|
Clad
Cladding is an outer layer of material covering another. It may refer to the following: *Cladding (boiler), the layer of insulation and outer wrapping around a boiler shell *Cladding (construction), materials applied to the exterior of buildings **Wall cladding, exterior material applied to the walls of a building **Copper cladding, applying copper to the exterior of buildings **Rainscreen cladding, an exterior wall detail to create a capillary break and to allow drainage and evaporation of water *Cladding (fiber optics), fiber optics property to contain light in the core of the fiber by total internal reflection *Cladding (metalworking), a bonding together of dissimilar metals *Cladding (nuclear fuel) Cladding is an outer layer of material covering another. It may refer to the following: *Cladding (boiler), the layer of insulation and outer wrapping around a boiler shell *Cladding (construction), materials applied to the exterior of buildings ..., the outer layer of the fuel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladding (construction)
Cladding is the application of one material over another to provide a skin or layer. In construction, cladding is used to provide a degree of thermal insulation and weather resistance, and to improve the appearance of buildings. Cladding can be made of any of a wide range of materials including wood, metal, brick, vinyl, and composite materials that can include aluminium, wood, blends of cement and recycled polystyrene, wheat/rice straw fibres. Rainscreen cladding is a form of weather cladding designed to protect against the elements, but also offers thermal insulation. The cladding does not itself need to be waterproof, merely a control element: it may serve only to direct water or wind safely away in order to control run-off and prevent its infiltration into the building structure. Cladding may also be a control element for noise, either entering or escaping. Cladding can become a fire risk by design or material. Description Cladding in construction is material applied over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladding (metalworking)
Cladding is the bonding together of dissimilar metals. It is different from fusion welding or gluing as a method to fasten the metals together. Cladding is often achieved by extruding two metals through a die as well as pressing or rolling sheets together under high pressure. The United States Mint uses cladding to manufacture coins from different metals. This allows a cheaper metal to be used as a filler. For example, dimes and quarters struck since 1965 have cores made from pure copper, with a clad layer consisting of 75% copper and 25% nickel added during production. Laser cladding is an additive manufacturing approach for metal coatings or precise piece restorations by using high power multi-mode optical fiber laser. Roll bonding In roll bonding, two or more layers of different metals are thoroughly cleaned and passed through a pair of rollers under sufficient pressure to bond the layers. The pressure is high enough to deform the metals and reduce the combined thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
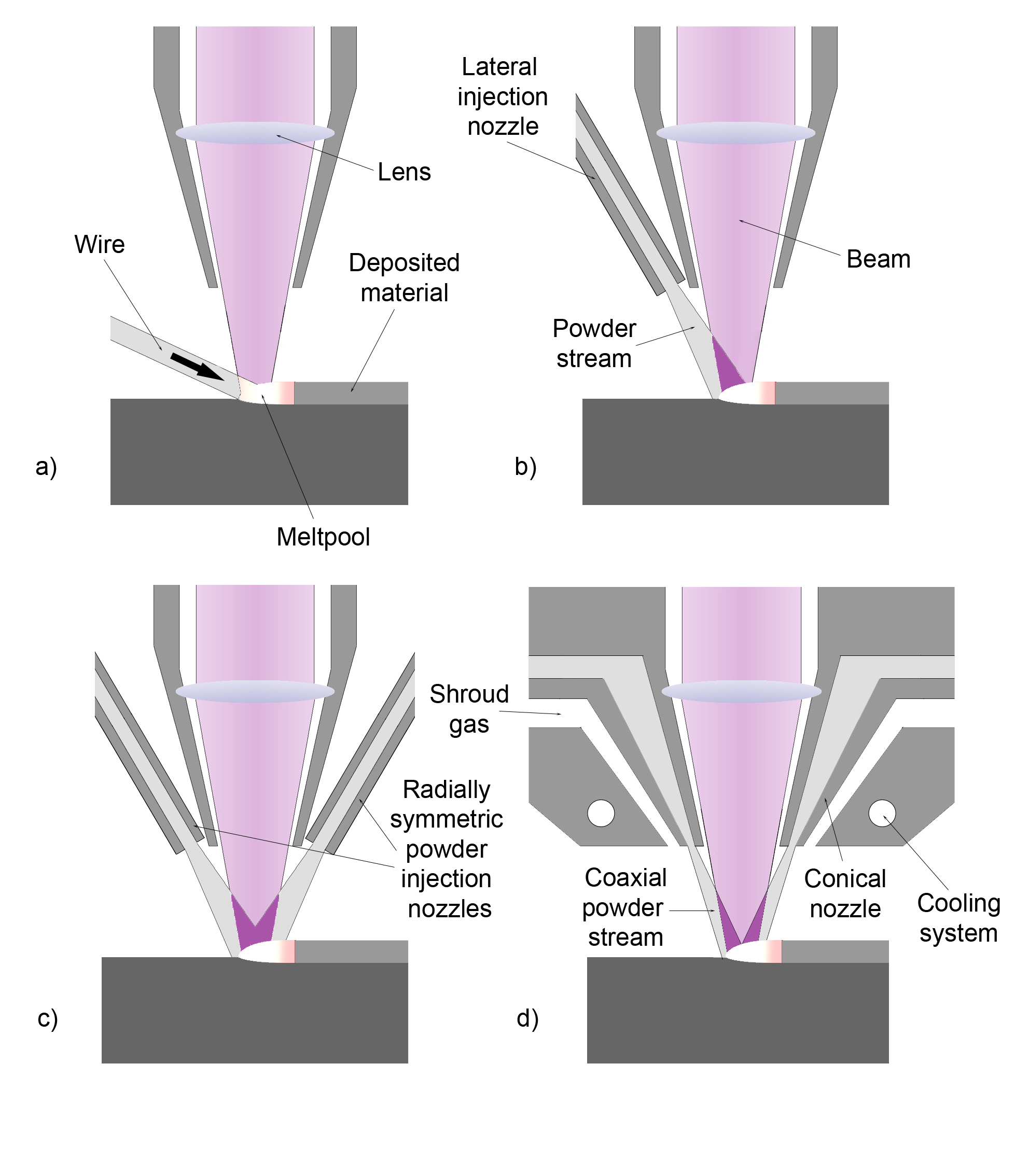
Cladding (nuclear Fuel)
Cladding is an outer layer of material covering another. It may refer to the following: *Cladding (boiler), the layer of insulation and outer wrapping around a boiler shell *Cladding (construction), materials applied to the exterior of buildings **Wall cladding, exterior material applied to the walls of a building **Copper cladding, applying copper to the exterior of buildings **Rainscreen cladding, an exterior wall detail to create a capillary break and to allow drainage and evaporation of water *Cladding (fiber optics), fiber optics property to contain light in the core of the fiber by total internal reflection *Cladding (metalworking), a bonding together of dissimilar metals *Cladding (nuclear fuel) Cladding is an outer layer of material covering another. It may refer to the following: *Cladding (boiler), the layer of insulation and outer wrapping around a boiler shell *Cladding (construction), materials applied to the exterior of buildings ..., the outer layer of the fuel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainscreen
A rainscreen is an exterior wall detail where the siding (wall cladding) stands off from the moisture- resistant surface of an air/water barrier applied to the sheathing to create a capillary break and to allow drainage and evaporation. The ''rainscreen'' is the cladding or siding itself but the term rainscreen implies a system of building. Ideally the rainscreen prevents the wall air/water barrier from getting wet but because of cladding attachments and penetrations (such as windows and doors) water is likely to reach this point, and hence materials are selected to be moisture tolerant and integrated with flashing. In some cases a rainscreen wall is called a ''pressure-equalized rainscreen'' wall where the ventilation openings are large enough for the air pressure to nearly equalize on both sides of the rain screen,Brown, W. C, Rousseau, M. Z., and Dalgliesh, W. A., "Field Testing of Pressure-Equalized Rain Screen Walls," Donaldson, Barry, ed.. ''Exterior wall systems: glass and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladding (boiler)
Boilers for generating steam or hot water have been designed in countless shapes, sizes and configurations. An extensive terminology has evolved to describe their common features. This glossary provides definitions for these terms. Terms which relate solely to boilers used for space heating or generating hot water are identified by (HVAC). A-B ; : A container beneath the furnace, catching ash and clinker that falls through the #Firebar, firebars. This may be made of brickwork for a stationary boiler, or steel sheet for a locomotive. Ashpans are often the location of the #Damper, damper. They may also be shaped into hoppers, for easy cleaning during #Disposal, disposal. ; Blastpipe: Part of the exhaust system that discharges exhaust steam from the cylinders into the smokebox beneath the chimney in order to increase the draught through the fire. ; Boiler blowdown, Blow-down: Periodic venting of water from the boiler. This water contains the most concentrated precursors for #Sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Cladding
There are four main techniques used today in the UK and mainland Europe for copper cladding a building: * seamed-cladding (typically 0.7mm thick copper sheet on the facade): max 600mm by 4000mm 'seam centres'. * shingle-cladding (typically made from 0.7mm thick copper sheet): max 600mm by 4000mm 'seam centres'. * slot-in panels (typically made from 1.0mm thick copper sheet): max 350mm wide for 1.0mm, by nominal 4 m length. * cassettes (typically made from 1.0mm up to 1.5mm thick copper sheet): largest-format cladding elements, more subframing is needed: can be 900mm x nominal 4000mm length. When selecting size of a cladding element, take wind-loadings into account, and also consider the standard sizes available of the sheet (or coil) pre-material, to minimise material wastage through off-cuts. This helps to reduce costs. The choice of which system to use depends on the aesthetic effect required, and building geometry can also have an influence on the choice. Copper clad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladding (fiber Optics)
Cladding in optical fibers is one or more layers of materials of lower refractive index, in intimate contact with a core material of higher refractive index. The cladding causes light to be confined to the core of the fiber by total internal reflection at the boundary between the two. Light propagation within the cladding is typically suppressed for most fibers. However, some fibers can support ''cladding modes'' in which light propagates through the cladding as well as the core. Depending upon the quantity of modes that are supported, they are referred to as multi-mode fibers and single-mode fibers. Improving transmission through fibers by applying a cladding was discovered in 1953 by Dutch scientist Bram van Heel. History The fact that transmission through fibers could be improved by applying a cladding was discovered in 1953 by Dutch scientist Bram van Heel, who used it to demonstrate image transmission through a bundle of optical fibers. Early cladding materials included oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall Cladding
Siding or wall cladding is the protective material attached to the exterior side of a wall of a house or other building. Along with the roof, it forms the first line of defense against the elements, most importantly sun, rain/snow, heat and cold, thus creating a stable, more comfortable environment on the interior side. The siding material and style also can enhance or detract from the building's beauty. There is a wide and expanding variety of materials to side with, both natural and artificial, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Masonry walls as such do not require siding, but any wall can be sided. Walls that are internally framed, whether with wood, or steel I-beams, however, must always be sided. Most siding consists of pieces of weather-resistant material that are smaller than the wall they cover, to allow for expansion and contraction of the materials due to moisture and temperature changes. There are various styles of joining the pieces, from board and batton, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |