|
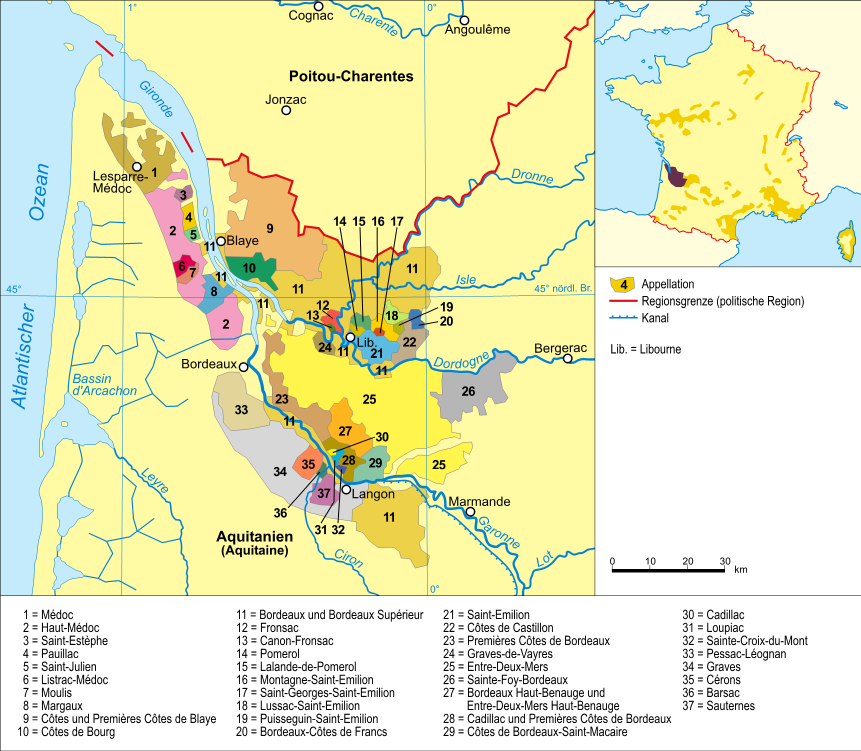
Château Pavie-Macquin
Château Pavie-Macquin is a Bordeaux wine from the appellation Saint-Émilion, ranked ''Premier grand cru classé B'' in the Classification of Saint-Émilion wine. The winery is one of three Pavie estates, along with Château Pavie and Château Pavie-Decesse, located in the Right Bank of France’s Bordeaux wine region in the commune of Saint-Émilion in the department Gironde. Having risen in esteem in the 1990s, it was promoted to Premier Grand Cru Classé in 2006. The château also produces a second wine named Les Chênes de Macquin (''The Oaks of Macquin''). History Once a part of the large estate of Ferdinand Bouffard, a 19th-century Bordeaux négociant, it was acquired by Albert Macquin, also the owner of the neighbouring Château La Serre, who would become known as a pioneer in the battle against phylloxera, and whose vines at Pavie-Macquin were among the first to be grafted onto American rootstocks. After studying viticulture at the ''Ecole d'Agriculture'' in Montpellier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux Wine
Bordeaux wine ( oc, vin de Bordèu, french: vin de Bordeaux) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the broad estuary called the Gironde; the Gironde department, with a total vineyard area of over 120,000 hectares, is the largest wine growing area in France. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of wine, ranging from large quantities of everyday table wine, to some of the most expensive and prestigious wines in the world. The vast majority of wine produced in Bordeaux is red (sometimes called "claret" in Britain), with sweet white wines (most notably Sauternes), dry whites, and (in much smaller quantities) rosé and sparkling wines ( Crémant de Bordeaux) collectively making up the remainder. Bordeaux wine is made by more than 8,500 producers or ''châteaux''. There are 54 appellations of Bordeaux wine. History Viticultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rootstock
A rootstock is part of a plant, often an underground part, from which new above-ground growth can be produced. It could also be described as a stem with a well developed root system, to which a bud from another plant is grafted. It can refer to a rhizome or underground stem. In grafting, it refers to a plant, sometimes just a stump, which already has an established, healthy root system, onto which a cutting or a bud from another plant is grafted. In some cases, such as vines of grapes and other berries, cuttings may be used for rootstocks, the roots being established in nursery conditions before planting them out. The plant part grafted onto the rootstock is usually called the scion. The scion is the plant that has the properties that propagator desires above ground, including the photosynthetic activity and the fruit or decorative properties. The rootstock is selected for its interaction with the soil, providing the roots and the stem to support the new plant, obtaining the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabernet Franc
Cabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone, as in the Loire's Chinon. In addition to being used in blends and produced as a varietal in Canada and the United States, it is sometimes made into ice wine in those regions. Cabernet Franc is lighter than Cabernet Sauvignon, making a bright pale red wine that contributes finesse and lends a peppery perfume to blends with more robust grapes. Depending on the growing region and style of wine, additional aromas can include tobacco, raspberry, bell pepper, cassis, and violets. Records of Cabernet Franc in Bordeaux go back to the end of the 18th century, although it was planted in Loire long before that time. DNA analysis indicates that Cabernet Franc is one of two parents of Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Carménère. History Cabernet Franc is believed to have been established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merlot
Merlot is a dark blue–colored wine grape variety, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name ''Merlot'' is thought to be a diminutive of ''merle'', the French name for the blackbird, probably a reference to the color of the grape. Its softness and "fleshiness," combined with its earlier ripening, make Merlot a popular grape for blending with the sterner, later-ripening Cabernet Sauvignon, which tends to be higher in tannin. Along with Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, Malbec and Petit Verdot, Merlot is one of the primary grapes used in Bordeaux wine, and it is the most widely planted grape in the Bordeaux wine regions. Merlot is also one of the most popular red wine varietals in many markets. This flexibility has helped to make it one of the world's most planted grape varieties. As of 2004, Merlot was estimated to be the third most grown variety at globally.J. Robinson (ed) ''The Oxford Companion to Wine'' Third Edition, Oxford Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and winemaking is known as oenology. A winemaker may also be called a vintner. The growing of grapes is viticulture and there are many varieties of grapes. Winemaking can be divided into two general categories: still wine production (without carbonation) and sparkling wine production (with carbonation – natural or injected). Red wine, white wine, and rosé are the other main categories. Although most wine is made from grapes, it may also be made from other plants. (See fruit wine.) Other similar light alcoholic drinks (as opposed to beer or spirits) include mead, made by fermenting honey and water, cider ("apple cider"), made by fermenting the juice of apples, and perry ("pear cider"), made by fermenting the juice of pears, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodynamic Wine
Biodynamic wines are wines made employing the biodynamic methods both to grow the fruit and during the post-harvest processing. Biodynamic wine production uses organic farming methods (''e.g.,'' employing compost as fertilizer and avoiding most pesticides) while also employing soil supplements prepared according to Rudolf Steiner's formulas, following a planting calendar that depends upon astrological configurations, and treating the earth as "a ''living and receptive'' organism." Biodynamic viticulture Biodynamic methods are used in viticulture (grape growing) in a variety of countries, including France, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Austria, Germany, Australia, Argentina, Chile, Peru, South Africa, Canada, and the United States. In 2013, over 700 vineyards worldwide comprising more than 10,000 ha/24,710 acres were certified biodynamic. A number of very high-end, high-profile commercial growers have converted recently to biodynamic practices. According to an article in '' Fortune'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stéphane Derenoncourt
Stéphane Derenoncourt is a French ''vigneron'' working as a consultant for numerous estates in Bordeaux and other wine producers worldwide. With his wife, Christine Derenoncourt, he runs Vignerons Consultants and owns Domaine de l'A in the Côtes de Castillon and Derenoncourt California in Napa Valley. He is entirely self-taught. Biography Derenoncourt was born in Dunkirk in 1963. The start of his career in viticulture began when he arrived as a hitch-hiker in Fronsac in 1982, and worked several harvests before he found employment at Château Fronsac in 1985. After two years working at various vineyards, he began working in the cellar at Château La Fleur Cailleau. In 1990, Derenoncourt was offered a position at the Corre-Macquin family’s cellar at the Château Pavie-Macquin vineyard, and in 1996 was hired as a winemaker by Stephan von Neipperg to his estates, including Château Canon-la-Gaffelière and the '' "super cuvée"'' La Mondotte. Consultant work Derenoncourt began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oenologist
Oenology (also enology; ) is the science and study of wine and winemaking. Oenology is distinct from viticulture, which is the science of the growing, cultivation, and harvesting of grapes. The English word oenology derives from the Greek word ''oinos'' ( οἶνος) "wine" and the suffix ''–logia'' ( -λογία) the "study of". An oenologist is an expert in the science of wine and of the arts and techniques for making wine. Education and training University programs in oenology and viticulture usually feature a concentration in science for the degree of Bachelor of Science (B.S, B.Sc., Sc.B), and as a terminal master's degree — either in a scientific or in a research program for the degree of Master of Science (M.S., Sc.M.), e.g. the master of professional studies degree. Oenologists and viticulturalists with doctorates often have a background in horticulture, plant physiology, and microbiology. Related to oenology are the professional titles of ''sommelier'' and master o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Enjalbert
Henri Enjalbert (1910 – June 19, 1983) was a French professor of geography at the University of Bordeaux. He was considered an eminent specialist in wine geology, whose expert opinion frequently overlapped into the fields of oenology, and wine and ''terroir'' history, within the Bordeaux region and beyond. Among other credits, he has been called "Bordeaux's most diligent geologist" and "the discoverer of Mas de Daumas Gassac. Among his contentions are that Albania, the Ionian Islands of Greece, and southern Dalmatia in present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina may have been the last European refuge of the grape vine after the Ice Age. Publications Enjalbert's publications range from studies on Château Latour, Château Haut-Brion and Saint-Émilion, to book titles such as ''Les Grands Vins de St-Emilion, Pomerol et Fronsac'' (English translation: ''Great Bordeaux Wines''), ''L'Origine de la Qualité'' and ''L'histoire de la vigne & du vin'' ( en, The History of Wine and the Vine) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitis Vinifera
''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between List of grape varieties, 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of ''Vitis vinifera'' grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production. The wild grape is often classified as ''Vitis vinifera'' ''sylvestris'' (in some classifications considered ''Vitis sylvestris''), with ''Vitis vinifera'' ''vinifera'' restricted to cultivated forms. Domesticated vines have hermaphrodite#Botany, hermaphrodite flowers, but ''sylvestris'' is plant sexuality, dioecious (male and female flowers on separate plants) and pollination is required for fruit to develop. Grapes can be eaten fresh or dried to produce raisins, Sultana (grape)#Raisins, sultanas, and Zante currant, currants. Grape leaves ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitis Labrusca
''Vitis labrusca'', the fox grape, is a species of grapevines belonging to the '' Vitis'' genus in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The vines are native to eastern North America and are the source of many grape cultivars, including Catawba, Concord, Delaware, Isabella, Niagara, and many hybrid grape varieties such as Agawam, Alexander and Onaka. Among the characteristics of this vine species in contrast to the European wine grape ''Vitis vinifera'' are its "slip-skin" that allows the skin of the grape berries to easily slip off when squeezed, instead of crushing the pulp, and the presence of tendrils on every node of the cane. Another contrast with European ''vinifera'' is the characteristic "foxy" musk of ''V. labrusca'', best known to most people through the Concord grape. Jancis Robinson (ed.) ''The Oxford Companion to Wine'' (Oxford University Press, third edition 2006, ), pp 19-20 This musk is not related to the mammalian fox, but rather to the strong, earthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people lived in the city, while its Functional area (France), metropolitan area had a population of 787,705.Comparateur de territoire INSEE, retrieved 20 June 2022. The inhabitants are called Montpelliérains. In the Middle Ages, Montpellier was an important city of the Crown of Aragon (and was the birthplace of James I of Aragon, James I), and then of Kingdom of Majorca, Majorca, before its sale to France in 1349. Established in 1220, the University of Montpellier is one of the List of oldest univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


