|
Chronicon Terrae Prussiae
''Chronicon terræ Prussiæ'' (Latin for "The Chronicle of the Prussian Land") is a chronicle of the Teutonic Knights, by Peter of Dusburg, finished in 1326. The manuscript is the first major chronicle of the Teutonic Order in Prussia and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, completed some 100 years after the conquest of the crusaders into the Baltic region. It is a major source for information on the Order's battles with Old Prussians and Lithuanians. The chronicle is written in Latin and consists of four volumes. The first volume gives the background of the Order and its crusades in Outremer. The second volume narrates how the Order arrived to the Prussian land, while the third volume details wars with Old Prussians and other Baltic tribes. The fourth volume provides a historical context of other contemporary events in the world. The chronicle has an addendum of another 20 chapters dealing with events of 1326-1330, which may also have been written by Peter of Dusburg. The chronicle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, United Kingdom, Brazil, Russia, and Canada. Their native language is Lithuanian, one of only two surviving members of the Baltic language family along with Latvian. According to the census conducted in 2021, 84.6% of the population of Lithuania identified themselves as Lithuanians, 6.5% as Poles, 5.0% as Russians, 1.0% as Belarusians, and 1.1% as members of other ethnic groups. Most Lithuanians belong to the Catholic Church, while the Lietuvininkai who lived in the northern part of East Prussia prior to World War II, were mostly Lutherans. History The territory of the Balts, including modern Lithuania, was once inhabited by several Baltic tribal entities ( Aukštaitians, Sudovians, Old Lithuanians, Curonians, Semigallians, Selonians, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the German R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Chronicles
The Lithuanian Chronicles ( lt, Lietuvos metraščiai, also called Belarusian-Lithuanian Chronicles) are three redactions of chronicles compiled in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. All redactions were written in the Ruthenian language and served the needs of Lithuanian patriotism. The first edition, compiled in the 1420s, glorified Vytautas the Great and supported his side in power struggles. The second redaction, prepared in the first half of the 16th century, started the myth of Lithuanian Roman origin: it gave a fanciful genealogy of Palemon, a noble from the Roman Empire who founded the Grand Duchy. This noble origin of Lithuanians was important in cultural rivalry with the Kingdom of Poland. The third redaction, known as the Bychowiec Chronicle, elaborated even further on the legend, but also provided some useful information about the second half of the 15th century. The three redactions, the first known historical accounts produced within the Grand Duchy, gave rise to the historiog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century History Books
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 14th century was a century lasting from 1 January 1301 ( MCCCI), to 31 December 1400 ( MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of Charles IV, King of France led to a claim to the French throne by Edward III, King of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagiography
A hagiography (; ) is a biography of a saint or an ecclesiastical leader, as well as, by extension, an adulatory and idealized biography of a founder, saint, monk, nun or icon in any of the world's religions. Early Christian hagiographies might consist of a biography or ', a description of the saint's deeds or miracles (from Latin ''vita'', life, which begins the title of most medieval biographies), an account of the saint's martyrdom (called a ), or be a combination of these. Christian hagiographies focus on the lives, and notably the miracles, ascribed to men and women canonized by the Roman Catholic church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox churches, and the Church of the East. Other religious traditions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, Taoism, Islam, Sikhism and Jainism also create and maintain hagiographical texts (such as the Sikh Janamsakhis) concerning saints, gurus and other individuals believed to be imbued with sacred power. Hagiographic works, especi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malbork Castle
The Castle of the Teutonic Order in Malbork ( pl, Zamek w Malborku; german: Ordensburg Marienburg) is a 13th-century Teutonic castle and fortress located near the town of Malbork, Poland. It is the largest castle in the world measured by land area and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was originally constructed by the Teutonic Knights, a German Catholic religious order of crusaders, in a form of an Ordensburg fortress. The Order named it ''Marienburg'' in honour of Mary, mother of Jesus. In 1457, during the Thirteen Years’ War, it was sold by Bohemian mercenaries to King Casimir IV of Poland in lieu of indemnities and it then served as one of several Polish royal residences and the seat of Polish offices and institutions, interrupted by several years of Swedish occupation, fulfilling this function until the First Partition of Poland in 1772. From then on the castle was under German rule for over 170 years until 1945, albeit largely falling into disrepair as military techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Masters Of The Teutonic Knights
The Grand Master of the Teutonic Order (german: Hochmeister des Deutschen Ordens; la, Magister generalis Ordo Teutonicus) is the supreme head of the Teutonic Order. It is equivalent to the Grand master (order), grand master of other Military order (religious society), military orders and the superior general in non-military Religious order (Catholic), Roman Catholic religious orders. ''Hochmeister'', literally "high master", is only used in reference to the Teutonic Order, as ''Großmeister'' ("grand master") is used in German to refer to the leaders of other orders of knighthood. An early version of the full title in Latin was ''Magister Hospitalis Sanctae Mariae Alemanni, Alemannorum Hierosolymitani''. Since 1216, the full title ''Magister Hospitalis Domus Sanctae Mariae Teutons, Teutonicorum Hierosolymitani'' ("Master of the Hospital House of the Blessed Virgin Mary of the Germans of Jerusalem") was used. The offices of ''Hochmeister'' and ''Deutschmeister'' (''Magister Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Tribes
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. One of the features of Baltic languages is the number of conservative or archaic features retained. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians and Latvians (including Latgalians) — all Eastern Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the Western Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct. Etymology Medieval German chronicler Adam of Bremen in the latter part of the 11th century AD was the first writer to use the term "Baltic" in reference to the sea of that name.Bojtár page 9. Before him various ancient places names, such as Balcia, were used in reference to a supposed island in the Baltic Sea. Adam, a speaker of German, connected ''Balt-'' with ''belt'', a word with which he was familiar. In Germanic languages there was some form of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outremer
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political intrigue. The four states were the County of Edessa (10981150), the Principality of Antioch (10981287), the County of Tripoli (11021289), and the Kingdom of Jerusalem (10991291). The Kingdom of Jerusalem covered what is now Israel and Palestine, the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and adjacent areas. The other northern states covered what are now Syria, south-eastern Turkey, and Lebanon. The description "Crusader states" can be misleading, as from 1130 very few of the Frankish population were crusaders. The term Outremer, used by medieval and modern writers as a synonym, is derived from the French for ''overseas''. In 1098, the armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem passed through Syria. The crusader Baldwin of Boulogne replaced the Greek Orthodox ruler o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
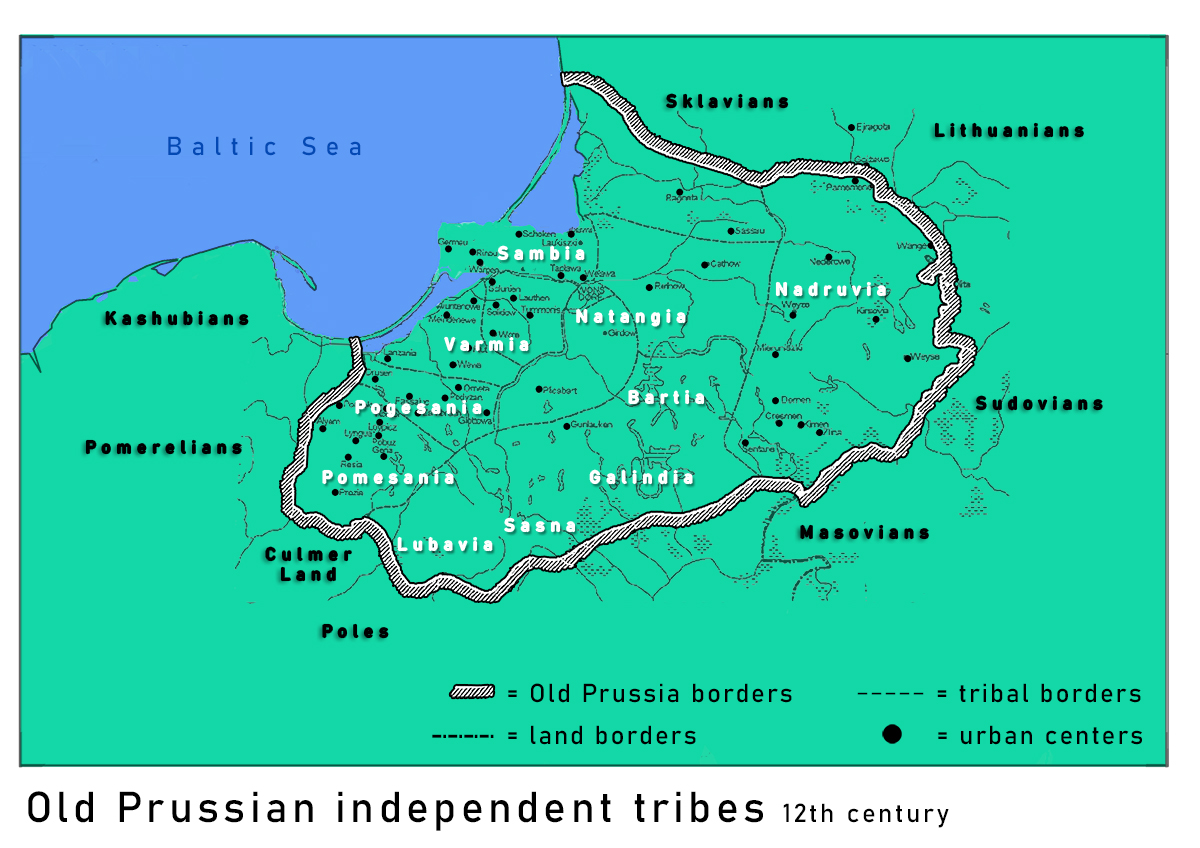
Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians (Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that inhabited the region of Prussia, at the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. The Old Prussians, who spoke an Indo-European language now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities, lent their name, despite very few commonalities, to the later, predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order. The remaining Old Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |