|
Climate Simulation
Numerical climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the important drivers of climate, including atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate. Climate models may also be qualitative (i.e. not numerical) models and also narratives, largely descriptive, of possible futures. Quantitative climate models take account of incoming energy from the sun as short wave electromagnetic radiation, chiefly visible and short-wave (near) infrared, as well as outgoing long wave (far) infrared electromagnetic. An imbalance results in a change in temperature. Quantitative models vary in complexity. For example, a simple radiant heat transfer model treats the earth as a single point and averages outgoing energy. This can be expanded vertically (radiative-convective models) and/or horizontally. Coupled atmosphere–ocean–sea ice global climate models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Climate Model
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources (radiation, latent heat). These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs (AGCM and OGCM) are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components. GCMs and global climate models are used for weather forecasting, understanding the climate, and forecasting climate change. Versions designed for decade to century time scale climate applications were originally created by Syukuro Manabe and Kirk Bryan at the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) in Princeton, New Jersey. These models are based on the integration of a variety of fluid dynamical, chemical and sometimes biological equations. Terminology The acronym ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth System Model
Earth system science (ESS) is the application of systems science to the Earth. In particular, it considers interactions and 'feedbacks', through material and energy fluxes, between the Earth's sub-systems' cycles, processes and "spheres"—atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, geosphere, pedosphere, lithosphere, biosphere, and even the magnetosphere—as well as the impact of human societies on these components. At its broadest scale, Earth system science brings together researchers across both the natural and social sciences, from fields including ecology, economics, geography, geology, glaciology, meteorology, oceanography, climatology, paleontology, sociology, and space science. Like the broader subject of systems science, Earth system science assumes a holistic view of the dynamic interaction between the Earth's spheres and their many constituent subsystems fluxes and processes, the resulting spatial organization and time evolution of these systems, and their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation. Surface albedo is defined as the ratio of radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While bi-hemispherical reflectance is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds (as obtained from flux measurements) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Constant
The solar constant (''GSC'') is a flux density measuring mean solar electromagnetic radiation ( total solar irradiance) per unit area. It is measured on a surface perpendicular to the rays, one astronomical unit (au) from the Sun (roughly the distance from the Sun to the Earth). The solar constant includes radiation over the entire electromagnetic spectrum. It is measured by satellite as being 1.361 kilowatts per square meter (kW/m2) at solar minimum (the time in the 11-year solar cycle when the number of sunspots is minimal) and approximately 0.1% greater (roughly 1.362 kW/m2) at solar maximum. The solar "constant" is not a physical constant in the modern CODATA scientific sense; that is, it is not like the Planck constant or the speed of light which are absolutely constant in physics. The solar constant is an average of a varying value. In the past 400 years it has varied less than 0.2 percent.http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/sorce/data/tsi-data/ Total Solar Irradiance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan–Boltzmann Law
The Stefan–Boltzmann law describes the power radiated from a black body in terms of its temperature. Specifically, the Stefan–Boltzmann law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body across all wavelengths per unit time j^ (also known as the black-body '' radiant emittance'') is directly proportional to the fourth power of the black body's thermodynamic temperature ''T'': : j^ = \sigma T^. The constant of proportionality ''σ'', called the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, is derived from other known physical constants. Since 2019, the value of the constant is : \sigma=\frac = 5.670374419\times 10^\, \mathrm, where ''k'' is the Boltzmann constant, ''h'' is Planck's constant, and ''c'' is the speed of light in a vacuum. The radiance from a specified angle of view (watts per square metre per steradian) is given by : L = \frac\pi = \frac\sigma\pi T^. A body that does not absorb all incident radiation (sometimes known as a grey body) emits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Equilibrium
Radiative equilibrium is the condition where the total thermal radiation leaving an object is equal to the total thermal radiation entering it. It is one of the several requirements for thermodynamic equilibrium, but it can occur in the absence of thermodynamic equilibrium. There are various types of radiative equilibrium, which is itself a kind of dynamic equilibrium. Definitions Equilibrium, in general, is a state in which opposing forces are balanced, and hence a system does not change in time. Radiative equilibrium is the specific case of thermal equilibrium, for the case in which the exchange of heat is done by radiative heat transfer. There are several types of radiative equilibrium. Prevost's definitions An important early contribution was made by Pierre Prevost in 1791. Prevost considered that what is nowadays called the photon gas or electromagnetic radiation was a fluid that he called "free heat". Prevost proposed that free radiant heat is a very rare fluid, rays of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-compartment Model
A multi-compartment model is a type of mathematical model used for describing the way materials or energies are transmitted among the ''compartments'' of a system. Sometimes, the physical system that we try to model in equations is too complex, so it is much easier to discretize the problem and reduce the number of parameters. Each compartment is assumed to be a homogeneous entity within which the entities being modeled are equivalent. A multi-compartment model is classified as a lumped parameters model. Similar to more general mathematical models, multi-compartment models can treat variables as continuous, such as a differential equation, or as discrete, such as a Markov chain. Depending on the system being modeled, they can be treated as stochastic or deterministic. Multi-compartment models are used in many fields including pharmacokinetics, epidemiology, biomedicine, systems theory, complexity theory, engineering, physics, information science and social science. The circuits sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
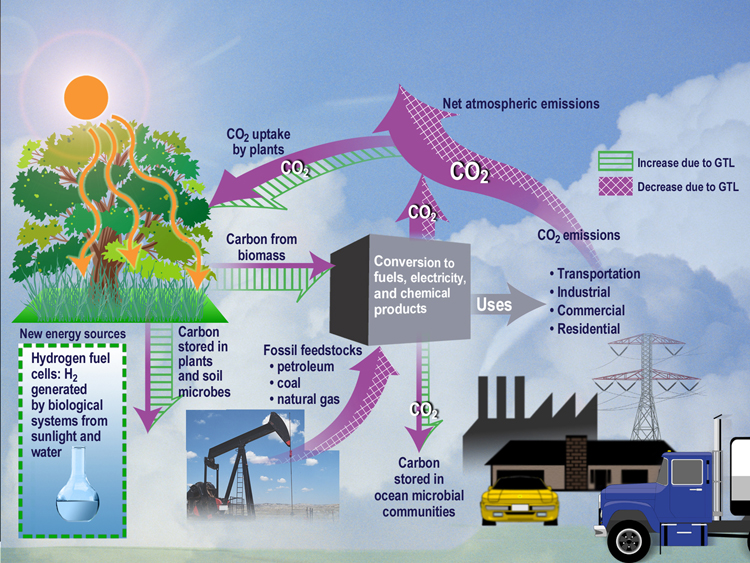
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many minerals such as limestone. Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle, the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to make Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration to and release from carbon sinks. Carbon sinks in the land and the ocean each currently take up about one-quarter of anthropogenic carbon emissions each year. Humans have disturbed the biological carbon cycle for many centuries by modifying land use, and moreover with the recent industrial-scale mining of fossil carbon (coal, petroleum and gas extraction, and cement manufacture) from the geosphere. Carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Circulation
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other areas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Species
A chemical species is a chemical substance or ensemble composed of chemically identical molecular entities that can explore the same set of molecular energy levels on a characteristic or delineated time scale. These energy levels determine the way the chemical species will interact with others (engaging in chemical bonds, etc.). The species can be an atom, molecule, ion, or radical, and it has a specific chemical name and chemical formula. The term is also applied to a set of chemically identical atomic or molecular structural units in a solid array. In supramolecular chemistry, chemical species are those supramolecular structures whose interactions and associations are brought about via intermolecular bonding and debonding actions, and function to form the basis of this branch of chemistry. For instance: * The chemical species argon is an atomic species of formula Ar; * dioxygen and ozone are different molecular species, of respective formulas O and O; * chloride is an ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |