|
Clay-shoveler Fracture
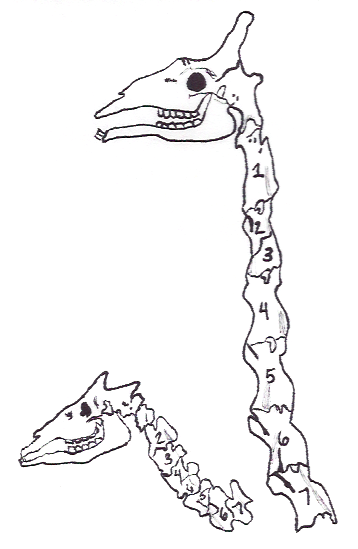
Clay-shoveler's fracture is a stable fracture through the spinous process of a vertebra occurring at any of the lower cervical or upper thoracic vertebrae, classically at C6 or C7. In Australia in the 1930s, men digging deep ditches tossed clay 10 to 15 feet above their heads using long handled shovels. Instead of separating, the sticky clay would sometimes stick to the shovel. At the top of the arc of motion, with the arms extended, the worker may hear a pop and feel a sudden pain between the shoulder blades, unable to continue working. The mechanism of injury is believed to be secondary to muscle pull and reflex with force transmission through the supraspinous ligaments. The tremendous force pulls on the spinous process producing an avulsion fracture An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United States In the United States, a neurosurgeon must generally complete four years of undergraduate education, four years of medical school, and seven years of residency (PGY-1-7). Most, but not all, residency programs have some component of basic science or clinical research. Neurosurgeons may pursue additional training in the form of a fellowship after residency, or, in some cases, as a senior resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''comminuted fracture''. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture. Signs and symptoms Although bone tissue contains no pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: * Breaking in the continuity of the periosteum, with or without similar discontinuity in endosteum, as both contain multiple pain receptors. * Edema and hematoma of nearby soft tissues caused by ruptured bone marrow evokes pressure pain. * Involuntary muscle spasms trying to hold bone fragments in place. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
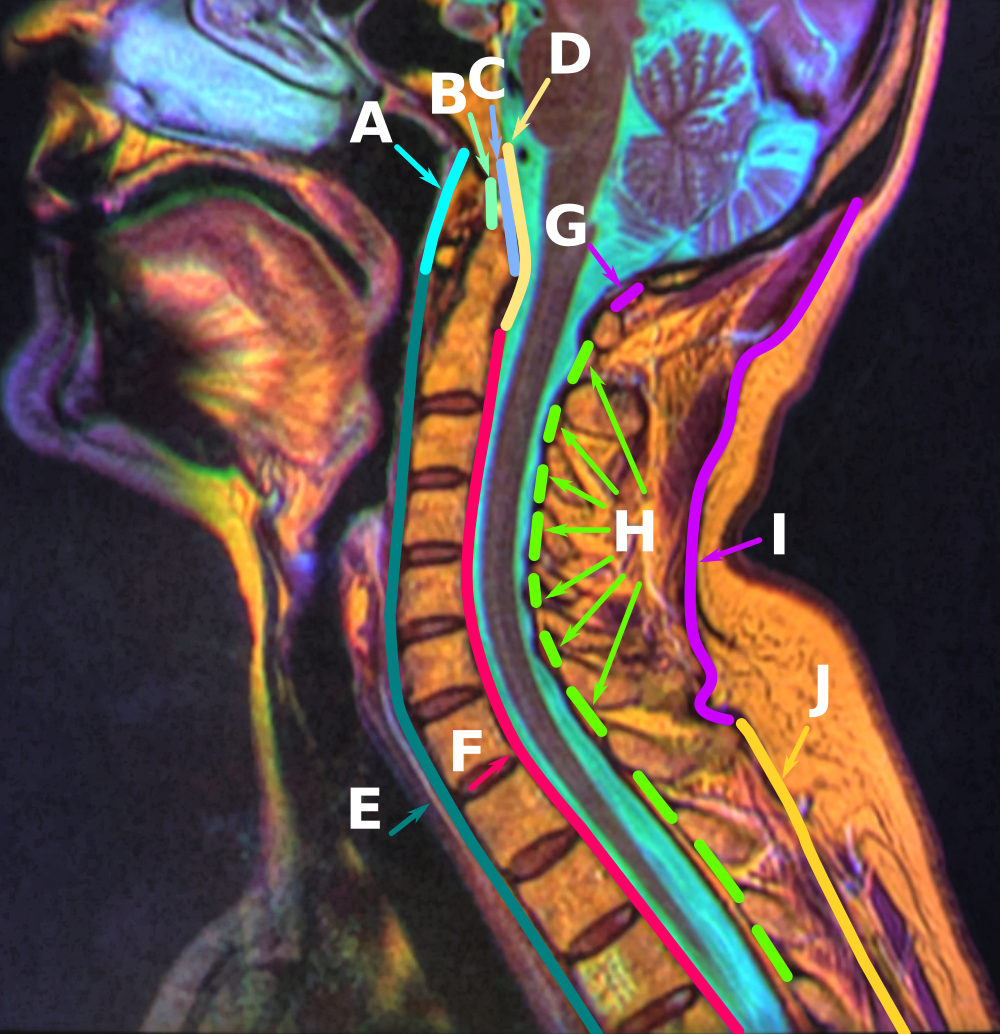
Spinous Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebra 6
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen (hole) in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebra 7
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen (hole) in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, and inferio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinous Ligaments
The supraspinous ligament, also known as the supraspinal ligament, is a ligament found along the vertebral column. Structure The supraspinous ligament connects the tips of the spinous processes from the seventh cervical vertebra to the sacrum. Above the seventh cervical vertebra, the supraspinous ligament is continuous with the nuchal ligament. Between the spinous processes it is continuous with the interspinous ligaments. It is thicker and broader in the lumbar than in the thoracic region, and intimately blended, in both situations, with the neighboring fascia. The most superficial fibers of this ligament extend over three or four vertebrae; those more deeply seated pass between two or three vertebrae while the deepest connect the spinous processes of neighboring vertebrae. Development Function The supraspinous ligament, along with the posterior longitudinal ligament, interspinous ligaments and ligamentum flavum, help to limit hyperflexion of the vertebral column. Clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avulsion Fracture
An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body (such as a fall or pull) or at the tendon by a muscular contraction that is stronger than the forces holding the bone together. Generally muscular avulsion is prevented by the neurological limitations placed on muscle contractions. Highly trained athletes can overcome this neurological inhibition of strength and produce a much greater force output capable of breaking or avulsing a bone. Types Dental avulsion Traumatic complete displacement of a tooth from its socket in alveolar bone. It is a serious dental emergency in which prompt management (within 20–40 minutes of injury) affects the prognosis of the tooth. Tuberosity avulsion of the 5th metatarsal left, Proximal fractures of 5th metatarsa The tuberosity avulsion fracture (also known as pseud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian networks * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR Problem Diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law copy right remover block Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR Computerized Assessment System * Computer-assisted diagnosis * Differential diagnosis * Medical di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Fractures
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''comminuted fracture''. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture. Signs and symptoms Although bone tissue contains no pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: * Breaking in the continuity of the periosteum, with or without similar discontinuity in endosteum, as both contain multiple pain receptors. * Edema and hematoma of nearby soft tissues caused by ruptured bone marrow evokes pressure pain. * Involuntary muscle spasms trying to hold bone fragments in place. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |