Cladding (metalworking) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cladding is the bonding together of dissimilar
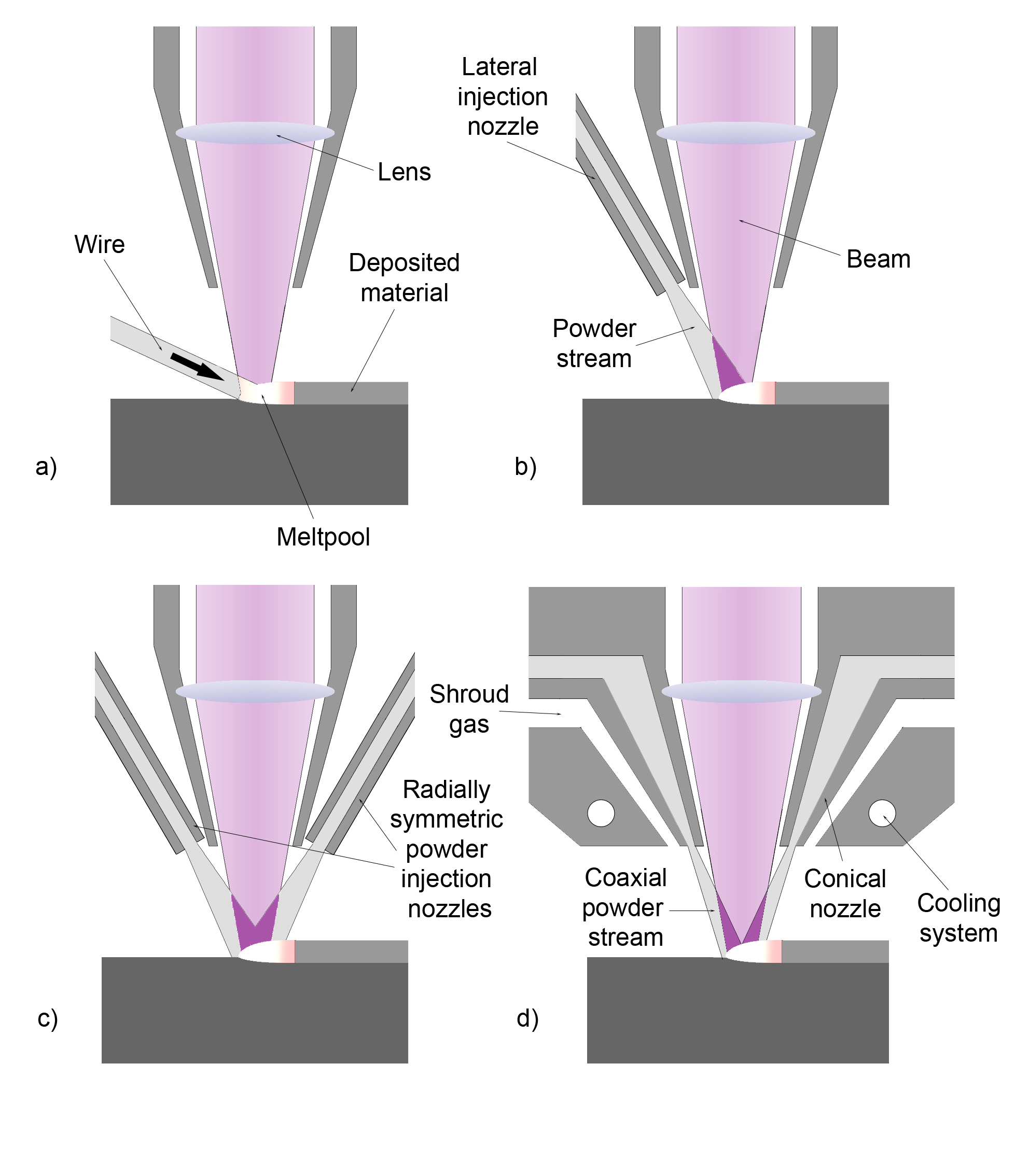 Automatic laser cladding machines are the subject of ongoing research and development. Many of the process parameters must be manually set, such as laser power, laser focal point, substrate velocity, powder injection rate, etc., and thus require the attention of a specialized technician to ensure proper results. By use of sensors to monitor the deposited track height and width, metallurgical properties, and temperature, constant observation from a technician is no longer required to produce a final product. Further research has been directed to forward processing where system parameters are developed around specific metallurgical properties for user defined applications (such as microstructure, internal stresses, dilution zone gradients, and clad contact angle).
Automatic laser cladding machines are the subject of ongoing research and development. Many of the process parameters must be manually set, such as laser power, laser focal point, substrate velocity, powder injection rate, etc., and thus require the attention of a specialized technician to ensure proper results. By use of sensors to monitor the deposited track height and width, metallurgical properties, and temperature, constant observation from a technician is no longer required to produce a final product. Further research has been directed to forward processing where system parameters are developed around specific metallurgical properties for user defined applications (such as microstructure, internal stresses, dilution zone gradients, and clad contact angle).
repairing parts
(ideal if the mould of the part no longer exist or too much time is needed for a new fabrication). * Most suitable technique for graded material application. * Well adapted for near-net-shape manufacturing. * Low dilution between track and substrate (unlike other welding processes and strong metallurgical bond. * Low deformation of the substrate and small heat affected zone (HAZ). * High cooling rate => fine microstructure. * A lot of material flexibility (metal, ceramic, even polymer). * Built part is free of crack and porosity. * Compact technology.
metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
s. It is different from fusion welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
or gluing as a method to fasten the metals together. Cladding is often achieved by extruding two metals through a die as well as pressing or rolling
Rolling is a Motion (physics)#Types of motion, type of motion that combines rotation (commonly, of an Axial symmetry, axially symmetric object) and Translation (geometry), translation of that object with respect to a surface (either one or the ot ...
sheets together under high pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
.
The United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bull ...
uses cladding to manufacture coin
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
s from different metals. This allows a cheaper metal to be used as a filler. For example, dimes and quarters struck since 1965 have cores made from pure copper, with a clad layer consisting of 75% copper and 25% nickel added during production. Half dollars struck from 1965 to 1969 for circulation and in 1970 for collectors also incorporated cladding, albeit in the case of those coins, the core was a mixture of 20.9% silver and 79.1% copper, and its clad layer was 80% silver and 20% copper. Half dollars struck since 1971 are produced identically to the dimes and quarters.
Laser cladding is an additive manufacturing approach for metal coatings or precise piece restorations by using high power multi-mode optical fiber laser.
Roll bonding
Inroll bonding
Roll bonding is a solid state, cold welding process, obtained through Rolling (metalworking), flat rolling of sheet metals. In roll bonding, two or more layers of different metals are passed through a pair of flat rollers under sufficient pressure ...
, two or more layers of different metals are thoroughly cleaned and passed through a pair of rollers under sufficient pressure to bond the layers. The pressure is high enough to deform the metals and reduce the combined thickness of the clad material. Heat may be applied, especially when metals are not ductile
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversi ...
enough. As an example of application, bonding of the sheets can be controlled by painting a pattern on one sheet; only the bare metal surfaces bond, and the un-bonded portion can be inflated if the sheet is heated and the coating vaporizes. This is used to make heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contac ...
s for refrigeration equipment.Bralla, James G. ''Handbook of Manufacturing Processes'' Industrial Press 2007 pages 310-312
Explosive welding
In explosive welding, the pressure to bond the two layers is provided bydetonation
Detonation () is a type of combustion involving a supersonic exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front propagating directly in front of it. Detonations propagate supersonically through shock waves with ...
of a sheet of chemical explosive. No heat-affected zone is produced in the bond between metals. The explosion propagates across the sheet, which tends to expel impurities and oxides from between the sheets. Pieces up to 4 x 16 metres can be manufactured. The process is useful for cladding metal sheets with a corrosion-resistant layer.
Laser cladding
''Laser cladding'' is a method of depositing material by which a powdered or wire feedstock material is melted and consolidated by use of alaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
in order to coat part of a substrate or fabricate a near-net shape part ( additive manufacturing technology).
It is often used to improve mechanical properties or increase corrosion resistance, repair worn out parts, and fabricate metal matrix composite
In materials science, a metal matrix composite (MMC) is a composite material with fibers or particles dispersed in a metallic matrix, such as copper, aluminum, or steel. The secondary phase is typically a ceramic (such as alumina or silicon carb ...
s. Surface material may be laser cladded directly onto a highly stressed component, i.e. to make a self- lubricating surface. However, such a modification requires further industrialization of the cladding process to adapt it for efficient mass production. Further research on the detailed effects from surface topography, material composition of the laser cladded material and the composition of the additive package in the lubricants on the tribological properties and performance are preferably studied with tribometric testing.
Process
A laser is used to melt metallic powder dropped on a substrate to be coated. The melted metal forms a pool on the substrate; moving the substrate allows the melt pool to solidify in a track of solid metal. Some processes involve moving the laser and powder nozzle assembly over a stationary substrate to produce solidified tracks. The motion of the substrate is guided by aCAM
Cam or CAM may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cam (mechanism), a mechanical linkage which translates motion
* Camshaft, a shaft with a cam
* Camera or webcam, a device that records images or video
In computing
* Computer-aided manufacturin ...
system which interpolates solid objects into a set of tracks, thus producing the desired part at the end of the trajectory.
 Automatic laser cladding machines are the subject of ongoing research and development. Many of the process parameters must be manually set, such as laser power, laser focal point, substrate velocity, powder injection rate, etc., and thus require the attention of a specialized technician to ensure proper results. By use of sensors to monitor the deposited track height and width, metallurgical properties, and temperature, constant observation from a technician is no longer required to produce a final product. Further research has been directed to forward processing where system parameters are developed around specific metallurgical properties for user defined applications (such as microstructure, internal stresses, dilution zone gradients, and clad contact angle).
Automatic laser cladding machines are the subject of ongoing research and development. Many of the process parameters must be manually set, such as laser power, laser focal point, substrate velocity, powder injection rate, etc., and thus require the attention of a specialized technician to ensure proper results. By use of sensors to monitor the deposited track height and width, metallurgical properties, and temperature, constant observation from a technician is no longer required to produce a final product. Further research has been directed to forward processing where system parameters are developed around specific metallurgical properties for user defined applications (such as microstructure, internal stresses, dilution zone gradients, and clad contact angle).
Advantages
* Best technique for coating any shape => increase lifetime of wearing parts. * Particular dispositions forepairing parts
(ideal if the mould of the part no longer exist or too much time is needed for a new fabrication). * Most suitable technique for graded material application. * Well adapted for near-net-shape manufacturing. * Low dilution between track and substrate (unlike other welding processes and strong metallurgical bond. * Low deformation of the substrate and small heat affected zone (HAZ). * High cooling rate => fine microstructure. * A lot of material flexibility (metal, ceramic, even polymer). * Built part is free of crack and porosity. * Compact technology.
See also
* Additive manufacturing * All-Clad * Copper-clad aluminum wire * Copper-clad steel * GoldbeatingReferences
External links
* {{Authority control Laser applications Metalworking