|
Cobalt Boride
Cobalt borides are inorganic compounds with the general formula CoxBy. The two main cobalt borides are CoB and Co2B. These are refractory materials. Applications Materials science Cobalt borides are known to be exceptionally resistant to oxidation, a chemical property which makes them useful in the field of materials science. For instance, studies suggest cobalt boride can increase the lifespan of metal parts when used as a coating, imparting surfaces with higher corrosion and wear resistance. These properties have been exploited in the field of biomedical sciences for the design of specialized drug delivery systems. Renewable energy Cobalt boride has also been studied as a catalyst for hydrogen storage and fuel cell technologies. Organic synthesis Cobalt boride is also an effective hydrogenation catalyst used in organic synthesis. In one study, cobalt boride was found to be the most selective transition metal based catalyst available for the production of primary amines v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
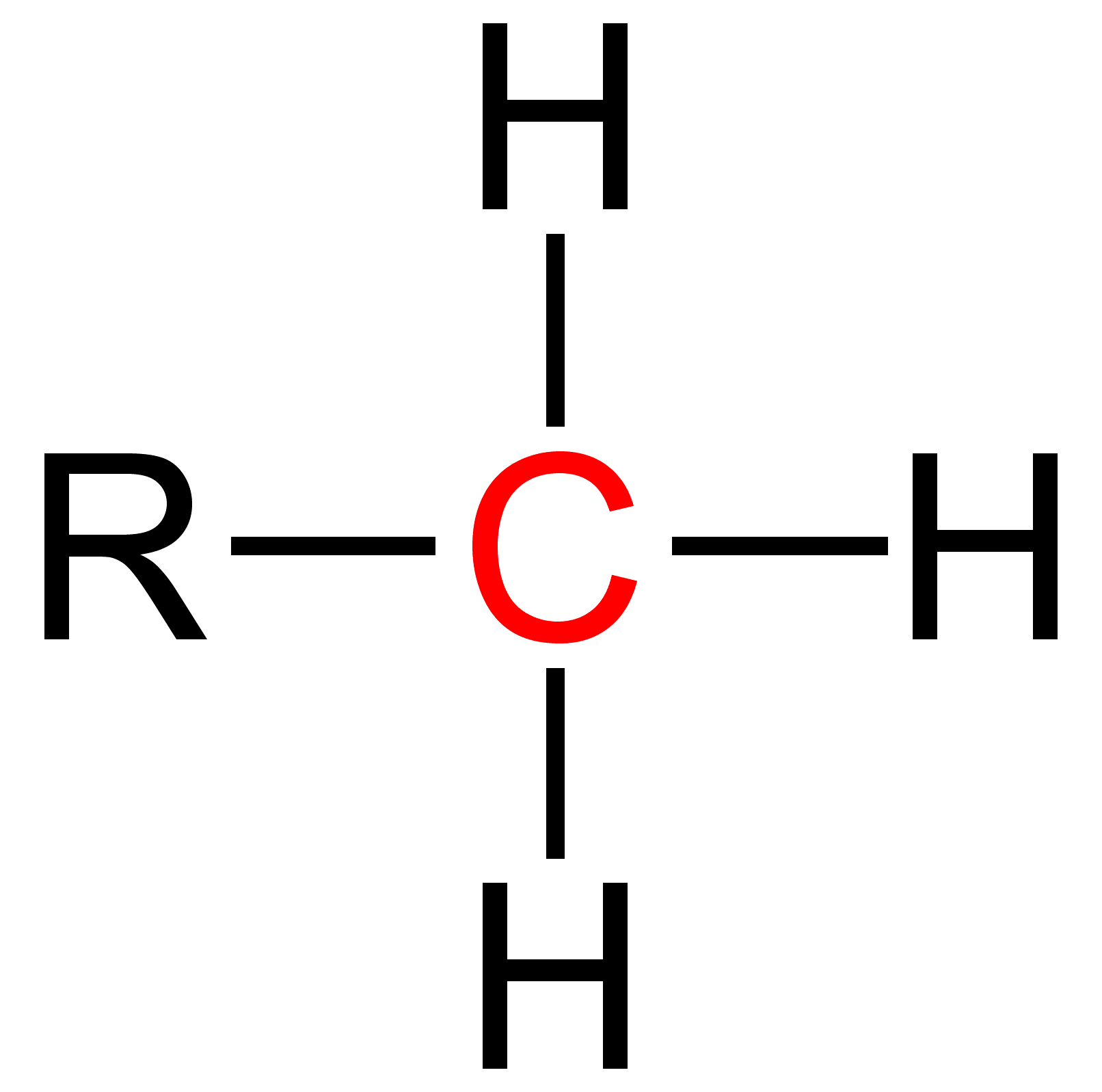
Primary (chemistry)
Primary is a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds (e.g. alcohols, alkyl halides, amines) or reactive intermediates (e.g. alkyl radicals, carbocations). {{clear See also * Secondary (chemistry) * Tertiary (chemistry) * Quaternary (chemistry) Quaternary is a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds (e. g. amines and ammonium salts).Paula Yurkanis Bruice: ''Organic Chemistry'', Pearson Education Inc., 2004, 4. Ed., p. 78, 104, 893, and 912, . {{clear See ... References Chemical nomenclature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borides
A boride is a compound between boron and a less electronegative element, for example silicon boride (SiB3 and SiB6). The borides are a very large group of compounds that are generally high melting and are covalent more than ionic in nature. Some borides exhibit very useful physical properties. The term boride is also loosely applied to compounds such as B12As2 (N.B. Arsenic has an electronegativity higher than boron) that is often referred to as icosahedral boride. Ranges of compounds The borides can be classified loosely as boron rich or metal rich, for example the compound YB66 at one extreme through to Nd2Fe14B at the other. The generally accepted definition is that if the ratio of boron atoms to metal atoms is 4:1 or more, the compound is boron rich; if it is less, then it is metal rich. Boron rich borides (B:M 4:1 or more) The main group metals, lanthanides and actinides form a wide variety of boron-rich borides, with metal:boron ratios up to YB66. The properties of this g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urushibara Nickel
Urushibara nickel is a nickel based hydrogenation catalyst, named after Yoshiyuki Urushibara. History It was discovered by Yoshiyuki Urushibara in 1951, while doing research on the reduction of estrone to estradiol. Preparation First nickel is precipitated in metallic form by reacting a solution of a nickel salt with an excess of zinc. This precipitated nickel contains relatively large amounts of zinc and zinc oxide. Then the catalyst is activated by digesting with either base or acid. There are different designations for differently prepared Urushibara nickel catalysts. The most common is U-Ni-A and U-Ni-B. U-Ni-A is prepared by digesting the precipitated nickel with an acid such as acetic acid. U-Ni-B is prepared by digesting with a base such as sodium hydroxide. After the digestion with acid most of the zinc and zinc oxide is dissolved from the catalyst, while after digestion with base it still contains considerable amounts of zinc and zinc oxide. It is also possible to prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Boride
Nickel boride is the common name of materials composed chiefly of the elements nickel and boron that are widely used as catalysts in organic chemistry. Their approximate chemical composition is Ni2.5B, and they are often incorrectly denoted "" in organic chemistry publications. Nickel boride catalysts are typically prepared by reacting a salt of nickel with sodium borohydride. The composition and properties vary depending on the specific preparation method. The two most common forms, described and evaluated in detail by Herbert C. Brown and Charles Allan Brown in 1963, are known as P−1 nickel and P−2 nickel. These catalysts are usually obtained as black granules (P−1) or colloidal suspensions (P−2). They are air-stable, non-magnetic and non-pyrophoric, but slowly react with water to form nickel hydroxide . They are insoluble in all solvents, but react with concentrated mineral acids. They are claimed to be more effective hydrogenation catalysts than Raney nickel. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is a form of carbon commonly used to filter contaminants from water and air, among many other uses. It is processed (activated) to have small, low-volume pores that increase the surface area available for adsorption (which is not the same as absorption) or chemical reactions. Activation is analogous to making popcorn from dried corn kernels: popcorn is light, fluffy, and has a surface area that is much larger than the kernels. ''Activated'' is sometimes replaced by ''active''. Due to its high degree of microporosity, one gram of activated carbon has a surface area in excess of as determined by gas adsorption. Charcoal, before activation, has a specific surface area in the range of . An activation level sufficient for useful application may be obtained solely from high surface area. Further chemical treatment often enhances adsorption properties. Activated carbon is usually derived from waste products such as coconut husks; waste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst Support
In chemistry, a catalyst support is the material, usually a solid with a high surface area, to which a catalyst is affixed. The activity of heterogeneous catalysts is mainly promoted by atoms present at the accessible surface of the material. Consequently, great effort is made to maximize the specific surface area of a catalyst. One popular method for increasing surface area involves distributing the catalyst over the surface of the support. The support may be inert or participate in the catalytic reactions. Typical supports include various kinds of carbon, alumina, and silica. Applying catalysts to supports Two main methods are used to prepare supported catalysts. In the impregnation method, a suspension of the solid support is treated with a solution of a precatalyst, and the resulting material is then activated under conditions that will convert the precatalyst (often a metal salt) to a more active state, perhaps the metal itself. In such cases, the catalyst support is usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of one-dimensional curves, or of the surface area for polyhedra (i.e., objects with flat polygonal faces), for which the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces. Smooth surfaces, such as a sphere, are assigned surface area using their representation as parametric surfaces. This definition of surface area is based on methods of infinitesimal calculus and involves partial derivatives and double integration. A general definition of surface area was sought by Henri Lebesgue and Hermann Minkowski at the turn of the twentieth century. Their work led to the development of geometric measure theory, which studies various notions of surface area for irregular objects of any dimension. An important example is the Minkowski cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula Na BH4. This white solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution, is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis. The compound was discovered in the 1940s by H. I. Schlesinger, who led a team seeking volatile uranium compounds.Hermann I Schlesinger and Herbert C Brown (1945)Preparation of alkali metal compounds. US Patent 2461661. Granted on 1949-02-15; expired on 1966-02-15. Results of this wartime research were declassified and published in 1953. Properties The compound is soluble in alcohols, certain ethers, and water, although it slowly hydrolyzes. Sodium borohydride is an odorless white to gray-white microcrystalline powder that often forms lumps. It can be purified by recrystallization from warm (50 °C) diglyme. Sodium borohydride is soluble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt(II) Nitrate
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments (cobalt blue) have been used since ancient times for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass, but the color was for a long time thought to be due to the known metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name ''kobold ore'' (German for ''goblin ore'') for some of the blue-pigment-producing minerals; they were so named because they were poor in known metals, and gave poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted. In 1735, such ores were found to be reducible to a new metal (the first discovered since ancient times), and this was ultimately named for the ''kobold''. Today, some cobalt is produced specifically from one of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticles
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are usually distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 µm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Boride
Iron boride refers to various inorganic compounds with the formula FexBy. Two main iron borides are FeB and Fe2B. Some iron borides possess useful properties such as magnetism, electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance and extreme hardness. Some iron borides have found use as hardening coatings for iron. Iron borides have properties of ceramics such as high hardness, and properties of metal properties, such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. Boride coatings on iron are superior mechanical, frictional, and anti-corrosive. Iron monoboride (FeB) is a grey powder that is insoluble in water. FeB is harder than Fe2B, but is more brittle and more easily fractured upon impact. Formation Thermochemical Formation Iron borides can be formed by thermochemically reacting boron rich compounds on an iron surface to form a mixture of iron borides, in a process known as boriding. There are a number of ways of forming boride coatings, including gas boriding, molten salt bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |