above ground level, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stall (flight)
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack increases.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 486. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. This occurs when the critical angle of attack of the foil is exceeded. The critical angle of attack is typically about 15°, but it may vary significantly depending on the fluid, foil, and Reynolds number. Stalls in fixed-wing flight are often experienced as a sudden reduction in lift as the pilot increases the wing's angle of attack and exceeds its critical angle of attack (which may be due to slowing down below stall speed in level flight). A stall does not mean that the engine(s) have stopped working, or that the aircraft has stopped moving—the effect is the same even in an unpowered glider aircraft. Vectored thrust in aircraft is used to maintain altitude or controlled flight with wings stalled by replacing lost wing lift with engine or propeller t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Load Factor (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, the load factor is the ratio of the lift of an aircraft to its weightHurt, page 37 and represents a global measure of the stress ("load") to which the structure of the aircraft is subjected: : n = \frac, where : n is the load factor, : L is the lift : W is the weight. Since the load factor is the ratio of two forces, it is dimensionless. However, its units are traditionally referred to as g, because of the relation between load factor and apparent acceleration of gravity felt on board the aircraft. A load factor of one, or 1 g, represents conditions in straight and level flight, where the lift is equal to the weight. Load factors greater or less than one (or even negative) are the result of maneuvers or wind gusts. Load factor and g The fact that the load factor is commonly expressed in ''g'' units does not mean that it is dimensionally the same as the acceleration of gravity, also indicated with ''g''. The load factor is strictly non-dimensional. The use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mach Tuck
Mach tuck is an aerodynamic effect whereby the nose of an aircraft tends to pitch downward as the airflow around the wing reaches supersonic speeds. This diving tendency is also known as tuck under. The aircraft will first experience this effect at significantly below Mach 1. Causes Mach tuck is usually caused by two things, a rearward movement of the centre of pressure of the wing and a decrease in wing downwash velocity at the tailplane both of which cause a nose down pitching moment. For a particular aircraft design only one of these may be significant in causing a tendency to dive, delta-winged aircraft with no foreplane or tailplane in the first case and, for example, the Lockheed P-38 in the second case. Alternatively, a particular design may have no significant tendency, for example the Fokker F28 Fellowship. As an aerofoil generating lift moves through the air, the air flowing over the top surface accelerates to a higher local speed than the air flowing over the botto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
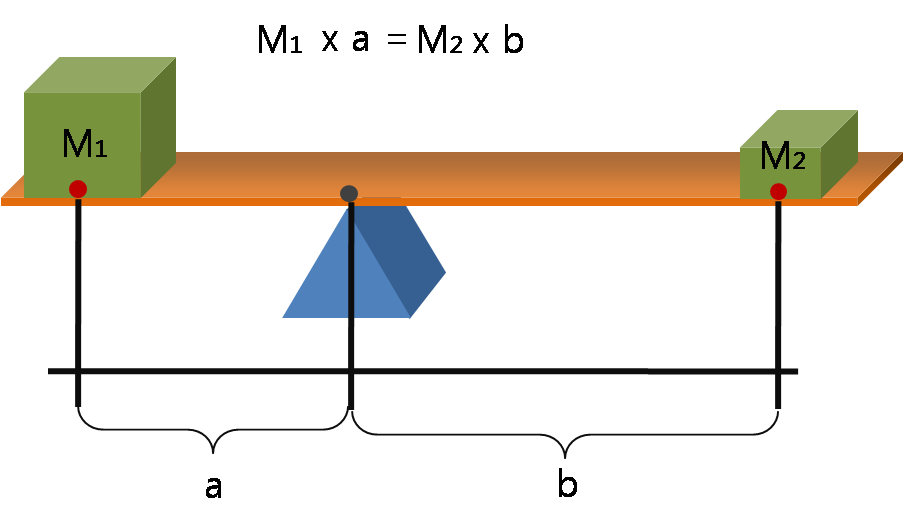
Moment (physics)
In physics, a moment is a mathematical expression involving the product of a distance and physical quantity. Moments are usually defined with respect to a fixed reference point and refer to physical quantities located some distance from the reference point. In this way, the moment accounts for the quantity's location or arrangement. For example, the moment of force, often called torque, is the product of a force on an object and the distance from the reference point to the object. In principle, any physical quantity can be multiplied by a distance to produce a moment. Commonly used quantities include forces, masses, and electric charge distributions. Elaboration In its most basic form, a moment is the product of the distance to a point, raised to a power, and a physical quantity (such as force or electrical charge) at that point: : \mu_n = r^n\,Q, where Q is the physical quantity such as a force applied at a point, or a point charge, or a point mass, etc. If the quantity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Pressure (fluid Mechanics)
In fluid mechanics, the center of pressure is the point where the total sum of a pressure field acts on a body, causing a force to act through that point. The total force vector acting at the center of pressure is the surface integral of the pressure vector field across the surface of the body. The resultant force and center of pressure location produce an equivalent force and moment on the body as the original pressure field. Pressure fields occur in both static and dynamic fluid mechanics. Specification of the center of pressure, the reference point from which the center of pressure is referenced, and the associated force vector allows the moment generated about any point to be computed by a translation from the reference point to the desired new point. It is common for the center of pressure to be located on the body, but in fluid flows it is possible for the pressure field to exert a moment on the body of such magnitude that the center of pressure is located outside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag Divergence Mach Number
The drag-divergence Mach number (not to be confused with critical Mach number) is the Mach number at which the aerodynamic drag on an airfoil or airframe begins to increase rapidly as the Mach number continues to increase. This increase can cause the drag coefficient to rise to more than ten times its low-speed value. The value of the drag-divergence Mach number is typically greater than 0.6; therefore it is a transonic effect. The drag-divergence Mach number is usually close to, and always greater than, the critical Mach number. Generally, the drag coefficient peaks at Mach 1.0 and begins to decrease again after the transition into the supersonic regime above approximately Mach 1.2. The large increase in drag is caused by the formation of a shock wave on the upper surface of the airfoil, which can induce flow separation and adverse pressure gradients on the aft portion of the wing. This effect requires that aircraft intended to fly at supersonic speeds have a large amount of thrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Waves
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distance. When a shock wave passes through m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mach Number
Mach number (M or Ma) (; ) is a dimensionless quantity in fluid dynamics representing the ratio of flow velocity past a boundary to the local speed of sound. It is named after the Moravian physicist and philosopher Ernst Mach. : \mathrm = \frac, where: : is the local Mach number, : is the local flow velocity with respect to the boundaries (either internal, such as an object immersed in the flow, or external, like a channel), and : is the speed of sound in the medium, which in air varies with the square root of the thermodynamic temperature. By definition, at Mach1, the local flow velocity is equal to the speed of sound. At Mach0.65, is 65% of the speed of sound (subsonic), and, at Mach1.35, is 35% faster than the speed of sound (supersonic). Pilots of high-altitude aerospace vehicles use flight Mach number to express a vehicle's true airspeed, but the flow field around a vehicle varies in three dimensions, with corresponding variations in local Mach number. The local spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Standard Atmosphere
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is a static atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes or elevations. It has been established to provide a common reference for temperature and pressure and consists of tables of values at various altitudes, plus some formulas by which those values were derived. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) publishes the ISA as an international standard, ISO 2533:1975.International Organization for Standardization, Standard Atmosphere', ISO 2533:1975, 1975. Other standards organizations, such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the United States Government, publish extensions or subsets of the same atmospheric model under their own standards-making authority. Description The ISA mathematical model divides the atmosphere into layers with an assumed linear distribution of absolute temperature ''T'' against geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere; which are two of the five layers of the atmosphere of Earth. The tropopause is a thermodynamic gradient-stratification layer, that marks the end of the troposphere, and lies approximately above the equatorial regions, and approximately above the polar regions. Definition Rising from the planetary surface of the Earth, the tropopause is the atmospheric level where the air ceases to become cool with increased altitude, and becomes dry, devoid of water vapor. The tropopause is the boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere, and is the part of the atmosphere where there occurs an abrupt change in the environmental lapse rate (ELR), from a positive rate in the troposphere to a negative rate in the stratosphere. The ELR indicates the lowest level at which the lapse rate decreases to 2°C/km or less, provided that the average lapse-rate, between that level and all othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)