|
Clocental
Clocental (dolcental) is a carbamate-derived sedative hypnotic. It can be prepared by the ethynylation of cyclohexanone followed by reaction with allophanyl chloride. See also * 1-Ethynylcyclohexanol * Methylpentynol Methylpentynol (Methylparafynol, Dormison, Atemorin, Oblivon) is a tertiary hexynol with hypnotic/sedative and anticonvulsant effects and an exceptionally low therapeutic index. It was discovered by Bayer in 1913 and was used shortly thereafter f ... References {{GABAAR PAMs Ethynyl compounds Carbamates Hypnotics Sedatives GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clocental Synthesis
Clocental (dolcental) is a carbamate-derived sedative hypnotic. It can be prepared by the ethynylation of cyclohexanone followed by reaction with allophanyl chloride. See also * 1-Ethynylcyclohexanol * Methylpentynol Methylpentynol (Methylparafynol, Dormison, Atemorin, Oblivon) is a tertiary hexynol with hypnotic/sedative and anticonvulsant effects and an exceptionally low therapeutic index. It was discovered by Bayer in 1913 and was used shortly thereafter f ... References {{GABAAR PAMs Ethynyl compounds Carbamates Hypnotics Sedatives GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-Ethynylcyclohexanol
1-Ethynylcyclohexanol (ECX) is an alkynyl alcohol derivative which is both a synthetic precursor to, and an active metabolite of the tranquilizer ethinamate, and has similar sedative, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects. It has been sold as a designer drug, first being identified in the UK in March 2012. Preparation 1-Ethynylcyclohexanol can be prepared from cyclohexanone by the reacting it with sodium acetylide in liquid ammonia, followed by an acidic work-up. See also * 1,6-Dioxecane-2,7-dione * 2-Methyl-2-butanol * 2-Methyl-2-pentanol * 3-Methyl-3-pentanol * Clocental * Ethchlorvynol * Methylpentynol * Prenderol Prenderol (Diethylpropanediol) is a simple alkyl diol which has sedative, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects. It is closely related in structure to meprobamate and numerous other alkyl alcohols and diols with generally comparable activity ... References Alcohols Muscle relaxants Ethynyl compounds {{musculoskeletal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylpentynol
Methylpentynol (Methylparafynol, Dormison, Atemorin, Oblivon) is a tertiary hexynol with hypnotic/sedative and anticonvulsant effects and an exceptionally low therapeutic index. It was discovered by Bayer in 1913 and was used shortly thereafter for the treatment of insomnia, but its use was quickly phased out in response to newer drugs with far more favorable safety profiles. The drug was marketed again in the United States, Europe and elsewhere from 1956 well into the 1960s as a rapid-acting sedative. The drug was quickly overshadowed at that point by benzodiazepines and is no longer sold anywhere. Synthesis Methylpentynol is prepared by reaction of butanone (MEK) with sodium acetylide. This reaction must be done in anhydrous conditions and in an inert atmosphere. Applications As building block in the synthesis of: # Phthalofyne (1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, mono(1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-propynyl) ester) 31-67-9# Anansiol (1-ethyl-1-methylprop-2-ynyl carbamate) 02-66-9# Bason ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
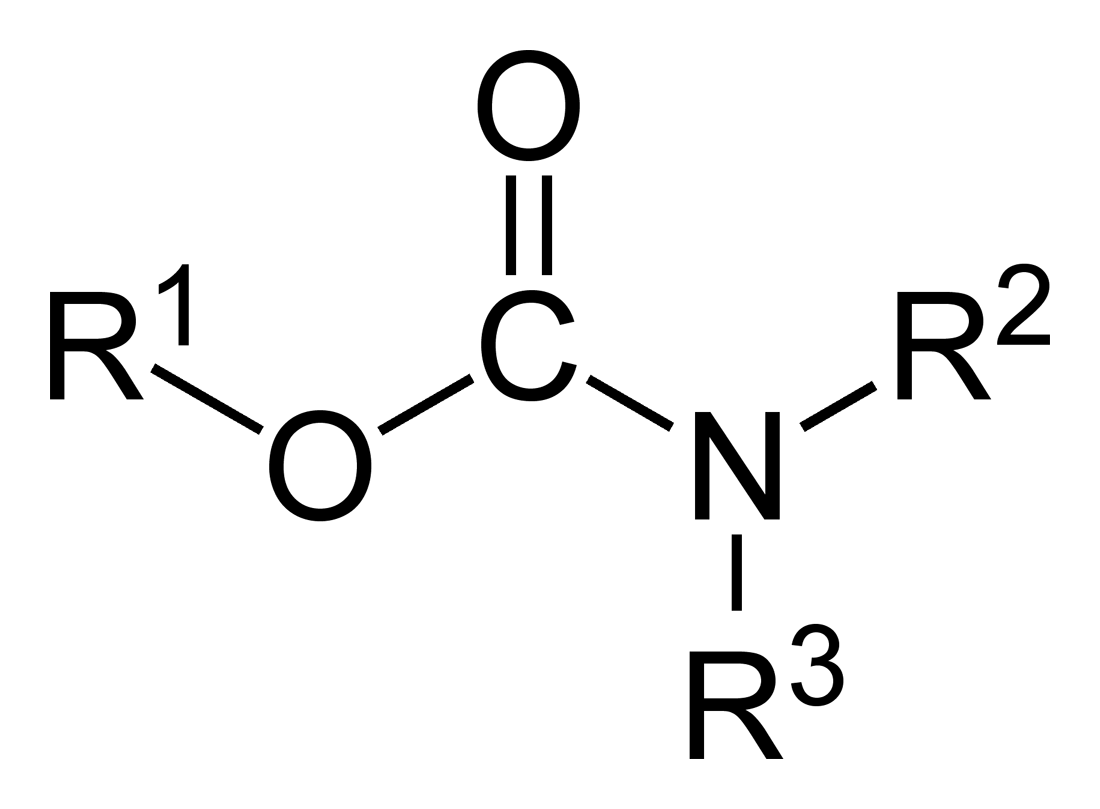
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate immediatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedative Hypnotic
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In spite of the fact that each sedative acts in its own way, most produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness) they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative-hypnotic'' drugs. Sedatives can be used to produce an overly-calming effect (alcohol being the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkynation
In organic chemistry, alkynylation is an addition reaction in which a terminal alkyne () is added to a carbonyl group () to form an α-alkynyl alcohol (). When the acetylide is formed from acetylene (), the reaction gives an α-ethynyl alcohol. This process is often referred to as ethynylation. Such processes often involve metal acetylide intermediates. Scope The principal reaction of interest involves the addition of the acetylene () to a ketone () or aldehyde (): :RR'C=O + HC#CR'' -> RR'C(OH)C#CR'' The reaction proceeds with retention of the triple bond. For aldehydes and unsymmetrical ketones, the product is chiral, hence there is interest in asymmetric variants. These reactions invariably involve metal-acetylide intermediates. This reaction was discovered by chemist John Ulric Nef in 1899 while experimenting with reactions of elemental sodium, phenylacetylene, and acetophenone. For this reason, the reaction is sometimes referred to as Nef synthesis. Sometimes this rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. Production Cyclohexanone is produced by the oxidation of cyclohexane in air, typically using cobalt catalysts: :C6H12 + O2 → (CH2)5CO + H2O This process forms cyclohexanol as a by-product, and this mixture, called "KA Oil" for ketone-alcohol oil, is the main feedstock for the production of adipic acid. The oxidation involves radicals and the hydroperoxide C6H11O2H as an intermediate. In some cases, purified cyclohexanol, obtained by hydration of cyclohexene, is the precursor. Alternatively, cyclohexanone can be produced by the partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethynyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, the term ethynyl designates a functional group with a double bond with 2 carbon atoms both with sp hybridisation and a triple bond(1 sigma and 2 pi bond) . It is a species similar to acetylene (or in IUPAC ethyne ) with a less H atom thus joined to root chain. * An ethynyl group (HC≡C–), also designated as acetylenic group (from acetylene), and referred to in IUPAC chemical nomenclature as -yne suffix. Also sometimes designed as ''ethinyl'' in compounds (ethinylestradiol, ethisterone (ethinyltestosterone)). See main page alkynes. * The ethynyl radical (HC≡C·), the compound found in interstellar medium, and transiently on earth during chemical reactions. * The ethynyl carbanion Acetylide (HC≡C−) See also * Ethynylation * Propynyl In organic chemistry, a propynyl group is a propyl In organic chemistry, propyl is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate immediately, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnotics
Hypnotic (from Greek ''Hypnos'', sleep), or soporific drugs, commonly known as sleeping pills, are a class of (and umbrella term for) psychoactive drugs whose primary function is to induce sleep (or surgical anesthesiaWhen used in anesthesia to produce and maintain unconsciousness, "sleep" is metaphorical as there are no regular sleep stages or cyclical natural states; patients rarely recover from anesthesia feeling refreshed and with renewed energy. The word is also used in art.) and to treat insomnia (sleeplessness). This group of drugs is related to sedatives''. ''Whereas the term sedative describes drugs that serve to calm or relieve anxiety, the term hypnotic generally describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness), they are often referred to collectively as sedative-hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedatives
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In spite of the fact that each sedative acts in its own way, most produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness) they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative-hypnotic'' drugs. Sedatives can be used to produce an overly-calming effect (alcohol being the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |