|
Clinical Attachment Loss
Clinical attachment loss (CAL) is the predominant clinical manifestation and determinant of periodontal disease. Anatomy of the attachment Teeth are attached to the surrounding and supporting alveolar bone by periodontal ligament (PDL) fibers; these fibers run from the bone into the cementum that naturally exists on the entire root surface of teeth. They are also attached to the gingival (gum) tissue that covers the alveolar bone by an attachment apparatus; because this attachment exists superficial to the crest, or height, of the alveolar bone, it is termed the ''supracrestal attachment apparatus''. The supracrestal attachment apparatus is composed of two layers: the coronal junctional epithelium and the more apical gingival connective tissue fibers.Itoiz, ME; Carranza, FA: The Gingiva. In Newman, MG; Takei, HH; Carranza, FA; editors: ''Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology'', 9th Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2002. pages 26-7. The two layers together form the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide.V. Baelum and R. Lopez, “Periodontal epidemiology: towards social science or molecular biology?,”Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 239–249, 2004.Nicchio I, Cirelli T, Nepomuceno R, et al. Polymorphisms in Genes of Lipid Metabolism Are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis, as Comorbidities, and with the Subjects' Periodontal, Glycemic, and Lipid Profiles Journal of Diabetes Research. 2021 Jan;2021. PMCID: PMC8601849. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Bad breath may also occur. Periodontal disease is generally due to bacteria in the mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Fiber
The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits. It inserts into root cementum one side and onto alveolar bone on the other. Structure The PDL consists of principal fibres, loose connective tissue, blast and clast cells, oxytalan fibres and Cell Rest of Malassez. Alveolodental ligament The main principal fiber group is the alveolodental ligament, which consists of five fiber subgroups: alveolar crest, horizontal, oblique, apical, and interradicular on multirooted teeth. Principal fibers other than the alveolodental ligament are the transseptal fibers. All these fibers help the tooth withstand the naturally substantial compressive forces that occur during chewing and remain embedded in the bone. The ends of the principal fibers that are within either cementum or alveolar bone proper are considered Sharpey fibers. * Alveolar crest fibers ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementum
Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. The cementum is the part of the periodontium that attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone by anchoring the periodontal ligament.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 170. Structure The cells of cementum are the entrapped cementoblasts, the cementocytes. Each cementocyte lies in its lacuna, similar to the pattern noted in bone. These lacunae also have canaliculi or canals. Unlike those in bone, however, these canals in cementum do not contain nerves, nor do they radiate outward. Instead, the canals are oriented toward the periodontal ligament and contain cementocytic processes that exist to diffuse nutrients from the ligament because it is vascularized. After the apposition of cementum in layers, the cementoblasts that do not become entrapped in cementum line up along the cemental surface along the length of the outer covering of the perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
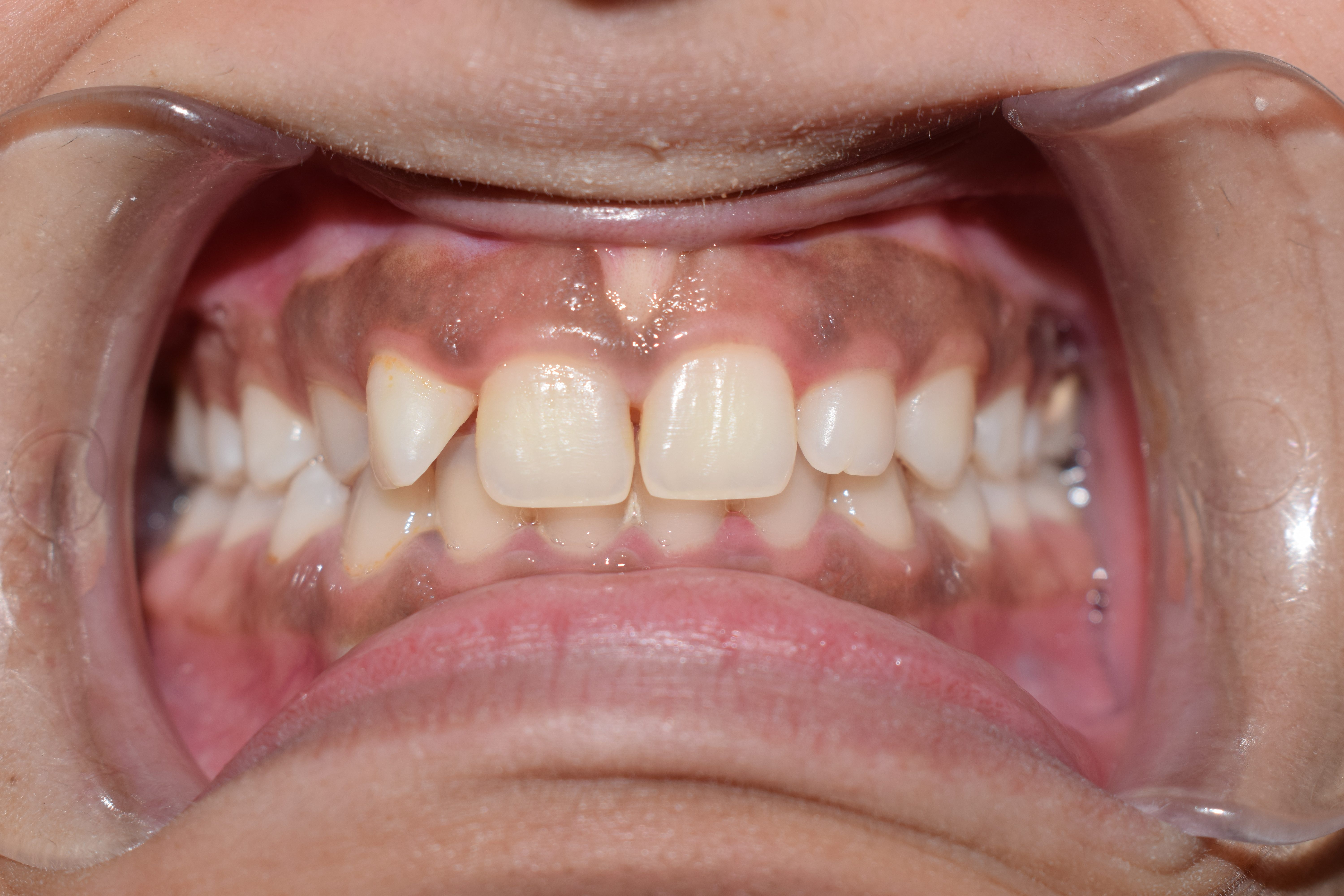
Gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonly Used Terms Of Relationship And Comparison In Dentistry
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body. Terms Combining of terms Most of the principal terms can be combined using their corresponding combining forms (such as ''mesio-'' for ''mesial'' and ''disto-'' for ''distal''). They provide names for directions (vectors) and axes; for example, the coronoapical axis is the long axis of a tooth. Such combining yields terms such as those in the following list. The abbreviations should be used only in restricted contexts, where they are explicitly defined and help avoid extensive repetition (for example, a journal article that uses the term "mesiodistal" dozens of times might use the abbreviation "MD"). The abbreviations are ambiguous: (1) they are not spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junctional Epithelium
The junctional epithelium (JE) is that epithelium which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus. The probing depth of the gingival sulcus is measured by a calibrated periodontal probe. In a healthy-case scenario, the probe is gently inserted, slides by the sulcular epithelium (SE), and is stopped by the epithelial attachment (EA). However, the probing depth of the gingival sulcus may be considerably different from the true histological gingival sulcus depth. Location The junctional epithelium, a nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, lies immediately apical to the sulcular epithelium, which lines the gingival sulcus from the base to the free gingival margin, where it interfaces with the epithelium of the oral cavity. The gingival sulcus is bounded by the enamel of the crown of the tooth and the sulcular epithelium. Immediately apical to the base of the pocket, and coronal to the most coronal of the gingival fibers is the junctional epithelium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingival Fibers
The gingival fibers are the connective tissue fibers that inhabit the gingival tissue adjacent to teeth and help hold the tissue firmly against the teeth. They are primarily composed of type I collagen, although type III fibers are also involved. These fibers, unlike the fibers of the periodontal ligament, in general, attach the tooth to the gingival tissue, rather than the tooth to the alveolar bone. Functions of the gingival fibers The gingival fibers accomplish the following tasks: *They hold the marginal gingiva against the tooth *They provide the marginal gingiva with enough rigidity to withstand the forces of mastication without distorting *They serve to stabilize the marginal gingiva by uniting it with both the tissue of the more rigid attached gingiva as well as the cementum layer of the tooth. Gingival fibers and periodontitis In theory, gingival fibers are the protectors against periodontitis, as once they are breached, they cannot be regenerated. When destroyed, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biologic Width
Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist, or more frequently a specialist periodontist. There are a number of reasons for considering crown lengthening in a treatment plan. Commonly, the procedure is used to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically. However, other indications include accessing subgingival caries, accessing perforations and to treat aesthetic disproportions such as a gummy smile. There are a number of procedures used to achieve an increase in crown length. Biomechanical considerations Biologic width Biologic width is the distance established by "the junctional epithelium and connective tissue attachment to the root surface" of a tooth. The concept was first published by Ingber JS, Rose LF and Coslet JG. - The "Biologic Width"—A Concept in Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry in 1977 in the Alpha Omegan. It was based on cadaver measurements by Gargiulo, Wentz and Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |