|
Clapp Oscillator
The Clapp oscillator or Gouriet oscillator is an LC electronic oscillator that uses a particular combination of an inductor and three capacitors to set the oscillator's frequency. LC oscillators use a transistor (or vacuum tube or other gain element) and a positive feedback network. The oscillator has good frequency stability. History The Clapp oscillator design was published by James Kilton Clapp in 1948 while he worked at General Radio. According to Czech engineer Jiří Vackář, oscillators of this kind were independently developed by several inventors, and one developed by Gouriet had been in operation at the BBC since 1938. Circuit The Clapp oscillator uses a single inductor and three capacitors to set its frequency. The Clapp oscillator is often drawn as a Colpitts oscillator that has an additional capacitor () placed in series with the inductor. The oscillation frequency in Hertz (cycles per second) for the circuit in the figure, which uses a field-effect transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LC Circuit
An LC circuit, also called a resonant circuit, tank circuit, or tuned circuit, is an electric circuit consisting of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C, connected together. The circuit can act as an electrical resonator, an electrical analogue of a tuning fork, storing energy oscillating at the circuit's resonant frequency. LC circuits are used either for generating signals at a particular frequency, or picking out a signal at a particular frequency from a more complex signal; this function is called a bandpass filter. They are key components in many electronic devices, particularly radio equipment, used in circuits such as oscillators, filters, tuners and frequency mixers. An LC circuit is an idealized model since it assumes there is no dissipation of energy due to resistance. Any practical implementation of an LC circuit will always include loss resulting from small but non-zero resistance within the components and conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillation, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillation, Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current (AC) signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices ranging from simplest clock generators to digital instruments (like calculators) and complex computers and peripherals etc. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by Transmitter, radio and television transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and the sounds produced by electronic beepers and video games. Oscillators are often characterized by the frequency of their output signal: *A Low-frequency oscillation, low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an electronic oscillator that generates a frequency below approximately 20 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil. When the current flowing through the coil changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces an electromotive force (''emf'') (voltage) in the conductor, described by Faraday's law of induction. According to Lenz's law, the induced voltage has a polarity (direction) which opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors oppose any changes in current through them. An inductor is characterized by its inductance, which is the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of inductance is the henry (H) named for 19th century American scientist Joseph Henry. In the measurement of magnetic circuits, it is equivalent to . Inductors have values that typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
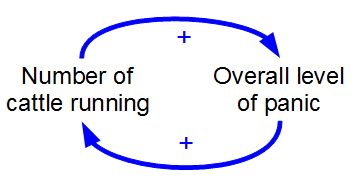
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is Phase (waves), in phase with the input, in the sense that it adds to make the input larger. Positive feedback tends to cause Control theory#Stability, system i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Kilton Clapp
James Kilton Clapp (December 30, 1897 – 1965) was an American electrical engineer who worked for General Radio Corporation. He was born in Denver, Colorado and graduated from Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1923, obtaining a master's degree there in 1926. He taught at MIT and then joined General Radio Corporation in 1928, until his retirement in 1957. He became a member of the IRE in 1928 and in 1933 was named "Fellow". Several of Clapp's inventions became the basis of General Radio products. He invented a quartz-crystal oscillator frequency standard in 1930, and patented a temperature control oven for crystal oscillators. Clapp's name is best known in the field of electronics for his description in 1948 of an improved form of Colpitts oscillator known as the Clapp oscillator The Clapp oscillator or Gouriet oscillator is an LC electronic oscillator that uses a particular combination of an inductor and three capacitors to set the oscillator's frequency. LC oscillator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Radio
General Radio Company (later, GenRad) was a broad-line manufacturer of electronic test equipment in Massachusetts, U.S. from 1915 to 2001. History On June 14, 1915, Melville Eastham and a small group of investors started General Radio Company in Cambridge, Massachusetts, a few blocks northwest of Massachusetts Institute of Technology. During the 1950s, the company moved to West Concord, Massachusetts, where it became a major player in the automatic test equipment (ATE) business, manufacturing a line of testers for assembled printed circuit boards. It also produced extensive lines of electrical component measuring equipment, sound and vibration measurement and RLC standards. In 1975, the company name was changed to GenRad. In 1991, a startup QuadTech was founded as spinoff of GenRad's Instrumentation division and Precision Product lines, as well as the rights to use the "GenRad" and "General Radio" names. In 2000, IET Labs acquired from QuadTech the GenRad RLC standards, imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proc
Proc may refer to: * Proč, a village in eastern Slovakia * '' Proč?'', a 1987 Czech film * procfs or proc filesystem, a special file system (typically mounted to ) in Unix-like operating systems for accessing process information * Protein C (PROC) * Proc, a term in video game terminology * Procedures or process, in the programming language ALGOL 68 * People's Republic of China, the formal name of China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ... * the official acronym for the Canadian House of Commons Standing Committee on Procedure and House Affairs {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey G
Geoffrey, Geoffroy, Geoff, etc., may refer to: People * Geoffrey (name), including a list of people with the name * Geoffroy (surname), including a list of people with the name * Geoffrey of Monmouth (c. 1095–c. 1155), clergyman and one of the major figures in the development of British history * Geoffrey I of Anjou (died 987) * Geoffrey II of Anjou (died 1060) * Geoffrey III of Anjou (died 1096) * Geoffrey IV of Anjou (died 1106) * Geoffrey V, Count of Anjou (1113–1151), father of King Henry II of England * Geoffrey II, Duke of Brittany (1158–1186), one of Henry II's sons * Geoffrey, Archbishop of York (c. 1152–1212) * Geoffroy du Breuil of Vigeois, 12th century French chronicler * Geoffroy de Charney (died 1314), Preceptor of the Knights Templar * Geoffroy IV de la Tour Landry (c. 1320–1391), French nobleman and writer * Geoffrey the Baker (died c. 1360), English historian and chronicler * Geoffroy (musician) (born 1987), Canadian singer, songwriter and multi-instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clapp Oscillator
The Clapp oscillator or Gouriet oscillator is an LC electronic oscillator that uses a particular combination of an inductor and three capacitors to set the oscillator's frequency. LC oscillators use a transistor (or vacuum tube or other gain element) and a positive feedback network. The oscillator has good frequency stability. History The Clapp oscillator design was published by James Kilton Clapp in 1948 while he worked at General Radio. According to Czech engineer Jiří Vackář, oscillators of this kind were independently developed by several inventors, and one developed by Gouriet had been in operation at the BBC since 1938. Circuit The Clapp oscillator uses a single inductor and three capacitors to set its frequency. The Clapp oscillator is often drawn as a Colpitts oscillator that has an additional capacitor () placed in series with the inductor. The oscillation frequency in Hertz (cycles per second) for the circuit in the figure, which uses a field-effect transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)