|
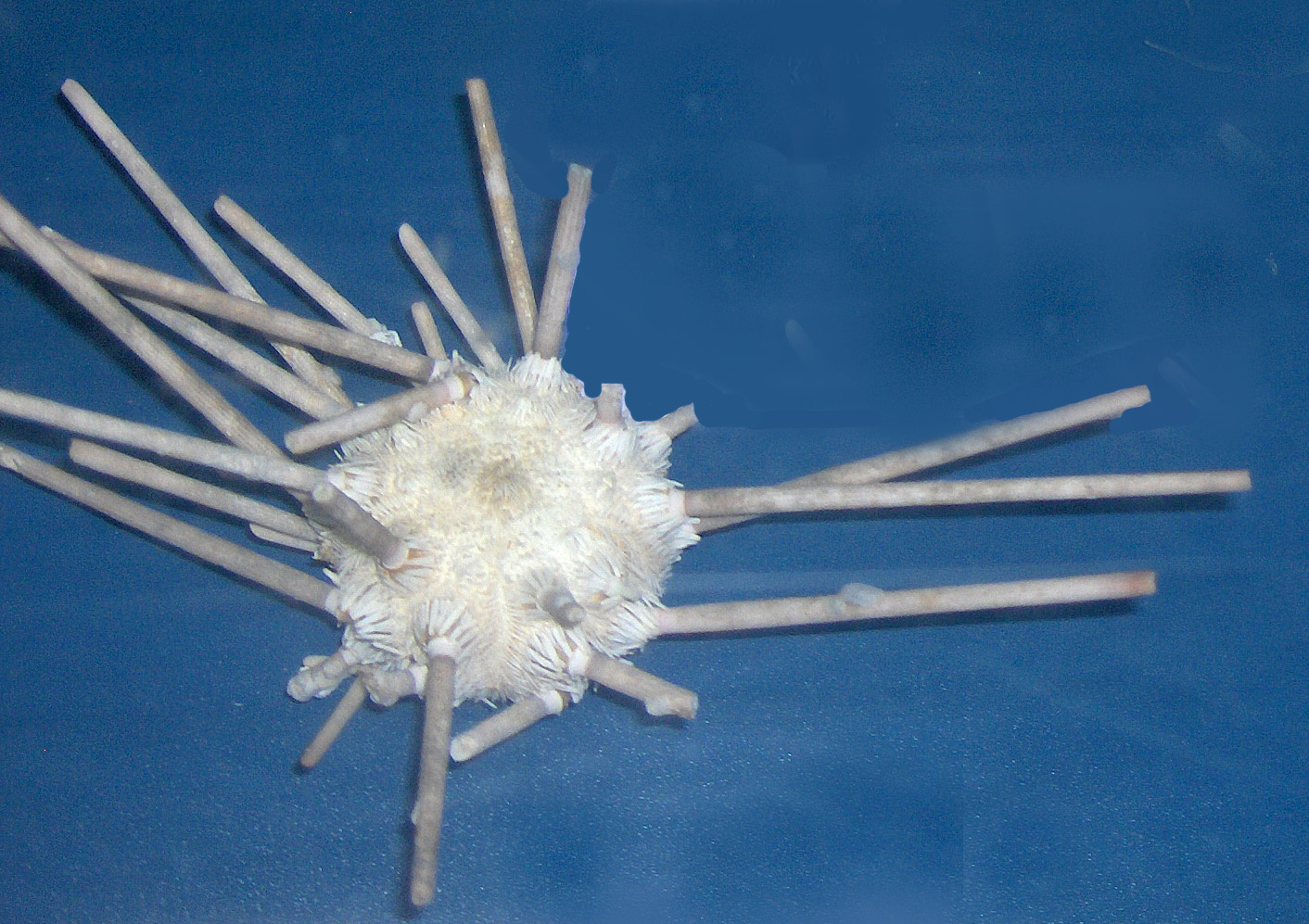
Cidaris Abyssicola
''Cidaris abyssicola'' is a species of sea urchin in the Family Cidaridae. ''Cidaris abyssicola'' was first scientifically described in 1869 by Alexander Emanuel Agassiz.Kroh, A. (2010). ''Cidaris abyssicola'' (Alexander Agassiz, 1869). In: Kroh, A. & Mooi, R. (2010World Echinoidea Database at the World Register of Marine Species. See also * '' Chorocidaris micca'' * ''Cidaris'' * ''Cidaris blakei ''Cidaris blakei'' is a species of sea urchins of the family Cidaridae. Its armour is covered with spines of three types, one unique type being extended and fan-like, making it easily recognized. Alexander Agassiz first described it scientificall ...'' References Animals described in 1869 Cidaridae Taxa named by Alexander Agassiz {{echinoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Agassiz
Alexander Emmanuel Rodolphe Agassiz (December 17, 1835March 27, 1910), son of Louis Agassiz and stepson of Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz, was an American scientist and engineer. Biography Agassiz was born in Neuchâtel, Switzerland and immigrated to the United States with his parents, Louis and Cecile (Braun) Agassiz, in 1846. He graduated from Harvard University in 1855, subsequently studying engineering and chemistry, and taking the degree of Bachelor of Science at the Lawrence Scientific School of the same institution in 1857; in 1859 became an assistant in the United States Coast Survey. Thenceforward he became a specialist in marine ichthyology. Agassiz was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1862. Up until the summer of 1866, Agassiz worked as assistant curator in the museum of natural history that his father founded at Harvard. E. J. Hulbert, a friend of Agassiz's brother-in-law, Quincy Adams Shaw, had discovered a rich copper lode known as the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of sea urchins are round and spiny, ranging in diameter from . Sea urchins move slowly, crawling with tube feet, and also propel themselves with their spines. Although algae are the primary diet, sea urchins also eat slow-moving (sessile) animals. Predators that eat sea urchins include a wide variety of fish, starfish, crabs, marine mammals. Sea urchins are also used as food especially in Japan. Adult sea urchins have fivefold symmetry, but their pluteus larvae feature bilateral (mirror) symmetry, indicating that the sea urchin belongs to the Bilateria group of animal phyla, which also comprises the chordates and the arthropods, the annelids and the molluscs, and are found in every ocean and in every climate, from the tropics to the pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cidaridae
Cidaridae is a family of sea urchins in the order Cidaroida. Description and characteristics Cidarid sea urchins are characterized by their stout skeleton : the test is thick and hard, with massive perforated tubercles (never crenulated) surrounded by a crown of secondary tubercles, but no primary tubercles in the interambulacra regions. These tubercles hold massive spines, thick, strong and often very long, and showing sometimes odd shapes (thorny spines, fans, clubs, Christmas trees...). The order Cidaroida is the basalmost of current sea urchins, and most of the species included in this family are abyssal, even if a handful of species remain quite common in tropical shallow waters, like ''Eucidaris'' or ''Phyllacanthus''. Genera According to the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS), the following genera are included in this family * Subfamily '' Cidarinae'' (Mortensen, 1928a) ** Genus ''Calocidaris'' (H.L. Clark, 1907) ** Genus '' Centrocidaris'' (A. Agassiz, 1904) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Emanuel Agassiz
Alexander Emmanuel Rodolphe Agassiz (December 17, 1835March 27, 1910), son of Louis Agassiz and stepson of Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz, was an American scientist and engineer. Biography Agassiz was born in Neuchâtel, Switzerland and immigrated to the United States with his parents, Louis and Cecile (Braun) Agassiz, in 1846. He graduated from Harvard University in 1855, subsequently studying engineering and chemistry, and taking the degree of Bachelor of Science at the Lawrence Scientific School of the same institution in 1857; in 1859 became an assistant in the United States Coast Survey. Thenceforward he became a specialist in marine ichthyology. Agassiz was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1862. Up until the summer of 1866, Agassiz worked as assistant curator in the museum of natural history that his father founded at Harvard. E. J. Hulbert, a friend of Agassiz's brother-in-law, Quincy Adams Shaw, had discovered a rich copper lode known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Register Of Marine Species
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms. Content The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scientific specialists on each group of organism. These taxonomists control the quality of the information, which is gathered from the primary scientific literature as well as from some external regional and taxon-specific databases. WoRMS maintains valid names of all marine organisms, but also provides information on synonyms and invalid names. It is an ongoing task to maintain the registry, since new species are constantly being discovered and described by scientists; in addition, the nomenclature and taxonomy of existing species is often corrected or changed as new research is constantly being published. Subsets of WoRMS content are made available, and can have separate badging and their own home/launch pages, as "subregisters", such as the ''World List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorocidaris Micca
''Chorocidaris micca'' is a species of sea urchins of the Family Cidaridae. Their armour is covered with spines. Chorocidaris micca was first scientifically described in 1941 by Ikeda.Kroh, A. (2010). ''Chorocidaris micca'' (Ikeda, 1941). In: Kroh, A. & Mooi, R. (2010World Echinoidea Database at the World Register of Marine Species. See also * ''Chondrocidaris brevispina'' * ''Chondrocidaris gigantea'' * ''Cidaris ''Cidaris'' is a genus of pencil sea urchins. Species According to the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS), the genus Cidaris contains the following extant species *'' Cidaris abyssicola'' ( Agassiz, 1869) *'' Cidaris annulata'' (Gray, ...'' References Animals described in 1941 Cidaridae {{echinoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cidaris
''Cidaris'' is a genus of pencil sea urchins. Species According to the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS), the genus Cidaris contains the following extant species *'' Cidaris abyssicola'' ( Agassiz, 1869) *'' Cidaris annulata'' (Gray, 1855) *'' Cidaris baculosa'' (Lamarck, 1816) *'' Cidaris blakei'' ( Agassiz 1878) *''Cidaris cidaris'' (Linnaeus, 1758) *'' Cidaris mabahissae'' ( Mortensen, 1939) *'' Cidaris nuda'' ( Mortensen, 1903) *'' Cidaris rugosa'' (Clark, 1907) *'' Cidaris thouarsii'' ( Agassiz & Desor, 1846) Extinct species or names brought to synonymy * †''Cidaris aculeata'' * †''Cidaris aialensis'' * †''Cidaris alpina'' * †''Cidaris alternata'' * †''Cidaris austriaca'' * †''Cidaris avena'' * †''Cidaris biconica'' * †''Cidaris biformis'' * †''Cidaris braunii'' * †''Cidaris buchii'' * †''Cidaris caudex'' * †''Cidaris cingulata'' * †''Cidaris coralliophila'' * †''Cidaris costalarensis'' * †''Cidaris costata'' * †''Cidaris costean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cidaris Blakei
''Cidaris blakei'' is a species of sea urchins of the family Cidaridae. Its armour is covered with spines of three types, one unique type being extended and fan-like, making it easily recognized. Alexander Agassiz first described it scientifically in 1878. It is present on the seabed in deep waters in the Gulf of Mexico and the Bahamas. Taxonomy ''Cidaris blakei'' was first described by the American zoologist Alexander Agassiz in 1878. It was among many deep sea animals dredged up from abyssal depths in the Gulf of Mexico during the explorations of the '' USC&GS George S. Blake'', one of the first United States oceanographic research vessels, and from which it derives its specific name. The genus name is Latin for a headdress or tiara worn by ancient Persian kings. Description Although their appearance is quite variable, other members of the genus ''Cidaris'' have long cylindrical blunt or pointed spines that are not covered with skin as are most sea urchin spines. As a result, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animals Described In 1869
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |