|
Church Of The Annunciation, Marble Arch
The Church of the Annunciation, Marble Arch, is a Church of England parish church in the Marble Arch district of London, England. It is dedicated to the Annunciation to the Blessed Virgin Mary. It is a Gothic revival building designed by Sir Walter Tapper and built in 1912–1913. It is a Grade II* listed building. Worship at the Annunciation is Anglo-Catholic and is supported by a tradition of choral singing. The church is closely linked to a local primary school, Hampden Gurney School. History The Church is near Bryanston Square and Montagu Square in the neoclassical Portman Estate area of London, which was developed by Henry William Portman in the 18th century. A chapel of ease called the Quebec Chapel was founded on the present site in 1787 to commemorate the Battle of Quebec. It is thought that this chapel was built on the site of the riding school of the Portman Barracks. By the early 20th century the chapel had fallen into disrepair and it was demolished in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain by the 3rd century and to the 6th-century Gregorian mission to Kent led by Augustine of Canterbury. The English church renounced papal authority in 1534 when Henry VIII failed to secure a papal annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. The English Reformation accelerated under Edward VI's regents, before a brief restoration of papal authority under Queen Mary I and King Philip. The Act of Supremacy 1558 renewed the breach, and the Elizabethan Settlement charted a course enabling the English church to describe itself as both Reformed and Catholic. In the earlier phase of the English Reformation there were both Roman Catholic martyrs and radical Protestant martyrs. The later phases saw the Penal Laws punish Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodist Church Of Great Britain
The Methodist Church of Great Britain is a Protestantism, Protestant List of Christian denominations, Christian denomination in Britain, and the mother church to Methodism, Methodists worldwide. It participates in the World Methodist Council, and the World Council of Churches among other ecumenical associations. Methodism began primarily through the work of John Wesley (1703–1791), who led an evangelical Christian revival, revival in 18th-century Britain. An Anglican priest, Wesley adopted unconventional and controversial practices, such as open-air preaching, to reach factory labourers and newly urbanised masses uprooted from their traditional village culture at the start of the Industrial Revolution. His preaching centred upon the universality of God's Grace in Christianity, grace for all, the Sanctification, transforming effect of faith on character, and the possibility of Christian perfection, perfection in love during this life. He organised the new converts locally and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglican Ministry
The Anglican ministry is both the leadership and agency of Christian service in the Anglican Communion. "Ministry" commonly refers to the office of ordained clergy: the ''threefold order'' of bishops, priests and deacons. More accurately, Anglican ministry includes many laypeople who devote themselves to the ministry of the church, either individually or in lower/assisting offices such as lector, acolyte, sub-deacon, Eucharistic minister, cantor, musicians, parish secretary or assistant, warden, vestry member, etc. Ultimately, all baptized members of the church are considered to partake in the ministry of the Body of Christ. Each of the provinces (usually corresponding to individual world nations) of the Anglican Communion has a high degree of independence from the other provinces, and each of them have slightly different structures for ministry, mission and governance. However, personal leadership is always vested in a member of the clergy (a bishop at provincial and diocesan l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Ross Williamson
Hugh Ross Williamson (1901–1978) was a prolific British popular historian, and a dramatist. Starting from a career in the literary world, and having a Nonconformist background, he became an Anglican priest in 1943.Joseph Pearce, ''Literary Converts: Spiritual Inspiration in an Age of Unbelief''. Ignatius Press, 2006 , (pp.285, 359). In 1955 he became a convert to Roman Catholicism and wrote many historical works in a Catholic apologist tone. In 1956, he published his autobiography, ''The Walled Garden''. Ross Williamson was critical of the reforms introduced by the Second Vatican Council. Notes Works * ''The poetry of T. S. Eliot'' (1932) * ''John Hampden: a life'' (1933) * ''Rose and glove: a play'' (1934) * ''After the event: a play in one act'' (1935) * ''King James I'' (1935) * ''Gods and mortals in love'' (1936) * ''The seven deadly virtues; In a glass darkly; Various heavens: a play sequence.'' (1936) * ''Cinderella's grandchild: a play in one act'' (1936) * ''Mr G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festival Of Britain
The Festival of Britain was a national exhibition and fair that reached millions of visitors throughout the United Kingdom in the summer of 1951. Historian Kenneth O. Morgan says the Festival was a "triumphant success" during which people: Labour cabinet member Herbert Morrison was the prime mover; in 1947 he started with the original plan to celebrate the centennial of the Great Exhibition of 1851. However, it was not to be another World Fair, for international themes were absent, as was the British Commonwealth. Instead the 1951 festival focused entirely on Britain and its achievements; it was funded chiefly by the government, with a budget of £12 million. The Labour government was losing support and so the implicit goal of the festival was to give the people a feeling of successful recovery from the war's devastation, as well as promoting British science, technology, industrial design, architecture and the arts. The Festival's centrepiece was in London on the South Bank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
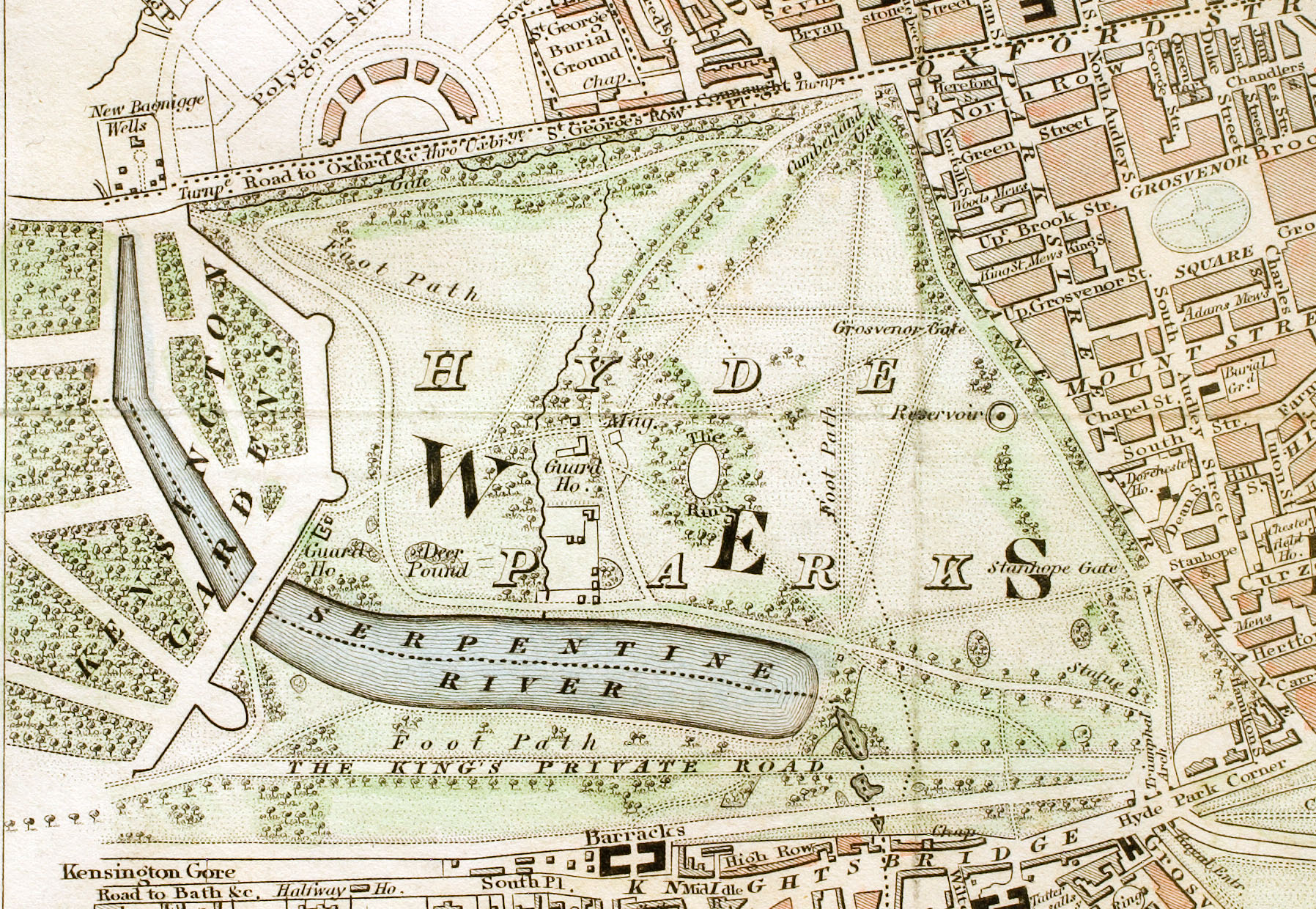
Hyde Park, London
Hyde Park is a Grade I-listed major park in Westminster, Greater London, the largest of the four Royal Parks that form a chain from the entrance to Kensington Palace through Kensington Gardens and Hyde Park, via Hyde Park Corner and Green Park past the main entrance to Buckingham Palace. The park is divided by the Serpentine and the Long Water lakes. The park was established by Henry VIII in 1536 when he took the land from Westminster Abbey and used it as a hunting ground. It opened to the public in 1637 and quickly became popular, particularly for May Day parades. Major improvements occurred in the early 18th century under the direction of Queen Caroline. Several duels took place in Hyde Park during this time, often involving members of the nobility. The Great Exhibition of 1851 was held in the park, for which The Crystal Palace, designed by Joseph Paxton, was erected. Free speech and demonstrations have been a key feature of Hyde Park since the 19th century. Speakers' Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdenominational
Interdenominationalism is an evangelical Protestant movement of cooperation among various Christian denominations. History The movement has its origins in the founding of the London Missionary Society, a missionary society, in 1795 by various evangelical denominations who had an interdenominational vision of the mission. It developed with the founding of the Evangelical Alliance in 1846 in London, England by 52 evangelical denominations. Various other evangelical organizations have also contributed to the interdenominational movement. In the Biblical studies, there was the International Fellowship of Evangelical Students in 1947. In the christian humanitarian aid, World Vision International in 1950. There is also had the emergence of various interdenominational Bible colleges. In 1951, the World Evangelical Alliance "(World Evangelical Fellowship)" was founded by evangelical leaders from 21 countries at the first general assembly in Woudschoten (Zeist) in Netherlands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecumenical Movement
Ecumenism (), also spelled oecumenism, is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjective ''ecumenical'' is thus applied to any initiative that encourages greater cooperation and union among Christian denominations and churches. The fact that all Christians belonging to mainstream Christian denominations profess faith in Jesus as Lord and Saviour over a believer's life, believe that the Bible is the infallible, inerrant and inspired word of God (John 1:1), and receive baptism according to the Trinitarian formula is seen as being a basis for ecumenism and its goal of Christian unity. Ecumenists cite John 17:20-23 as the biblical grounds of striving for church unity, in which Jesus prays that Christians "may all be one" in order "that the world may know" and believe the Gospel message. In 1920, the Ecumenical Patriarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Come, Ye Thankful People, Come
"Come, Ye Thankful People, Come" is an English Christian harvest festival hymn written in 1844 by Henry Alford. It is most often sung to the tune ''St. George's Windsor'' by George Job Elvey. History Alford wrote "Come, Ye Thankful People, Come" in 1844 while he was rector of Aston Sandford in Buckinghamshire, England. It was first published in ''Hymns and Psalms'' in 1844 with seven verses under the title "After Harvest". "Come, Ye Thankful People, Come" was set to George J. Elvey's hymn tune ''St. George's, Windsor'' in 1858. In 1865, Alford revised the hymn, and it was republished in his ''Poetical Works'' with only four verses. In 1861 there had been a number of unofficial revisions of the hymn, including one in ''Hymns Ancient and Modern'', which led to Alford publishing a footnote in ''Poetical Works'' stating his disapproval of these revisions that had been made without his agreement. Despite this, Alford revised the hymn again in 1867 in ''Year of Praise''. Alford was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Alford
Henry Alford (7 October 181012 January 1871) was an English churchman, theologian, textual critic, scholar, poet, hymnodist, and writer. Life Alford was born in London, of a Somerset family, which had given five consecutive generations of clergymen to the Anglican church. Alford's early years were passed with his widowed father, who was curate of Steeple Ashton in Wiltshire. He was a precocious boy, and before he was ten had written several Latin odes, a history of the Jews and a series of homiletic outlines. After a peripatetic school course he went up to Trinity College, Cambridge, in 1827 as a scholar. In 1832 he was 34th wrangler and 8th classic, and in 1834 was made fellow of Trinity. Service He had already taken orders, and in 1835 began his eighteen-year tenure of the vicarage of Wymeswold in Leicestershire, from which seclusion the twice-repeated offer of a colonial bishopric failed to draw him. He was Hulsean lecturer at Cambridge in 1841–1842, and steadily built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Quebec (1775)
The Battle of Quebec (french: Bataille de Québec) was fought on December 31, 1775, between American Continental Army forces and the British defenders of Quebec City early in the American Revolutionary War. The battle was the first major defeat of the war for the Americans, and it came with heavy losses. General Richard Montgomery was killed, Benedict Arnold was wounded, and Daniel Morgan and more than 400 men were taken prisoner. The city's garrison, a motley assortment of regular troops and militia led by Quebec's provincial governor, General Guy Carleton, suffered a small number of casualties. Montgomery's army had captured Montreal on November 13, and early in December they became one force that was led by Arnold, whose men had made an arduous trek through the wilderness of northern New England. Governor Carleton had escaped from Montreal to Quebec, the Americans' next objective, and last-minute reinforcements arrived to bolster the city's limited defenses before t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)