|
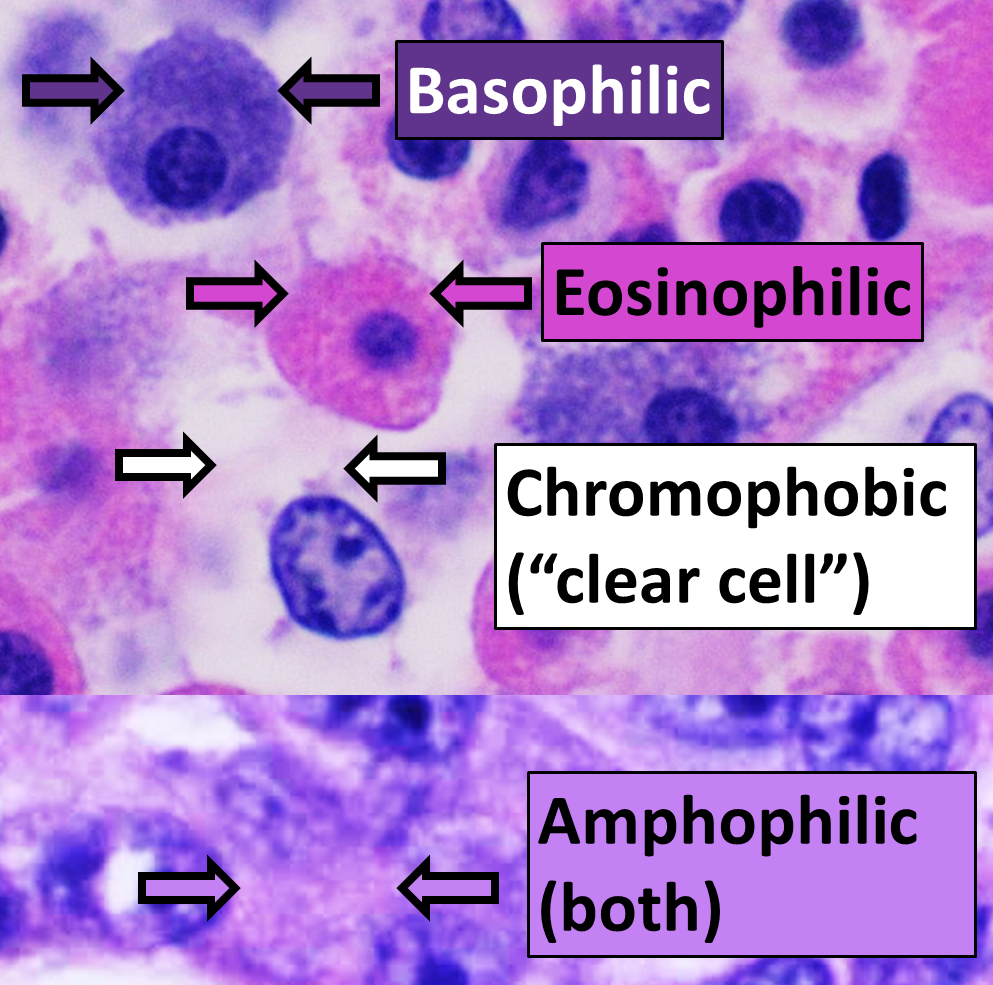
Clear Cell
In histology, a clear cell is a cell that shows a clear cytoplasm when stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Normal histology In the skin, some secretory cells in the epithelium appear as clear cells, and are one of the components of eccrine sweat glands. A clear cell's plasma membrane is highly folded, more so on the apical and lateral surfaces. The cytoplasm of clear cells contains large amounts of glycogen and many mitochondria. Melanocytes appear as clear cells when in the stratum basale of the skin, and Langerhans' cells appear as clear cells in the stratum spinosum. C cells, more commonly referred to as parafollicular cells are type of cell found in the thyroid gland which stain clear using H&E. Clear cell cancers Clear-cell adenocarcinomas are adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear-cell Adenocarcinoma
Clear-cell adenocarcinoma is a type of adenocarcinoma that shows clear cells. Types include: * Clear-cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina * Clear-cell ovarian carcinoma Ovarian clear-cell carcinoma, or clear-cell carcinoma of the ovary, also called ovarian clear-cell adenocarcinoma, is one of several subtypes of ovarian carcinoma – a subtype of epithelial ovarian cancer, in contrast to non-epithelial cancers. A ... * Uterine clear-cell carcinoma * Clear-cell adenocarcinoma of the lung (which is a type of Clear-cell carcinoma of the lung) See also * References External links Carcinoma {{oncology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocytes
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea), the inner ear, vaginal epithelium, meninges, bones, and heart. Melanin is a dark pigment primarily responsible for skin color. Once synthesized, melanin is contained in special organelles called melanosomes which can be transported to nearby keratinocytes to induce pigmentation. Thus darker skin tones have more melanosomes present than lighter skin tones. Functionally, melanin serves as protection against UV radiation. Melanocytes also have a role in the immune system. Function Through a process called melanogenesis, melanocytes produce melanin, which is a pigment found in the skin, eyes, hair, nasal cavity, and inner ear. This melanogenesis leads to a long-lasting pigmentation, which is in contrast to the pigmentation that originates from oxidation of already-existing melanin. There are both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenocarcinomas are part of the larger grouping of carcinomas, but are also sometimes called by more precise terms omitting the word, where these exist. Thus invasive ductal carcinoma, the most common form of breast cancer, is adenocarcinoma but does not use the term in its name—however, esophageal adenocarcinoma does to distinguish it from the other common type of esophageal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Several of the most common forms of cancer are adenocarcinomas, and the various sorts of adenocarcinoma vary greatly in all their aspects, so that few useful generalizations can be made about them. In the most specific usage (narrowest sense), the glandular origin or traits are exocrine; endocrine gland tumor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parafollicular Cell
Parafollicular cells, also called C cells, are neuroendocrine cells in the thyroid. The primary function of these cells is to secrete calcitonin. They are located adjacent to the thyroid follicles and reside in the connective tissue. These cells are large and have a pale stain compared with the follicular cells. In teleost and avian species these cells occupy a structure outside the thyroid gland named the ultimobranchial body. Structure Parafollicular cells are pale-staining cells found in small number in the thyroid and are typically situated basally in the epithelium, without direct contact with the follicular lumen. They are always situated within the basement membrane, which surrounds the entire follicle. Development Parafollicular cells are derived from pharyngeal endoderm. Embryologically, they associate with the ultimobranchial body, which is a ventral derivative of the fourth (or fifth) pharyngeal pouch. Parafollicular cells were previously believed to be derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratum Spinosum
The stratum spinosum (or spinous layer/prickle cell layer) is a layer of the epidermis found between the stratum granulosum and stratum basale. This layer is composed of polyhedral keratinocytes. These are joined with desmosomes. Their spiny (Latin, spinosum) appearance is due to shrinking of the microfilaments between desmosomes that occurs when stained with H&E. Keratinization begins in the stratum spinosum, although the actual keratinocytes begin in the stratum basale. They have large pale-staining nuclei as they are active in synthesizing fibrilar proteins, known as cytokeratin, which build up within the cells aggregating together forming tonofibrils. The tonofibrils go on to form the desmosomes, which allow for strong connections to form between adjacent keratinocytes. The stratum spinosum also contains Langerhans cells. Clinical significance Diffuse hyperplasia of the stratum spinosum is termed acanthosis. Additional images Image:Normal Epidermis and Dermis w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langerhans' Cells
A Langerhans cell (LC) is a tissue-resident macrophage of the skin. These cells contain organelles called Birbeck granules. They are present in all layers of the epidermis and are most prominent in the stratum spinosum. They also occur in the papillary dermis, particularly around blood vessels, as well as in the mucosa of the mouth, foreskin, and vaginal epithelium. They can be found in other tissues, such as lymph nodes, particularly in association with the condition Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH). Function In skin infections, the local Langerhans cells take up and process microbial antigens to become fully functional antigen-presenting cells. Generally, tissue-resident macrophages are involved in immune homeostasis and the uptake of apoptotic bodies. However, Langerhans cells can also take on a dendritic cell-like phenotype and migrate to lymph nodes to interact with naive T-cells. Langerhans cells derive from primitive erythro-myeloid progenitors that arise in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratum Basale
The ''stratum basale'' (basal layer, sometimes referred to as ''stratum germinativum'') is the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the external covering of skin in mammals. The ''stratum basale'' is a single layer of columnar or cuboidal basal cells. The cells are attached to each other and to the overlying stratum spinosum cells by desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. The nucleus is large, ovoid and occupies most of the cell. Some basal cells can act like stem cells with the ability to divide and produce new cells, and these are sometimes called basal keratinocyte stem cells. Others serve to anchor the epidermis glabrous skin (hairless), and hyper-proliferative epidermis (from a skin disease).McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Pope, F.M. (2004). ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology'' (Seventh Edition). Blackwell Publishing. Pages 3.7. . They divide to form the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum, which migrate superficially. Other types of cells found within the ''stratum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, '' Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and '' cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. Glycogen functions as one of two forms of energy reserves, glycogen being for short-term and the other form being triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) for long-term storage. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight, and the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass) and the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 kg stores roughly 400 grams of glycogen. The amount of glycogen stored in the body—particularly within the muscles and liver—mostly depends on physical training, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |