|
Coax Cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ) is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric ( insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a protective outer sheath or jacket. The term '' coaxial'' refers to the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable is a type of transmission line, used to carry high-frequency electrical signals with low losses. It is used in such applications as telephone trunk lines, broadband internet networking cables, high-speed computer data busses, cable television signals, and connecting radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas. It differs from other shielded cables because the dimensions of the cable and connectors are controlled to give a precise, constant conductor spacing, which is needed for it to function efficiently as a transmission line. Coaxial cable was used in the first (1858) and followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RG-59
RG-59/U is a specific type of coaxial cable, often used for low-power video and RF signal connections. The cable has a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms, and a capacitance of around 20pF/ft (60pF/m). The 75 ohm impedance matches a dipole antenna in free space. ''RG'' (for ''radio guide'') was originally a unit indicator for bulk radio frequency (RF) cable in the U.S. military's Joint Electronics Type Designation System. The suffix ''/U'' means ''for general utility use''. The number ''59'' was assigned sequentially. The ''RG'' unit indicator is no longer part of the JETDS system (MIL-STD-196E) and cable sold today under the RG-59 label does not necessarily meet military specifications. RG-59 is often used at baseband video frequencies, such as composite video. It may also be used for broadcast frequencies, but its high-frequency losses are too high to allow its use over long distances; in these applications, RG-6 or RG-11 are used instead. In cases where the transmis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Signaling
Differential signalling is a method for electrically transmitting information using two complementary signals. The technique sends the same electrical signal as a differential pair of signals, each in its own conductor. The pair of conductors can be wires in a twisted-pair or ribbon cable or traces on a printed circuit board. Electrically, the two conductors carry voltage signals which are equal in magnitude, but of opposite polarity. The receiving circuit responds to the difference between the two signals, which results in a signal with a magnitude twice as large. The symmetrical signals of differential signalling may be referred to as ''balanced'', but this term is more appropriately applied to balanced circuits and balanced lines which reject common-mode interference when fed into a differential receiver. Differential signalling does not make a line balanced, nor does noise rejection in balanced circuits require differential signalling. Differential signallin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaxial Cable Cutaway
In geometry, coaxial means that several three-dimensional linear or planar forms share a common axis. The two-dimensional analog is ''concentric''. Common examples: A coaxial cable is a three-dimensional linear structure. It has a wire conductor in the centre (D), a circumferential outer conductor (B), and an insulating medium called the dielectric (C) separating these two conductors. The outer conductor is usually sheathed in a protective PVC outer jacket (A). All these have a common axis. The dimension and material of the conductors and insulation determine the cable's characteristic impedance and attenuation at various frequencies. Coaxial rotors are a three-dimensional planar structure: a pair of helicopter rotors (wings) mounted one above the other on concentric shafts, with the same axis of rotation (but turning in opposite directions). In loudspeaker A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI), also called radio-frequency interference (RFI) when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data. Both man-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI: ignition systems, cellular network of mobile phones, lightning, solar flares, and auroras (northern/southern lights). EMI frequently affects AM radios. It can also affect mobile phones, FM radios, and televisions, as well as observations for radio astronomy and atmospheric science. EMI can be used intentionally for radio jamming, as in electronic warfare. History Since the earliest days o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electric current is generated by the flow of negatively charged electrons, positively charged holes, and positive or negative ions in some cases. In order for current to flow within a closed electrical circuit, it is not necessary for one charged particle to travel from the component producing the current (the current source) to those consuming it (the loads). Instead, the charged particle simply needs to nudge its neighbor a finite amount, who will nudge ''its'' neighbor, and on and on until a particle is nudged into the consumer, thus powering it. Essentially what is occurring is a long chain of momentum transfer between mobile charge carriers; the Drude model of conduction describes this process more rigorously. This momentum transfer model makes metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical counterpart to the quantized electromagnetic field tensor in quantum electrodynamics (a quantum field theory). The electromagnetic field propagates at the speed of light (in fact, this field can be identified ''as'' light) and interacts with charges and currents. Its quantum counterpart is one of the four fundamental forces of nature (the others are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction.) The field can be viewed as the combination of an electric field and a magnetic field. The electric field is produced by stationary charges, and the magnetic field by moving charges (currents); these two are often described as the sources of the field. The way in which charges and currents interact with the electromagnetic field is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S/PDIF
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a type of digital audio interface used in consumer audio equipment to output audio over relatively short distances. The signal is transmitted over either a coaxial cable (using RCA or BNC connectors) or a fiber optic cable with TOSLINK connectors. S/PDIF interconnects components in home theaters and other digital high-fidelity systems. S/PDIF is based on the AES3 interconnect standard. S/PDIF can carry two channels of uncompressed PCM audio or compressed 5.1 surround sound (such as DTS audio codec or Dolby Digital codec); it cannot support lossless surround formats that require greater bandwidth. S/PDIF is a data link layer protocol as well as a set of physical layer specifications for carrying digital audio signals over either optical or electrical cable. The name stands for Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format but is also known as Sony/Philips Digital Interface. Sony and Philips were the primary designers of S/PDIF. S/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical samples in a continuous sequence. For example, in CD audio, samples are taken 44,100 times per second, each with 16-bit sample depth. Digital audio is also the name for the entire technology of sound recording and reproduction using audio signals that have been encoded in digital form. Following significant advances in digital audio technology during the 1970s and 1980s, it gradually replaced analog audio technology in many areas of audio engineering, record production and telecommunications in the 1990s and 2000s In a digital audio system, an analog electrical signal representing the sound is converted with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) into a digital signal, typically using pulse-code modulation (PCM). This digital signal can then be recorded, edited, modified, and copied using compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses coaxial cable as a shared medium, while the newer Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the latest , with rates up to under development. The Ethernet standards include several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer. Systems communicating over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
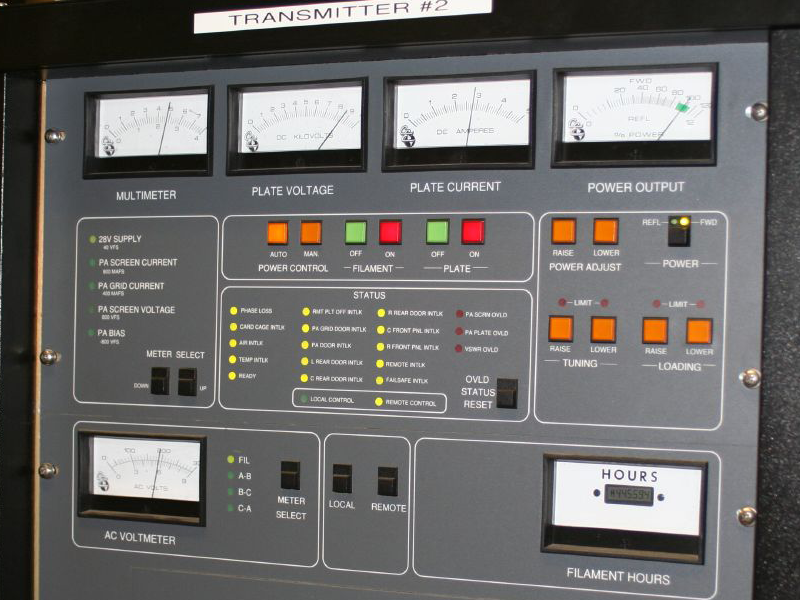
Radio Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio, such as radio and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves for communication purposes; or radiolocation, such as radar and navigational transmitters. Generators of radio waves for heating or industrial purposes, such as microwave ovens or diathermy equipment, are not usually called transmitters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |