|
Cochran's Q Test
In statistics, in the analysis of two-way randomized block designs where the response variable can take only two possible outcomes (coded as 0 and 1), Cochran's Q test is a non-parametric statistical test to verify whether ''k'' treatments have identical effects. It is named after William Gemmell Cochran. Cochran's Q test should not be confused with Cochran's C test, which is a variance outlier test. Put in simple technical terms, Cochran's Q test requires that there only be a binary response (e.g. success/failure or 1/0) and that there be more than 2 groups of the same size. The test assesses whether the proportion of successes is the same between groups. Often it is used to assess if different observers of the same phenomenon have consistent results (interobserver variability). Background Cochran's Q test assumes that there are ''k'' > 2 experimental treatments and that the observations are arranged in ''b'' blocks; that is, Description Cochran's Q test is :Null hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomized Block Design
In the statistical theory of the design of experiments, blocking is the arranging of experimental units in groups (blocks) that are similar to one another. Blocking can be used to tackle the problem of pseudoreplication. Use Blocking reduces unexplained variability. Its principle lies in the fact that variability which cannot be overcome (e.g. needing two batches of raw material to produce 1 container of a chemical) is confounded or aliased with a(n) (higher/highest order) interaction to eliminate its influence on the end product. High order interactions are usually of the least importance (think of the fact that temperature of a reactor or the batch of raw materials is more important than the combination of the two - this is especially true when more (3, 4, ...) factors are present); thus it is preferable to confound this variability with the higher interaction. Examples *Male and Female: An experiment is designed to test a new drug on patients. There are two levels of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-parametric
Nonparametric statistics is the branch of statistics that is not based solely on parametrized families of probability distributions (common examples of parameters are the mean and variance). Nonparametric statistics is based on either being distribution-free or having a specified distribution but with the distribution's parameters unspecified. Nonparametric statistics includes both descriptive statistics and statistical inference. Nonparametric tests are often used when the assumptions of parametric tests are violated. Definitions The term "nonparametric statistics" has been imprecisely defined in the following two ways, among others: Applications and purpose Non-parametric methods are widely used for studying populations that take on a ranked order (such as movie reviews receiving one to four stars). The use of non-parametric methods may be necessary when data have a ranking but no clear numerical interpretation, such as when assessing preferences. In terms of levels of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
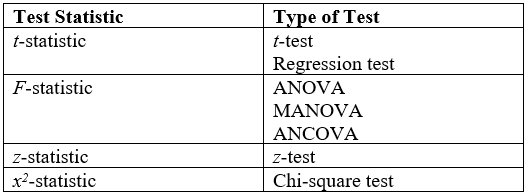
Statistical Test
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, " significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Gemmell Cochran
William Gemmell Cochran (15 July 1909 – 29 March 1980) was a prominent statistician. He was born in Scotland but spent most of his life in the United States. Cochran studied mathematics at the University of Glasgow and the University of Cambridge. He worked at Rothamsted Experimental Station from 1934 to 1939, when he moved to the United States. There he helped establish several departments of statistics. His longest spell in any one university was at Harvard, which he joined in 1957 and from which he retired in 1976. Writings Cochran wrote many articles and books. His books became standard texts: * ''Experimental Designs'' (with Gertrude Mary Cox Gertrude Mary Cox (January 13, 1900 – October 17, 1978) was an American statistician and founder of the department of Experimental Statistics at North Carolina State University. She was later appointed director of both the Institute of Statistic ...) 1950 * * ''Statistical Methods Applied to Experiments in Agriculture and Bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochran's C Test
In statistics, Cochran's C test, named after William G. Cochran, is a one-sided upper limit variance outlier test. The C test is used to decide if a single estimate of a variance (or a standard deviation) is significantly larger than a group of variances (or standard deviations) with which the single estimate is supposed to be comparable. The C test is discussed in many text books P. Konieczka, J. Namieśnik, Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Analytical Chemical Laboratory – A Practical Approach, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2009; . and has been recommended by IUPAC W. Horwitz, Harmonized protocol for the design and interpretation of collaborative studies, Trends in Analytical Chemistry 7(4), 118–120 (April 1988). and ISO.ISO Standard 5725–2:1994, “Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results – Part 2: Basic method for the determination of repeatability and reproducibility of a standard measurement method”, International Organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blocking (statistics)
In the statistical theory of the design of experiments, blocking is the arranging of experimental units in groups (blocks) that are similar to one another. Blocking can be used to tackle the problem of pseudoreplication. Use Blocking reduces unexplained variability. Its principle lies in the fact that variability which cannot be overcome (e.g. needing two batches of raw material to produce 1 container of a chemical) is confounded or aliased with a(n) (higher/highest order) interaction to eliminate its influence on the end product. High order interactions are usually of the least importance (think of the fact that temperature of a reactor or the batch of raw materials is more important than the combination of the two - this is especially true when more (3, 4, ...) factors are present); thus it is preferable to confound this variability with the higher interaction. Examples *Male and Female: An experiment is designed to test a new drug on patients. There are two levels of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
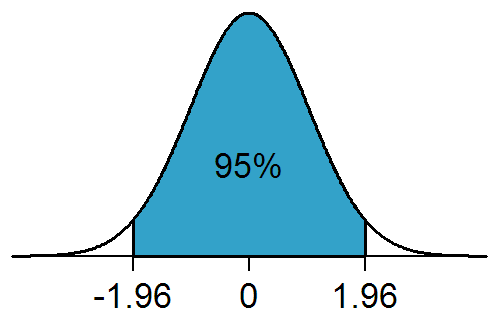
Significance Level
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or observation that involves drawing a sample from a population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the ''p''-value of an observed effect is less than (or equal to) the significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantile
In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities, or dividing the observations in a sample in the same way. There is one fewer quantile than the number of groups created. Common quantiles have special names, such as ''quartiles'' (four groups), ''deciles'' (ten groups), and ''percentiles'' (100 groups). The groups created are termed halves, thirds, quarters, etc., though sometimes the terms for the quantile are used for the groups created, rather than for the cut points. -quantiles are values that partition a finite set of values into subsets of (nearly) equal sizes. There are partitions of the -quantiles, one for each integer satisfying . In some cases the value of a quantile may not be uniquely determined, as can be the case for the median (2-quantile) of a uniform probability distribution on a set of even size. Quantiles can also be applied to continuous distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi-squared Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the chi-squared distribution (also chi-square or \chi^2-distribution) with k degrees of freedom is the distribution of a sum of the squares of k independent standard normal random variables. The chi-squared distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution and is one of the most widely used probability distributions in inferential statistics, notably in hypothesis testing and in construction of confidence intervals. This distribution is sometimes called the central chi-squared distribution, a special case of the more general noncentral chi-squared distribution. The chi-squared distribution is used in the common chi-squared tests for goodness of fit of an observed distribution to a theoretical one, the independence of two criteria of classification of qualitative data, and in confidence interval estimation for a population standard deviation of a normal distribution from a sample standard deviation. Many other statistical tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Comparisons
In statistics, the multiple comparisons, multiplicity or multiple testing problem occurs when one considers a set of statistical inferences simultaneously or infers a subset of parameters selected based on the observed values. The more inferences are made, the more likely erroneous inferences become. Several statistical techniques have been developed to address that problem, typically by requiring a stricter significance threshold for individual comparisons, so as to compensate for the number of inferences being made. History The problem of multiple comparisons received increased attention in the 1950s with the work of statisticians such as Tukey and Scheffé. Over the ensuing decades, many procedures were developed to address the problem. In 1996, the first international conference on multiple comparison procedures took place in Israel. Definition Multiple comparisons arise when a statistical analysis involves multiple simultaneous statistical tests, each of which has a pot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedman Test
The Friedman test is a non-parametric statistical test developed by Milton Friedman. Similar to the parametric repeated measures ANOVA, it is used to detect differences in treatments across multiple test attempts. The procedure involves ranking each row (or ''block'') together, then considering the values of ranks by columns. Applicable to complete block designs, it is thus a special case of the Durbin test. Classic examples of use are: * ''n'' wine judges each rate ''k'' different wines. Are any of the ''k'' wines ranked consistently higher or lower than the others? * ''n'' welders each use ''k'' welding torches, and the ensuing welds were rated on quality. Do any of the ''k'' torches produce consistently better or worse welds? The Friedman test is used for one-way repeated measures analysis of variance by ranks. In its use of ranks it is similar to the Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance by ranks. The Friedman test is widely supported by many statistical softwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |