|
Cinnamyl Alcohol
Cinnamyl alcohol or styron is an organic compound that is found in esterified form in storax, Balsam of Peru, and cinnamon leaves. It forms a white crystalline solid when pure, or a yellow oil when even slightly impure. It can be produced by the hydrolysis of storax. Cinnamyl alcohol has a distinctive odour described as "sweet, balsam, hyacinth, spicy, green, powdery, cinnamic" and is used in perfumery and as a deodorant. Cinnamyl alcohol is naturally occurrent only in small amount, so its industrial demand is usually fulfilled by chemical synthesis starting from cinnamaldehyde. Properties The compound is a solid at room temperature, forming colourless crystals that melt upon gentle heating. As is typical of most higher-molecular weight alcohols, it is sparingly soluble in water at room temperature, but highly soluble in most common organic solvents. Safety Cinnamyl alcohol has been found to have a sensitising effect on some people [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyacinth (plant)
''Hyacinthus'' is a small genus of bulbous, spring-blooming perennials. They are fragrant flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae and are commonly called hyacinths (). The genus is native to the area of the eastern Mediterranean from the south of Turkey to Palestine, although naturalized more widely. Several species of ''Brodiaea'', ''Scilla'', and other plants that were formerly classified in the Liliaceae family and have flower clusters borne along the stalk also have common names with the word "hyacinth" in them. Hyacinths should also not be confused with the genus '' Muscari'', which are commonly known as grape hyacinths. Description ''Hyacinthus'' grows from bulbs, each producing around four to six linear leaves and one to three spikes or racemes of flowers. In the wild species, the flowers are widely spaced, with as few as two per raceme in '' H. litwinovii'' and typically six to eight in '' H. orientalis'' which grows to a height ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Alcohols
A primary alcohol is an alcohol in which the hydroxy group In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ... is bonded to a primary carbon atom. It can also be defined as a molecule containing a “–CH2OH” group. In contrast, a secondary alcohol has a formula “–CHROH” and a tertiary alcohol has a formula “–CR2OH”, where “R” indicates a carbon-containing group. Examples of primary alcohols include ethanol and n-Butanol, 1-butanol. Methanol is also generally regarded as a primary alcohol, including the 1911 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica,. See also * Alcohol (chemistry), Alcohol (especially Nomenclature section for discussion on Secondary and Tertiary alcohols.) * Oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids References Primary alcohols, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavors
Flavor or flavour is either the sensory perception of taste or smell, or a flavoring in food that produces such perception. Flavor or flavour may also refer to: Science *Flavors (programming language), an early object-oriented extension to Lisp * Flavour (particle physics), a quantum number of elementary particles related to their weak interactions *Flavor of Linux, another term for any particular Linux distribution; by extension, "flavor" can be applied to any program or other computer code that exists in more than one current variant at the same time Film and TV * ''Flavors'' (film), romantic comedy concerning Asian-Indian immigrants in America Music Artists and bands *Flavor Flav (born 1959), former rap/hip-hop promoter and current reality television actor *Flavour N'abania (born 1983), Nigerian singer-songwriter * Flavor (band), minor hit with "Sally Had A Party" in 1968 Albums * ''Flavours'' (album), 1975 album by The Guess Who * ''Flavors'' (album), by American R&B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodiola Rosea
''Rhodiola rosea'' (commonly golden root, rose root, roseroot, Aaron's rod, Arctic root, king's crown, ''lignum rhodium'', orpin rose) is a perennial flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It grows naturally in wild Arctic regions of Europe (including Britain), Asia, and North America ( N.B., Nfld. and Labrador, N.S., QC.; Alaska, Maine, N.Y., N.C., Pa., Vt), and can be propagated as a groundcover. Although ''Rhodiola rosea'' has been used in traditional medicine, there is no high-quality clinical evidence of its effectiveness to treat any disease. The United States Food and Drug Administration has issued several warnings to manufacturers of ''R. rosea'' dietary supplements for making false health claims about its safety and efficacy. The plant is threatened in many countries due to rapidly growing demand. Supply comes mostly from wild harvesting on an industrial scale, and a combination of growing scarcity and a lack of regulation has led to environmental degradation, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosavin
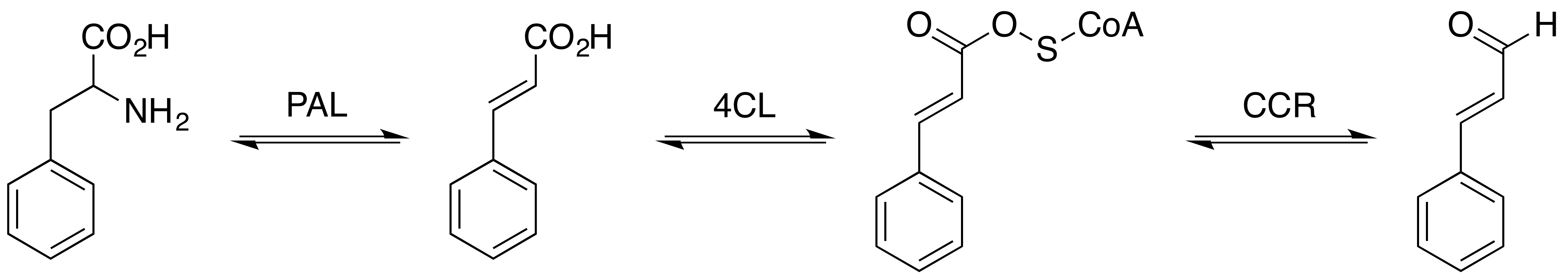
Rosavin (also known as rosin, rosavin, and rosarin) are a family of cinnamyl mono- and diglycosides that are key ingredients of ''Rhodiola rosea'' L., (''R. rosea''). ''R. rosea'' is an important medicinal plant commonly used throughout Europe, Asia, and North America, that has been recognized as a botanical adaptogen by the European Medicines Agency. Rosavin production is specific to ''R. rosea'' and ''R. sachalinenis'', and the biosynthesis of these glycosides occurs spontaneously in ''Rhodiola'' roots and rhizomes. The production of rosavins increases in plants as they get older, and the amount of the cinnamyl alcohol glycosides depends on the place of origin of the plant. Biosynthesis Cinnamyl alcohol glycosides are products of phenylpropanoid metabolism, derived from phenylalanine, which is produced from the shikimic-chorismic acid pathway. Shikimic acid is made from the precursor compounds erythrose-4-phosphate, and phosphoenolpyruvate. Shikimic acid is then converted to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosarin
Rosarin is a cinnamyl alcohol glycoside isolated from ''Rhodiola rosea ''Rhodiola rosea'' (commonly golden root, rose root, roseroot, Aaron's rod, Arctic root, king's crown, ''lignum rhodium'', orpin rose) is a perennial flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It grows naturally in wild Arctic regions of Europe ...''. References External links Purification of Phenylalkanoids and monoterpene glycosides from Rhodiola rosea L. roots by high-speed counter-current chromatography Phenylpropanoid glycosides {{organic-chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Fragrance Association
The International Fragrance Association (IFRA) is the global representative body of the fragrance industry. It seeks to represent the collective interests of the industry and promote the safe use of fragrances through regulation. The Association was founded in 1973 and has its head office in Geneva, Switzerland, and its operations centre in Brussels, Belgium. As of October 2022, its membership includes seven multinational companies (known as 'Regular Members') and 23 national associations. There are ten 'Supporting Members' from countries where and IFRA does not have a national association. IFRA is led by a President, Martina Bianchini, and by a Board headed by its Chairman, Hans Holger Gliewe. History In 2020, in response to the ongoing and increasing focus on sustainability in the beauty and fragrance sectors, IFRA, in association with the International Organization of the Flavor Industry (IOFI), launched the "IFRA-IOFI Sustainability Charter." Objectives and roles IFRA i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamaldehyde
Cinnamaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula(C9H8O) C6H5CH=CHCHO. Occurring naturally as predominantly the ''trans'' (''E'') isomer, it gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. It is a phenylpropanoid that is naturally synthesized by the shikimate pathway. This pale yellow, viscous liquid occurs in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus ''Cinnamomum''. The essential oil of cinnamon bark is about 90% cinnamaldehyde. Cinnamaldehyde decomposes to styrene because of oxidation as a result of bad storage or transport conditions. Styrene especially forms in high humidity and high temperatures. This is the reason why cinnamon contains small amounts of styrene. Structure and synthesis Cinnamaldehyde was isolated from cinnamon essential oil in 1834 by Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugène-Melchior Péligot and synthesized in the laboratory by the Italian chemist Luigi Chiozza in 1854. The natural product is ''trans''-cinnamaldehyde. The molecule consists of a benzene rin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |