|
Château Bouscaut
Château Bouscaut is a Bordeaux wine from the Pessac-Léognan appellation, ranked among the ''Crus Classés'' for red and dry white wine in the Classification of Graves wine of 1953 and 1959. The winery and vineyards are located south of the city of Bordeaux, in the commune of Cadaujac. In addition to red and dry white ''Grand vin'' the estate also produces the second wine Les Chênes de Bouscaut. History Viticulture began at the estate during the 18th century, though its reputation became established just before and after World War I. Under the ownership of Victor Place the 18th-century chateau suffered a serious fire in 1962, and was rebuilt, before the estate was sold to an American syndicate in 1968, with Wohlstetter-Sloan installed as new owners. In 1980 Bouscaut was acquired by Lucien Lurton, the owner of Château Brane-Cantenac. The current owners of Château Bouscaut are Sophie Cogombles-Lurton Laurent Cogombles. Production The vineyard area consists of 47 hectares, 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux Wine
Bordeaux wine ( oc, vin de Bordèu, french: vin de Bordeaux) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the broad estuary called the Gironde; the Gironde department, with a total vineyard area of over 120,000 hectares, is the largest wine growing area in France. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of wine, ranging from large quantities of everyday table wine, to some of the most expensive and prestigious wines in the world. The vast majority of wine produced in Bordeaux is red (sometimes called "claret" in Britain), with sweet white wines (most notably Sauternes), dry whites, and (in much smaller quantities) rosé and sparkling wines ( Crémant de Bordeaux) collectively making up the remainder. Bordeaux wine is made by more than 8,500 producers or ''châteaux''. There are 54 appellations of Bordeaux wine. History Viticultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
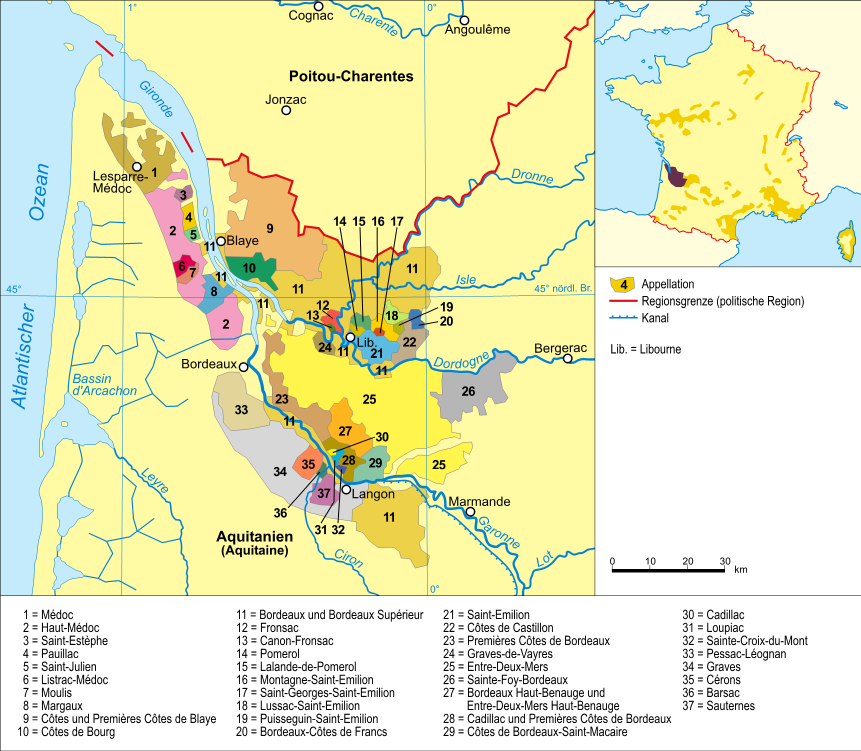
Pessac-Léognan
Pessac-Léognan () is a wine growing area and Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée, in the northern part of the Graves region of Bordeaux. Unlike most Bordeaux appellations, Pessac-Léognan is equally famous for both red and (dry) white wines, although red wine is still predominant. It includes the only red-wine producer outside the Haut-Médoc classified in the Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855, the ''premier cru'' Château Haut-Brion, and also includes all of the châteaux listed in the 1953/59 classification of Graves. These classed growths account for a third of the wine produced in Pessac-Léognan. Geography Pessac-Léognan, France lies on the left bank of the Garonne. It is immediately south of the city of Bordeaux (with a small portion to the west): indeed some of the northern vineyards of Pessac-Léognan are completely surrounded by the housing estates of Bordeaux, as a result of the city's southward expansion. It consists of 8 communes: (from north to south) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appellation D'origine Contrôlée
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical boundaries, such as what grapes may be grown, maximum grape yields, alcohol level, and other quality factors may also apply before an appellation name may legally appear on a wine bottle label. The rules that govern appellations are dependent on the country in which the wine was produced. History The tradition of wine appellation is very old. The oldest references are to be found in the Bible, where ''wine of Samaria'', ''wine of Carmel'', ''wine of Jezreel'', or ''wine of Helbon'' are mentioned. This tradition of appellation continued throughout the Antiquity and the Middle Ages, though without any officially sanctioned rules. Historically, the world's first exclusive (protected) vineyard zone was introduced in Chianti, Italy in 1716 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Graves Wine
The wines of Graves in the wine-growing region of Bordeaux were classified in 1953 by a jury appointed by Institute National des Appellations d'Origine, and approved by the Minister of Agriculture in August of that year. The selection was revised with a few additions in February 1959. The classification concerns both red and white wines, and all chateaux belong to the appellation Pessac-Léognan, which eventually came into effect on September 9, 1987. The 1959 classification See also * Regional wine classification * Bordeaux wine regions *History of Bordeaux wine Notes and references a. Also rated as a ''Premier Cru'' in the Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855. b. Château La Tour Haut-Brion was discontinued after the 2005 vintage. ;General * ;Footnotes {{Reflist External links Union of Classed Growths of Graves official site Appellations French wine Bordeaux Graves wine Graves (, ''gravelly land'') is an important Bordeaux wine regions, subre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winery
A winery is a building or property that produces wine, or a business involved in the production of wine, such as a wine company. Some wine companies own many wineries. Besides wine making equipment, larger wineries may also feature warehouses, bottling lines, laboratories, and large expanses of tanks known as tank farms. Wineries may have existed as long as 8,000 years ago. Ancient history The earliest known evidence of winemaking at a relatively large scale, if not evidence of actual wineries, has been found in the Middle East. In 2011 a team of archaeologists discovered a 6000 year old wine press in a cave in the Areni region of Armenia, and identified the site as a small winery. Previously, in the northern Zagros Mountains in Iran, jars over 7000 years old were discovered to contain tartaric acid crystals (a chemical marker of wine), providing evidence of winemaking in that region. Archaeological excavations in the southern Georgian region of Kvemo Kartli uncovered eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vineyards
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards are often characterised by their '' terroir'', a French term loosely translating as "a sense of place" that refers to the specific geographical and geological characteristics of grapevine plantations, which may be imparted to the wine itself. History The earliest evidence of wine production dates from between 6000 and 5000 BC. Wine making technology improved considerably with the ancient Greeks but it wasn't until the end of the Roman Empire that cultivation techniques as we know them were common throughout Europe. In medieval Europe the Church was a staunch supporter of wine, which was necessary for the celebration of the Mass. During the lengthy instability of the Middle Ages, the monasteries maintained and developed viticultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture of the Gironde department. Its inhabitants are called ''"Bordelais"'' (masculine) or ''"Bordelaises"'' (feminine). The term "Bordelais" may also refer to the city and its surrounding region. The city of Bordeaux proper had a population of 260,958 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , With its 27 suburban municipalities it forms the Bordeaux Metropolis, in charge of metropolitan issues. With a population of 814,049 at the Jan. 2019 census. it is the fifth most populated in France, after Paris, Lyon, Marseille and Lille and ahead of Toulouse. Together with its suburbs and exurbs, except satellite cities of Arcachon and Libourne, the Bordeaux metropolitan area had a population of 1,363,711 that same year (Jan. 2019 censu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadaujac
Cadaujac () is a commune in the Gironde department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France. Cadaujac station has rail connections to Langon and Bordeaux. Population International relations Twinned with Tramore, County Waterford, Ireland See also *Communes of the Gironde department The following is a list of the 535 communes of the Gironde department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Gironde {{Gironde-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Wine
Second wine or second label (French: ''Second vin'') is a term commonly associated with Bordeaux wine to refer to a second label wine made from '' cuvee'' not selected for use in the ''Grand vin'' or first label. In some cases a third wine or even fourth wine is also produced. Depending on the house winemaking style, individual plots of a vineyard may be selected, often those of the youngest vines, and fermented separately, with the best performing barrels being chosen for the house's top wine and the other barrels being bottled under a separate label and sold for a lower price than the ''Grand vin''. In less favorable vintages, an estate may choose to release only a second label wine rather than to release a smaller than normal quantity of its ''Grand vin'' or a wine that would not be consistent with past vintages under that name. The practice has its roots in the 18th century but became more commercially prominent in the 1980s when consumers discovered these wines as a more aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the Spanish flu, 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising French Third Republic, France, Russia, and British Empire, Britain) and the Triple A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château Brane-Cantenac
Château Brane-Cantenac is a winery in the Margaux appellation of the Bordeaux wine region of France. The wine produced here was classified as one of fifteen ''Deuxièmes Crus'' (Second Growths) in the original Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855. The estate also produces a second wine named Baron de Brane, a label named Château Notton, and a generic Margaux. History Previously a reputed estate named Château Gorce (sometimes recorded as Gorse), its wine was sold at high prices and was listed as a second growth in pre-1855 classifications such as ''Cocks & Féret''. It was acquired in 1833 by Baron Hector de Branne, termed the "Napoléon of the Vines", who named the estate after himself, a bold gesture for that period. Having once also owned the land that today is Château Mouton Rothschild, the sale of Château Brane-Mouton helped finance the purchase of this estate. With the Baron's total devotion to the vineyard, the wine was estimated to be the finest produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merlot
Merlot is a dark blue–colored wine grape variety, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name ''Merlot'' is thought to be a diminutive of ''merle'', the French name for the blackbird, probably a reference to the color of the grape. Its softness and "fleshiness," combined with its earlier ripening, make Merlot a popular grape for blending with the sterner, later-ripening Cabernet Sauvignon, which tends to be higher in tannin. Along with Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, Malbec and Petit Verdot, Merlot is one of the primary grapes used in Bordeaux wine, and it is the most widely planted grape in the Bordeaux wine regions. Merlot is also one of the most popular red wine varietals in many markets. This flexibility has helped to make it one of the world's most planted grape varieties. As of 2004, Merlot was estimated to be the third most grown variety at globally.J. Robinson (ed) ''The Oxford Companion to Wine'' Third Edition, Oxford Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |