|
Climacium Dendroides
''Climacium dendroides'', also known as tree climacium moss, belongs in the order Hypnales and family Climaciaceae, in class Bryopsida and subclass Bryidae. It is identified as a "tree moss" due to its distinctive morphological features, and has four species identified across the Northern Hemisphere. The species name "dendroides" describes the tree-like morphology of the plant, and its genus name came from the structure of the perforations of peristome teeth. This plant was identified by Weber and Mohr in 1804. They often have stems that are around 2-10 cm tall and growing in the form of patches, looking like small palm-trees. They have yellow-green branches at the tip of stems. The leaves are around 2.5-3 mm long, with rounder stem leaves and pointier branch leaves. Their sporophytes are only abundant in late winter and early spring, and appears as a red-brown shoot with long stalk and cylindrical capsules. Habitat and range This species mostly dominate in moist and damp regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnales
Hypnales is the botanical name of an order of Bryophyta or leafy mosses. This group is sometimes called feather mosses, referring to their freely branched stems. The order includes more than 40 families and more than 4,000 species, making them the largest order of mosses. Description Hypnales are mosses with pinnately or irregularly branched, reclining stems, with varying appearances. The stem contains only a reduced central vascular bundle, which is seen as a recent derived trait in mosses. The stems are covered with paraphyllia or pseudoparaphyllia, reduced filamentous or scaly leaves. The ordinary stem leaves are ovate to lanceolate, often with leaf wing cells. The midvein is often limited to the lower half of the leaf blade, or has completely disappeared. The cells of the leaf blade are prosenchymatic, many times longer than wide, with pointed ends interlocking. The sporophyte consists of a regularly shaped sporangium on a long stalk or seta. The spores are distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryopsida
The Bryopsida constitute the largest class of mosses, containing 95% of all moss species. It consists of approximately 11,500 species, common throughout the whole world. The group is distinguished by having spore capsules with teeth that are ''arthrodontous''; the teeth are separate from each other and jointed at the base where they attach to the opening of the capsule.Buck, William R. & Bernard Goffinet. (2000) "Morphology and classification of mosses", pages 71-123 ''in'' A. Jonathan Shaw & Bernard Goffinet (Eds.), ''Bryophyte Biology''. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press). Consequently, mosses in the Class Bryopsida are commonly known as the “joint-toothed” or “arthrodontous” mosses. These teeth are exposed when the covering operculum falls off. In other groups of mosses, the capsule is either ''nematodontous'' with an attached operculum, or else splits open without operculum or teeth. Morphological groups The Bryopsida can be simplified into three groups: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryidae
Bryidae is an important subclass of Bryopsida. It is common throughout the whole world. Members have a double peristome with alternating tooth segments. Classification The classification of the Bryidae.Buck, William R. & Bernard Goffinet. 2000. "Morphology and classification of mosses", pages 71-123 ''in'' A. Jonathan Shaw & Bernard Goffinet (Eds.), ''Bryophyte Biology''. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press). . Superorder: Bryanae :Bartramiales :Bryales :Hedwigiales :Orthotrichales :Rhizogoniales :Splachnales Superorder: Hypnanae :Hypnodendrales :Ptychomniales :Hookeriales :Hypnales Hypnales is the botanical name of an order of Bryophyta or leafy mosses. This group is sometimes called feather mosses, referring to their freely branched stems. The order includes more than 40 families and more than 4,000 species, making them ... References Plant subclasses Bryopsida {{Bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mire
A mire, peatland, or quagmire is a wetland area dominated by living peat-forming plants. Mires arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to water-logging and subsequent anoxia. All types of mires share the common characteristic of being saturated with water, at least seasonally with actively forming peat, while having their own ecosystem. Like coral reefs, mires are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface patterning. A quagmire is a floating (quaking) mire, bog, or any peatland being in a stage of hydrosere or hydrarch (hydroseral) succession, resulting in pond-filling yields underfoot. Ombrotrophic types of quagmire may be called quaking bog (quivering bog). Minerotrophic types can be named with the term quagfen. There are four types of mire: bog, fen, marsh and swamp. A bog is a mire that, due to its location relative to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protonema
A protonema (plural: protonemata) is a thread-like chain of cells that forms the earliest stage of development of the gametophyte (the haploid phase) in the life cycle of mosses. When a moss first grows from a spore, it starts as a ''germ tube'', which lengthens and branches into a filamentous complex known as a ''protonema'', which develops into a leafy gametophore, the adult form of a gametophyte in bryophytes. Moss spores germinate to form an alga-like filamentous structure called the protonema. It represents the juvenile gametophyte. While the protonema is growing by apical cell division, at some stage, under the influence of the phytohormone cytokinin, buds are induced which grow by three-faced apical cells. These give rise to gametophores, stems and leaf like structures. Bryophytes do not have true leaves (megaphylls A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametophore
Gametophores are prominent structures in seedless plants on which the reproductive organs are borne. The word gametophore and ‘-phore’ (Greek Φορά, "to be carried"). In mosses, liverworts and ferns (Archegoniata), the gametophores support gametangia (sex organs, female archegonia and male antheridia). If both archegonia and antheridia occur on the same plant, it is called monoecious. If there are separate female and male plants they are called dioecous. In Bryopsida the leafy moss plant (q. v. "Thallus") is the haploid gametophyte. It grows from its juvenile form, the protonema, under the influence of phytohormones (mainly cytokinins). Whereas the filamentous protonema grows by apical cell division, the gametophyte grows by division of three-faced apical cells. See also Rhizoid Rhizoids are protuberances that extend from the lower epidermal cells of bryophytes and algae. They are similar in structure and function to the root hairs of vascular land plants. Similar s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
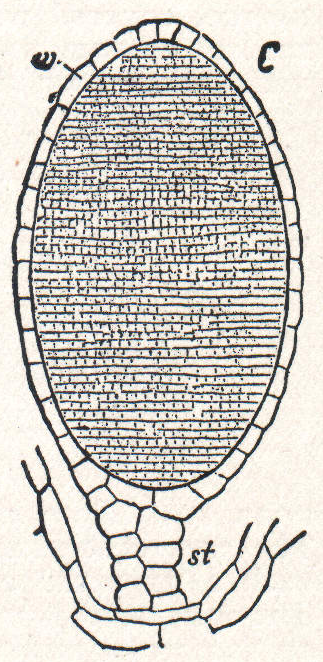
Archegonia
An archegonium (pl: archegonia), from the ancient Greek ''ἀρχή'' ("beginning") and ''γόνος'' ("offspring"), is a multicellular structure or organ of the gametophyte phase of certain plants, producing and containing the ovum or female gamete. The corresponding male organ is called the antheridium. The archegonium has a long neck canal or venter and a swollen base. Archegonia are typically located on the surface of the plant thallus, although in the hornworts they are embedded. Bryophytes In bryophytes and other cryptogams sperm reach the archegonium by swimming in water films, whereas in Pinophyta and Angiosperms the pollen are delivered by wind or animal vectors and the sperm are delivered by means of a pollen tube. In the moss ''Physcomitrella patens'', archegonia are not embedded but are located on top of the leafy gametophore (s. Figure). The Polycomb protein FIE is expressed in the unfertilized egg cell (right) as the blue colour after GUS staining reveals. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antheridia
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some Fungus, fungi, for example ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to Pollen, pollen grains and in most of these the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cell (biology), cells a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Broadcasting Of Latvia
Public Broadcasting of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas sabiedriskais medijs, lit=Latvian Public Media – LSM) is a publicly funded radio and television organization operated by both of Latvia's public broadcasters – Latvian Television and Radio Latvia. LSM provides news, analysis, culture, entertainment and new experimental content, produced mainly by Latvian Television and Radio Latvia, and by the portal’s editorial personnel. The site was launched on 3 February 2013. LSM content is also available in Russian and English. News content in English was made available from 1 July 2014. A unified news portal was one of the steps planned in a much wider convergence of both public broadcasters. In 2012, Latvia’s National Electronic Media Council (NEMC) approved the concept of creating a new Latvian public service media organization. NEMC members had to decide from 3 different scenarios: * partial convergence (institutional independence, but both media to engage in joint projects); * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucolepis Acanthoneuron
''Leucolepis'' is a genus of mosses in the family Mniaceae. Species * ''Leucolepis acanthoneura'' * ''Leucolepis menziesii ''Leucolepis'' is a genus of mosses in the family Mniaceae Mniaceae is a moss family in the order Bryales. Taxonomy The family Mniaceae includes the following genera: * '' Cinclidium'' * '' Cyrtomnium'' * '' Epipterygium'' * ''Leucolepi ...'' References Moss genera Mniaceae {{Bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Bulgaria
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |