|
Chung Riwoche
Chung Riwoche () is a large stupa of unusual design established in 1386 in the traditional Tibetan province of Ü-Tsang. It was later re-established and built by Mahasiddha Thangtong Gyalpo in 1426. Chung Riwoche is the seat of the Chakzampa (Thangtong Gyalpo) sub-lineage of the Shangpa Kagyu, and is still an active Kumbum A Kumbum ( "one hundred thousand holy images") is a multi-storied aggregate of Buddhist chapels in Tibetan Buddhism. The most famous Kumbum forms part of Palcho Monastery. The first Kumbum was founded in the fire sheep year 1427 by a Gyantse p ... with 9 monks as of 2014. References {{Buddhist monasteries in Tibet Buddhist temples in Tibet Stupas in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui settlers. Since Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
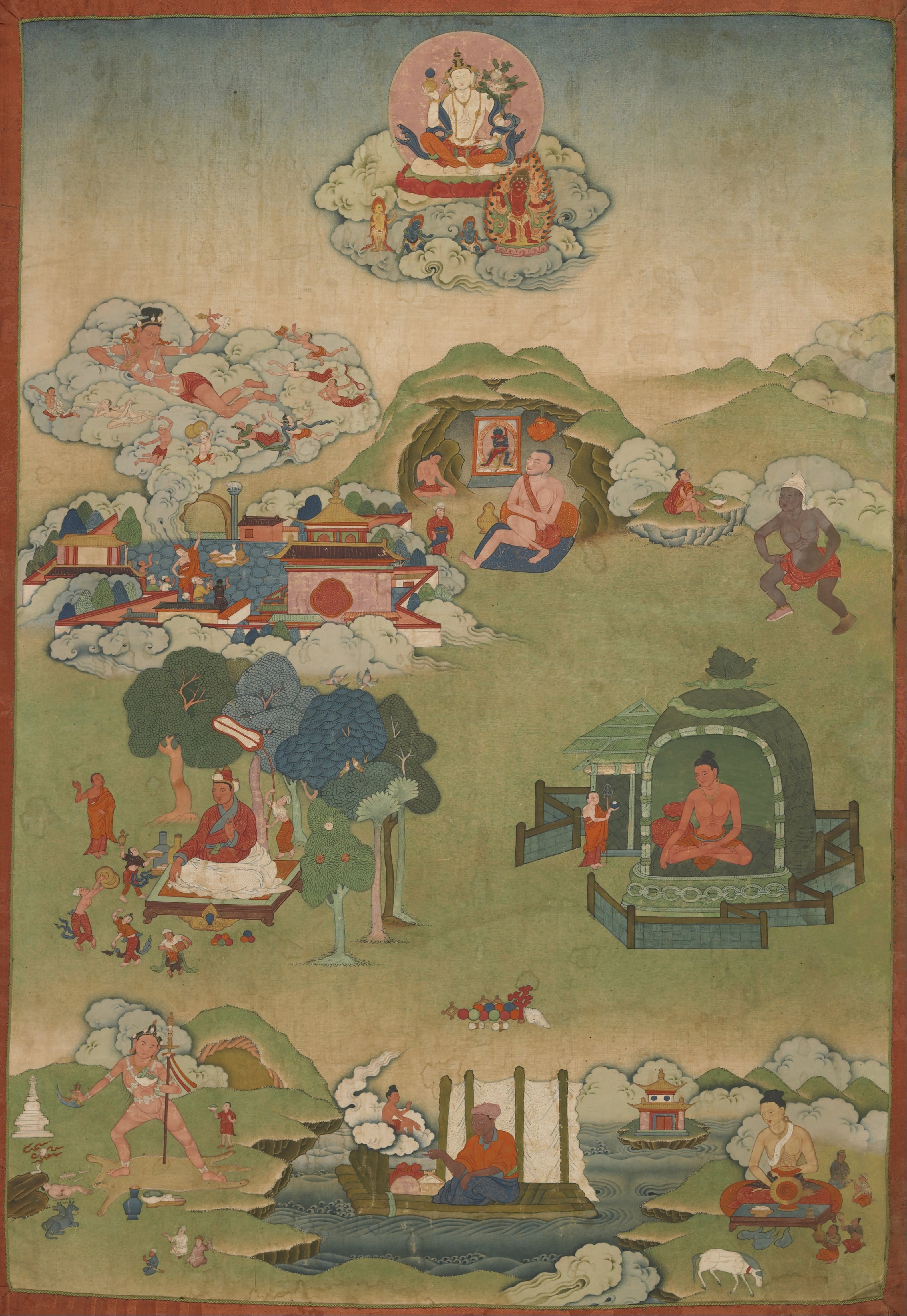
Thang Tong Gyalpo
Thangtong Gyalpo () (1385 CE–1464 CE or 1361 CE–1485 CE), also known as Chakzampa, the "Iron Bridge Maker" (), Tsöndrü Zangpo "Excellent Persistence" (), and the King of the Empty Plain.Sarah Harding. Niguma, Lady of Illusion. Snow Lion Publications. 2010. p. 265, n. 84 He was also known by a variation of this name, Madman of the Empty Valley. He was a great Buddhist adept, a Chöd master, yogi, physician, blacksmith, architect, and a pioneering civil engineer. He is considered a mind emanation of Padmasambhava and a reincarnation of Dolpopa Sherab Gyaltsen. He founded the Iron Chain lineage of the Shangpa Kagyu school of Tibetan Buddhism, and he recognized the first Samding Dorje Phagmo, Chökyi Drönma (1422–1455), the female incarnation lineage of Vajravārāhī. Thangtong Gyalpo is said to have built 58 iron chain suspension bridges around Tibet and Bhutan, several of which are still in use today. He also designed and built several large stupas of unusual design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shangpa Kagyu
The Shangpa Kagyu (, "Oral Tradition of the man from Shang") is known as the "secret lineage" of the Kagyu school of Vajrayana or Tibetan Buddhism and differs in origin from the better known Dagpo Kagyu schools. The Dagpo Kagyu are the lineage of Tilopa through his student Naropa, often traced through Naropa's famous student Marpa Lotsawa and thus called "Marpa Kagyu", while the Shangpa lineage descends from Tilopa's student Niguma, who was Naropa's sister, as well as from the teachings of Sukhasiddhi. Its founder was Khyungpo Naljor, the student of both women, whose monastery in the Shang Valley gave its name to the tradition. The principal Shangpa dharmapala is the six-armed Mahākāla. The Shangpa tradition was revitalized in the 20th century by the first Kalu Rinpoche, who had many students both in Tibet and in the West. Origins The Shangpa Kagyu lineage was founded by the eleventh-century Tibetan scholar Khyungpo Naljor. Seeking to increase his understanding of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or ''pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizontal discs spreadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
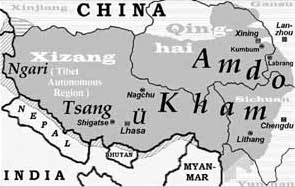
Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered the south-central of the Tibetan cultural area, including the Brahmaputra River watershed. The western districts surrounding and extending past Mount Kailash are included in Ngari, and much of the vast Changtang plateau to the north. The Himalayas defined Ü-Tsang's southern border. The present Tibet Autonomous Region corresponds approximately to what was ancient Ü-Tsang and western Kham. Ü-Tsang was formed by the merging of two earlier power centers: Ü () in central Tibet, controlled by the Gelug lineage of Tibetan Buddhism under the early Dalai Lamas, and Tsang () which extended from Gyantse to points west, controlled by the rival Sakya lineage. Military victories by the powerful Khoshut Mongol Güshi Khan that backed 5th Dalai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahasiddha
Mahasiddha (Sanskrit: ''mahāsiddha'' "great adept; ) is a term for someone who embodies and cultivates the " siddhi of perfection". A siddha is an individual who, through the practice of sādhanā, attains the realization of siddhis, psychic and spiritual abilities and powers. Mahasiddhas were practitioners of yoga and tantra, or ''tantrika''s. Their historical influence throughout the Indian subcontinent and the Himalayas was vast and they reached mythic proportions as codified in their songs of realization and hagiographies, or namtars, many of which have been preserved in the Tibetan Buddhist canon. The Mahasiddhas are the founders of Vajrayana traditions and lineages such as Dzogchen and Mahamudra. Robert Thurman explains the symbiotic relationship between Tantric Buddhist communities and the Buddhist universities such as Nalanda which flourished at the same time. Genealogy and historical dates The exact genealogy and historical dates of the Mahasiddhas are contentiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thangtong Gyalpo
Thangtong Gyalpo () (1385 CE–1464 CE or 1361 CE–1485 CE), also known as Chakzampa, the "Iron Bridge Maker" (), Tsöndrü Zangpo "Excellent Persistence" (), and the King of the Empty Plain.Sarah Harding. Niguma, Lady of Illusion. Snow Lion Publications. 2010. p. 265, n. 84 He was also known by a variation of this name, Madman of the Empty Valley. He was a great Buddhist adept, a Chöd master, yogi, physician, blacksmith, architect, and a pioneering civil engineer. He is considered a mind emanation of Padmasambhava and a reincarnation of Dolpopa Sherab Gyaltsen. He founded the Iron Chain lineage of the Shangpa Kagyu school of Tibetan Buddhism, and he recognized the first Samding Dorje Phagmo, Chökyi Drönma (1422–1455), the female incarnation lineage of Vajravārāhī. Thangtong Gyalpo is said to have built 58 iron chain suspension bridges around Tibet and Bhutan, several of which are still in use today. He also designed and built several large stupas of unusual design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumbum
A Kumbum ( "one hundred thousand holy images") is a multi-storied aggregate of Buddhist chapels in Tibetan Buddhism. The most famous Kumbum forms part of Palcho Monastery. The first Kumbum was founded in the fire sheep year 1427 by a Gyantse prince. It has nine ''lhakang''s or levels, is high surmounted by a golden dome, and contains 77 chapels which line its walls. Many of the statues were damaged during the Cultural Revolution but have since been replaced with clay images, though they lack the artistic merit of the originals. The 14th century murals showing Newar and Chinese influences, survived much better. The Kumbum or great ''gomang'' ("many-doored") stupa at Gyantse is a three-dimensional mandala meant to portray the Buddhist cosmos. The Kumbum, like other mandalas, which are portrayed by a circle within a square, enables the devotee to take part in the Buddhist perception of the universe and can depict one's potential as they move through it. Mandalas are meant to aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Tibet
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |