|
Coal Power In The US
Coal generated about 22% of the Electricity sector of the United States, electricity at utility-scale facilities in the United States in 2021, down from 39% in 2014. In 2021, coal supplied of primary energy to electric power plants, which made up 90% of coal's contribution to U.S. energy supply. Utilities buy more than 90% of the coal consumed in the United States. There were List of coal-fired power stations in the United States, over 200 coal powered units across the United States in 2022. Coal plants have been closing since the 2010s due to cheaper and cleaner natural gas and Renewable energy, renewables. But environmentalists say that political action is needed to close them faster, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States to better Climate change mitigation, limit climate change. Coal has been used to generate electricity in the United States since an Edison plant was built in New York City in 1882. The first AC power station was opened by General Elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Bowen
Plant Bowen, commonly known as Bowen Steam Plant, is a coal-fired power station located just outside Euharlee, Georgia, United States, approximately west-south-west from Cartersville. At over 3,450 megawatts, Plant Bowen is one of the largest coal-fired power plants in North America. The station is connected to the southeastern power grid by numerous 500 kV transmission lines, and is owned and operated by Georgia Power, a subsidiary of Southern Company. Description Plant Bowen consists of four units, with capacities of 806, 789, 952, and 952 megawatts, respectively. The first unit began operation in 1971, and additional units were brought online in 1972, 1974, and 1975, respectively. Bowen's four cooling towers are tall and in diameter and can cool per minute. Another per minute or per day of water is lost to evaporation which creates the distinctive white clouds rising from each tower. Bowen's two smokestacks are tall. Particulates are removed from the exhaust gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliant Energy
Reliant Energy is an American energy company based in Houston, Texas. History Headquartered in Houston, Texas, Reliant Energy, a subsidiary of NRG Energy, is one of the largest Texas electricity providers serving over 1.5 million Texans. Reliant provides over 23 million megawatts of power annually to residential and business customers. Reliant Energy was founded in 2000. In June 2009, NRG Energy purchased Reliant Energy's retail electricity business. At the time, Reliant had 1.8 million customers and was the second largest electric provider in Texas. The name Reliant Energy was retained and the surviving wholesale business was renamed RRI Energy, which was retired in 2012 after additional NRG acquisitions. In 2010, Reliant Energy received a $20 million grant from the U.S. Department of Energy as part of the DOE’s Recovery Act activities to fund a suite of Smart Grid products for upgrades of the nation’s electricity grid. Over the last six months of 2017, the Public Utility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semora, North Carolina
Semora is an unincorporated community in Caswell County, North Carolina, United States. It lies just northwest of Hyco Lake and has some presence in Person County. Semora is home to one of the oldest churches in North Carolina, the Red House Presbyterian Church. Neighboring North Carolina communities and municipalities include: Yanceyville, Milton, Roxboro, Leasburg, and Blanch. Alton, Virginia is a neighbor to the north. The population was 1,716 at the 2010 census. In addition to the Red House Presbyterian Church, Wildwood is listed on the National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v .... References {{authority control Unincorporated communities in Caswell County, North Carolina Unincorporated communities in Person County, North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roxboro Power Station
Roxboro Steam Plant is a coal-fired electrical generation facility in Semora, North Carolina. The plant has four units, the first opened in 1966. See also *List of largest power stations in the United States This article lists the largest electrical generating stations in the United States in terms of current installed electrical capacity. Non-renewable power stations are those that run on coal, fuel oils, nuclear, natural gas, oil shale and peat, ... References Coal-fired power stations in North Carolina Duke Energy {{US-powerstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Energy
Duke Energy Corporation is an American electric power and natural gas holding company headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. Overview Based in Charlotte, North Carolina, Duke Energy owns 58,200 megawatts of base-load and peak generation in the United States, which it distributes to its 7.2 million customers. The company has approximately 29,000 employees. Duke Energy's service territory covers with of distribution lines. Almost all of Duke Energy's Midwest generation comes from coal, natural gas, or oil, while half of its Carolinas generation comes from its nuclear power plants. During 2006, Duke Energy generated 148,798,332 megawatt-hours of electrical energy. Duke Energy Renewable Services (DERS), a subsidiary of Duke Energy, specializes in the development, ownership, and operation of various generation facilities throughout the United States. This segment of the company operates 1,700 megawatts of generation. 240 megawatts of wind generation were under construction and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powder River Basin
The Powder River Basin is a geologic structural basin in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming, about east to west and north to south, known for its extensive coal reserves. The former hunting grounds of the Oglala Lakota, the area is very sparsely populated and is known for its rolling grasslands and semiarid climate. The basin is both a topographic drainage and geologic structural basin, drained by the Powder River, Cheyenne River, Tongue River, Bighorn River, Little Missouri River, Platte River, and their tributaries. The major cities in the area include Gillette and Sheridan, Wyoming and Miles City, Montana. In 2007, the region produced 436 million short tons (396 million tonnes) of coal, more than twice the production of second-place West Virginia, and more than the entire Appalachian region. The Powder River Basin is the largest coal-producing region in the United States. The region includes the Black Thunder Coal Mine, the most productive in the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Subsidies
Energy subsidies are measures that keep prices for customers below market levels, or for suppliers above market levels, or reduce costs for customers and suppliers. Energy subsidies may be direct cash transfers to suppliers, customers, or related bodies, as well as indirect support mechanisms, such as tax exemptions and rebates, price controls, trade restrictions, and limits on market access. The International Renewable Energy Agency tracked some $634 billion in energy-sector subsidies in 2020, and found that around 70% were fossil fuel subsidies. About 20% went to renewable power generation, 6% to biofuels and just over 3% to nuclear. Overview of all sources of energy If governments choose to subsidize one particular source of energy more than another, that choice can impact the environment. That distinguishing factor informs the below discussion on all energy subsidies of all sources of energy in general. Main arguments for energy subsidies are: * Security of supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
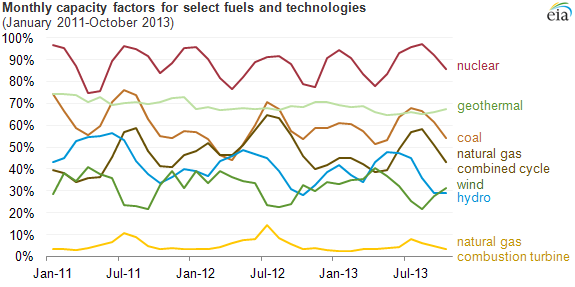
Capacity Factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor, or uptime during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, scheduled or unscheduled. Other fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury And Air Toxics Standards
Mercury commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg * Mercury (mythology), a Roman god Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Mercury (toy manufacturer), a brand of diecast toy cars manufactured in Italy * Mercury Communications, a British telecommunications firm set up in the 1980s * Mercury Drug, a Philippine pharmacy chain * Mercury Energy, an electricity generation and retail company in New Zealand * Mercury Filmworks, a Canadian independent animation studio * Mercury General, a multiple-line American insurance organization * Mercury Interactive, a software testing tools vendor * Mercury Marine, a manufacturer of marine engines, particularly outboard motors * Mercury Systems, a defense-related information technology company Computing * Mercury (programming language), a functional logic programming language * Mercury (metadata search system), a data search syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-State Air Pollution Rule
The Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) is a rule by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that requires member states of the United States to reduce power plant emissions that contribute to ozone and/or fine particle pollution in other states. The EPA describes this rule as one that "protects the health of millions of Americans by helping states reduce air pollution and attain clean air standards." Details The CSAPR requires 23 United States states to reduce their annual emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) to help downwind states attain the 24-hour National Ambient Air Quality Standards, and 25 states to reduce ozone season nitrogen oxide emissions to help downwind states attain the 8-hour NAAQS. The states that are required to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions are divided into two groups, both of which must reduce their emissions in 2012. Group 1 is required to make additional emissions reductions by 2014. History Reception The CSAP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Load Power Plant
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants, dispatchable generation, or by a collection of smaller intermittent energy sources, depending on which approach has the best mix of cost, availability and reliability in any particular market. The remainder of demand, varying throughout a day, is met by dispatchable generation which can be turned up or down quickly, such as load following power plants, peaking power plants, or energy storage. Power plants that do not change their power output quickly, such as large coal or nuclear plants, are generally called baseload power plants. Donald G. Fink, H. Wayne Beatty (ed), ''Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers'', Eleventh Edition, Mc-Graw Hill, 1978 , pp. 12-16 through 12-18 Historically, most or all of base load demand was met with baseload power plants, whereas new capacity based around renewables ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |