|
Cliff Retreat
Scarp retreat is a geological process through which the location of an escarpment changes over time. Typically the cliff is undermined, rocks fall and form a talus slope, the talus is chemically or mechanically weathered and then removed through water or wind erosion, and the process of undermining resumes. Scarps may retreat for tens of kilometers in this way over relatively short geological time spans, even in arid locations. Scarp profiles A scarp is a line of cliffs that has usually been formed by faulting or erosion. If it is protected by a strong caprock, or if it contains vertical fractures, it may retain its steep profile as it retreats. Scarps in dry climates typically have a near-vertical upper face, that may account for 10% - 75% of the total height, with a talus-covered sloping rampart forming the lower section. The caprock is undermined as the rampart and face are eroded, and eventually a section collapses. A strong caprock will typically create a relatively hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England (New South Wales)
New England is a vaguely defined region in the north of the state of New South Wales, Australia, about 60 km inland from the Tasman Sea. The area includes the Northern Tablelands (or New England Tablelands) and the North West Slopes regions. As of 2006, New England had a population of 202,160, with over a quarter of the people living in the area of Tamworth Regional Council. Shaw, John H., "Collins Australian Encyclopedia", William Collins Pty Ltd., Sydney, 1984, . History The region has been occupied by Indigenous Australians for tens of thousands of years, in the west by the Kamilaroi people. In the highlands, the original languages (which are now extinct) included Anaiwan to the south of Guyra and Ngarbal to the north of Guyra. The population of the tablelands has been estimated to be 1,100 to 1,200 at the time of colonisation – quite low in comparison to the Liverpool Plains and Gwyder River region, estimated to be 4,500 to 5,500. Conflict, disease and environmental dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Surface Processes And Landforms
''Earth Surface Processes and Landforms'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of the British Society for Geomorphology. It covers geomorphology and more in general all aspects of Earth sciences dealing with the Earth surface. The journal was established in 1976 as ''Earth Surface Processes'', obtaining its current name in 1981. The journal primarily publishes original research papers. It also publishes ''Earth Surface Exchanges'' which include commentaries on issues of particular geomorphological interest, discussions of published papers, shorter journal articles suitable for rapid publication, and commissioned reviews on key aspects of geomorphological science. Foci include the physical geography of rivers, valleys, glaciers, mountains, hills, slopes, coasts, deserts, and estuary environments, along with research into Holocene, Pleistocene, or Quaternary science. The editor-in-chief is Stuart Lane (University of Lausanne). Abstracting and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Journal Of Geology
The ''South African Journal of Geology'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Geological Society of South Africa that was established in March 1896 as the ''Transactions of the Geological Society of South Africa'', obtaining its current title in 1987. Incorporated into the volumes up to and including volume 73 (1970) were the ''Proceedings of the Geological Society of South Africa''. The journal publishes scientific papers, notes, stratigraphic descriptions, and discussions in the broadly defined fields of geoscience that are related directly or indirectly to the geology of Africa. Contributions relevant to former supercontinents such as Gondwana and Pangaea are also published as are topical studies on any geology-related discipline. GSSA Publications. Retrieved 01 June 2019. The journal is |
Timeline Of Mars Science Laboratory
The Mars Science Laboratory and its rover, ''Curiosity'', were launched from Earth on November 26, 2011. As of , , ''Curiosity'' has been on the planet Mars for sols ( total days; ') since landing on August 6, 2012. ''(See Current status.)'' Prelaunch (2004–2011) In April 2004, the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) called for scientific experiments and instruments proposals for the Mars Science Laboratory and rover mission. Launch was proposed for September 2009. By December 14, 2004, eight proposals were selected, including instruments from Russia and Spain. Testing of components also began in late 2004, including Aerojet's monopropellant engine with the ability to throttle from 15 to 100 percent thrust with a fixed propellant inlet pressure. By November 2008 most hardware and software development was complete, and testing continued. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillslope Evolution
Hillslope evolution is the changes in the erosion rates, erosion styles and form of slopes of hills and mountains over time. Conceptual models During most of the 20th century three models of hillslope evolution were widely diffused: slope decline, slope replacement and parallel slope retreat. Until the 1950s models of hillslope form evolution were central in geomorphology. The modern understanding is that the evolution of slopes is much more complex than the classical models of decline, replacement and retreat imply. Slope decline Slope decline was proposed by William Morris Davis in his cycle of erosion theory. It consists of a gradual decrease in slope angle as stream incision slows down. This is accompaigned as slopes becomes more gentle they accumulate with fine-grained regolith stemming from weathering. Slope replacement Slope replacement was first proposed by Walther Penck challenging Davis' ideas on slope development. Slope replacement describes an evolution of slopes tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lester Charles King
Lester Charles King (1907–1989) was an English geologist and geomorphologist known for his theories on scarp retreat. He offered a very different view of the origin of continental landscaping than that of William Morris Davis. Studying at university in New Zealand King was a disciple of Charles Cotton who was heavily influenced by Davis. While King's ideas were an attempt at refuting Davis' cycle of erosion they were themselves of cyclical nature and contributed to what Cliff Ollier has called "Davis bashing" — the ridicule of cyclical theories in geomorphology, in particular Davis' ones. Critics did however not propose alternative models. For him, the weathering of physical factors in arid areas causes the erosion of the hills, the deposition of the weathered material (pediments) and the deposition of these material in lower altitudes, contributing to the formation of the pediplain. He was also an early proponent of continental drift Continental drift is the hypothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drakensberg
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within the border region of South Africa and Lesotho. The Drakensberg escarpment stretches for more than from the Eastern Cape Province in the South, then successively forms, in order from south to north, the border between Lesotho and the Eastern Cape and the border between Lesotho and KwaZulu-Natal Province. Thereafter it forms the border between KwaZulu-Natal and the Free State, and next as the border between KwaZulu-Natal and Mpumalanga Province. The escarpment winds north from there, through Mpumalanga, where it includes features such as the Blyde River Canyon, Three Rondavels, and God's Window. It then extends farther north to Hoedspruit in southeastern Limpopo where it is known as 'Klein Drakensberg' by the Afrikaner. From Hoedspruit i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians (placentals) in the northern hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia) in the southern hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
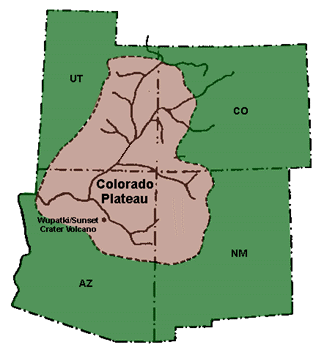
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuesta
A cuesta (from Spanish ''cuesta'' "slope") is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope on one side, and a steep slope on the other. In geology the term is more specifically applied to a ridge where a harder sedimentary rock overlies a softer layer, the whole being tilted somewhat from the horizontal. This results in a long and gentle backslope called a dip slope that conforms with the dip of resistant strata, called caprock. Where erosion has exposed the frontslope of this, a steep slope or escarpment occurs. The resulting terrain may be called scarpland. Definition In general usage, a cuesta is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope (backslope) on one side, and a steep slope (frontslope) on the other. The word is from Spanish: "flank or slope of a hill; hill, mount, sloping ground". In geology and geomorphology, cuesta refers specifically to an asymmetric ridge with a long and gentle backslope called a dip slope that conforms with the dip of a resistant stratum or strata, called cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Escarpment, Australia
The Great Escarpment in eastern Australia is an escarpment that runs east of the Great Dividing Range along most of the east of the continent. It was created due to formation of a new continental margin in the Mesozoic, followed by tectonic uplifting of the divide and then scarp retreat. The escarpment is estimated to be approximately in length, from north to south. Formation The Great Escarpment formed about 80 million years ago due to scarp retreat from a new continental edge formed by rifting. This was similar to the model in the western rift of East Africa. The Great Divide is an upwarp that lies tens or hundreds of kilometers from the chasmic fault of the continental margin, creating a drainage divide. The sequence of formation appears to have started with erosion of the plain and formation of a river pattern. The traces of these rivers can still be seen. There were then widespread flows of basalt, after which the Great Divide lifted, and finally the Great Escar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |