|
Chrysophyte
The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae or golden algae are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, ''Prymnesium parvum'', which causes fish kills. The Chrysophyceae should not be confused with the Chrysophyta, which is a more ambiguous taxon. Although "chrysophytes" is the anglicization of "Chrysophyta", it generally refers to the Chrysophyceae. Members Originally they were taken to include all such forms of the diatoms and multicellular brown algae, but since then they have been divided into several different groups (e.g., Haptophyceae, Synurophyceae) based on pigmentation and cell structure. Some heterotrophic flagellates as the bicosoecids and choanoflagellates were sometimes seen as related to golden algae too. They are now usually restricted to a core group of closely related forms, distinguished primarily by the structure of the flagella in motile cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
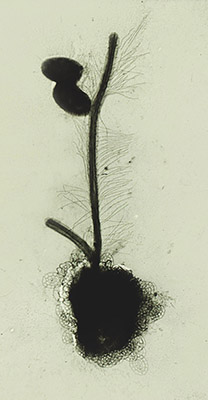
Synurid
The synurids (order Synurales) are a small group of heterokont algae, found mostly in freshwater environments, characterized by cells covered in silica scales. Characteristics They are covered in silicate scales and spines. In ''Synura'', these are formed on the surface of the chloroplasts, two of which are usually present, but sometimes only one divided into two lobes is seen. The cells have two heterokont flagella, inserted parallel to one another at the anterior, whose ultrastructure is a distinguishing characteristic of the group. Both asexual and isogamous sexual reproduction occur. Genera Two major genera are included here, divided into species mainly based on the structure of the scales. * ''Mallomonas'' species are free-living individual cells, usually 50-100 μm in length. They have ornate scales and generally long spines. * ''Synura'' species occur as spherical colonies, with the cells oriented so that the flagella point outwards, each usually around 30 μm in len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synurophyceae
The synurids (order Synurales) are a small group of heterokont algae, found mostly in freshwater environments, characterized by cells covered in silica scales. Characteristics They are covered in silicate scales and spines. In ''Synura'', these are formed on the surface of the chloroplasts, two of which are usually present, but sometimes only one divided into two lobes is seen. The cells have two heterokont flagella, inserted parallel to one another at the anterior, whose ultrastructure is a distinguishing characteristic of the group. Both asexual and isogamous sexual reproduction occur. Genera Two major genera are included here, divided into species mainly based on the structure of the scales. * ''Mallomonas'' species are free-living individual cells, usually 50-100 μm in length. They have ornate scales and generally long spines. * ''Synura'' species occur as spherical colonies, with the cells oriented so that the flagella point outwards, each usually around 30 μm in len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinobryon
''Dinobryon'' is a type of microscopic algae. It is one of the 22 genera in the family Dinobryaceae. ''Dinobryon'' are mixotrophs, capable of obtaining energy and carbon through photosynthesis and phagotrophy of bacteria. The genus comprises at least 37 described species. The best-known species are ''D. cylindricum'' and ''D. divergens'', which come to the attention of humans annually due to transient blooms in the photic zone of temperate lakes and ponds. Such blooms may produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that produce odors and affect water quality. ''Dinobryon'' can exist as free-living, solitary cells or in branching colonies. Ecology Though most commonly found in freshwater lakes and ponds, ''Dinobryon'' have also been documented flourishing in lotic and estuarine habitats. Large blooms of ''Dinobryon'' are documented most commonly in oligo- to meso- trophic temperate lakes and ponds, though they have also been observed in eutrophic waters. Such blooms regularly occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, the term "flagellate" is included in other terms (such as "dinoflagellate" and "choanoflagellata") which are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella often support hairs, called mastigonemes, or contain rods. Their ultrastructure plays an important role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscopic anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeboid
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic group whose members share common descent. Consequently, amoeboid organisms are no longer classified together in one group.Jan Pawlow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterokont
Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which are a primary component of plankton. Other notable members of the Stramenopiles include the (generally) parasitic oomycetes, including ''Phytophthora'', which caused the Great Famine of Ireland, and ''Pythium'', which causes seed rot and damping off. The name "heterokont" refers to the type of motile life cycle stage, in which the flagellated cells possess two differently arranged flagella (see zoospore). History In 1899, Alexander Luther created the term "Heterokontae" for some algae with unequal flagella, today called Xanthophyceae. Later, some authors (e.g., Copeland, 1956) included other groups in Heterokonta, expanding the name's sense. The term continues to be applied in different ways, leading to Heterokontophyta being applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stramenopiles
Stramenopile is a clade of organisms distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost (in which case relatedness to stramenopile ancestors is evident from other shared cytological features or from genetic similarity). Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, along with Alveolata and Rhizaria. Members of the clade are referred to as 'stramenopiles'. Stramenopiles are eukaryotes; since they are neither fungi, animals, nor plants, they are classified as protists. Most stramenopiles are single-celled, but some are multicellular algae including some brown algae. The group includes a variety of algal protists, heterotrophic flagellates, opalines and closely related proteromonad flagellates (all endobionts in other organisms); the actinophryid heliozoa, and oomycetes. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeothamniales
Phaeothamniales is an order of alga in the Ochrophyta The ochrophytes, subphylum Ochrophytina, is a group of mostly photosynthetic heterokonts. Their plastid is of red algal origin. The classification of the group is still being worked out. Originally, the ochrophytes were regarded as a phylum d .... References Ochrophyta Heterokont orders {{Heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |