|
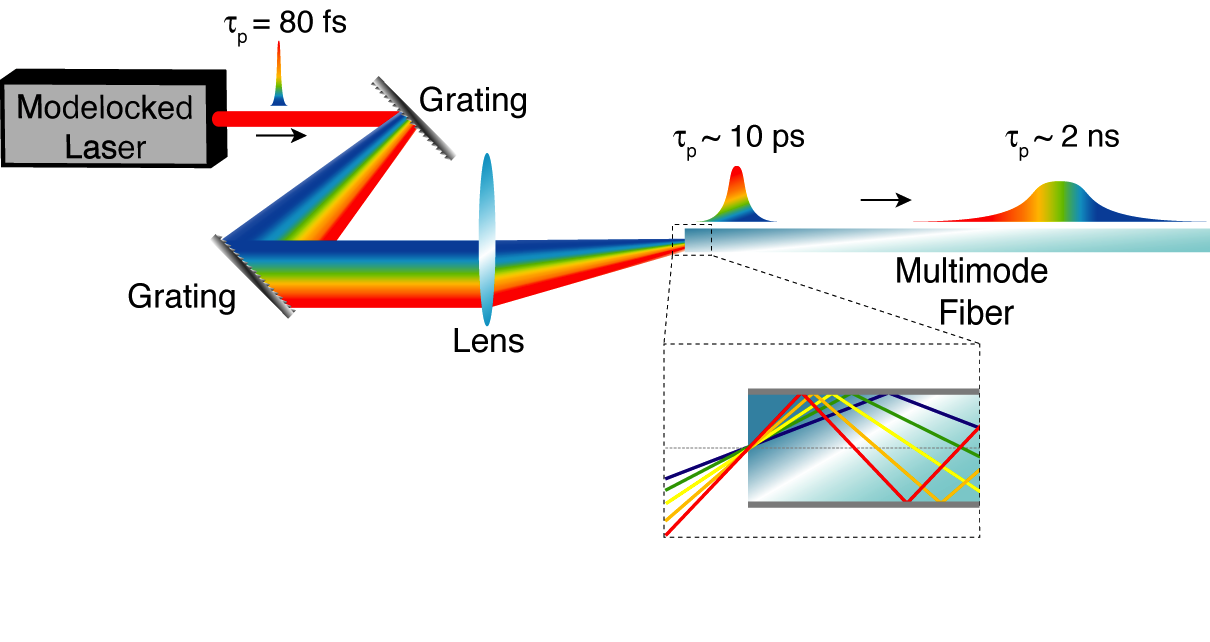
Chromo-modal Dispersion
Chromo-modal dispersion (CMD) results from exciting various modes of a multimode waveguide with unique spectral components of a broadband optical signal.E.D. Diebold et al., "Giant tunable optical dispersion using chromo-modal excitation of a multimode waveguide," Optics Express 19 (24) 2011. Modal dispersion during propagation in the waveguide then provides group velocity dispersion to the signal. The large modal dispersion inherent to multimode waveguides enables the dispersion per unit length of a chromo-modal dispersion device to be several orders of magnitude higher than that of diffraction grating or dispersion compensating fiber-based dispersive elements. Applications The ability to control chromatic dispersion is paramount in applications where the optical pulsewidth is critical, such as chirped pulse amplification and fiber-optic communications. Other devices Typically, devices used to generate large amounts (>100 ps/nm) of chromatic dispersion are based on diffrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMD Diagram
CMD may refer to: Entities * Cable Mágico Deportes, a Peruvian TV network * Center for Media and Democracy, advocacy organization in the US * Center for Molecular Design, Janssen Pharmaceutica * Coleg Meirion-Dwyfor, a college in Gwynedd, Wales * Creative Micro Designs, a defunct American computer peripheral company * CMD Technology, a defunct American computer storage controller company * Lakas–CMD, Lakas–Christian Muslim Democrats, a political party in the Philippines Medical * Congenital muscular dystrophy * Craniomandibular dysfunction * Custom-made device, a medical device designed and manufactured for the specific use of a particular patient. Technology * cmd.exe, command prompt on the OS/2 and Windows NT families of operating systems * CMD file (CP/M), the filename extension used by executable programs * Command key, usually abbreviated "cmd" * Concerted metalation deprotonation, a kind of chemical reaction Travel * Camden Road railway station, London, Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Common types of waveguides include acoustic waveguides which direct sound, optical waveguides which direct light, and radio-frequency waveguides which direct electromagnetic waves other than light like radio waves. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, waves would expand into three-dimensional space and their intensities would decrease according to the inverse square law. There are different types of waveguides for different types of waves. The original and most common meaning is a hollow conductive metal pipe used to carry high frequency radio waves, particularly microwaves. Dielectric waveguides are used at higher radio frequencies, and transparent dielectric waveguides and optical fibers serve as waveguides for light. In acoustics, air ducts and horns are used as waveguides for sound in musical instruments and loudspeakers, and specially-shaped metal rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modal Dispersion
Modal dispersion is a distortion mechanism occurring in multimode fibers and other waveguides, in which the signal is spread in time because the propagation velocity of the optical signal is not the same for all modes. Other names for this phenomenon include multimode distortion, multimode dispersion, modal distortion, intermodal distortion, intermodal dispersion, and intermodal delay distortion. In the ray optics analogy, modal dispersion in a step-index optical fiber may be compared to multipath propagation of a radio signal. Rays of light enter the fiber with different angles to the fiber axis, up to the fiber's acceptance angle. Rays that enter with a shallower angle travel by a more direct path, and arrive sooner than rays that enter at a steeper angle (which reflect many more times off the boundaries of the core as they travel the length of the fiber). The arrival of different components of the signal at different times distorts the shape. Modal dispersion limits th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Velocity Dispersion
In optics, group-velocity dispersion (GVD) is a characteristic of a dispersive medium, used most often to determine how the medium affects the duration of an optical pulse traveling through it. Formally, GVD is defined as the derivative of the inverse of group velocity of light in a material with respect to angular frequency, : \text(\omega_0) \equiv \frac \left( \frac \right)_, where \omega and \omega_0 are angular frequencies, and the group velocity v_g(\omega) is defined as v_g(\omega) \equiv \partial \omega / \partial k. The units of group-velocity dispersion are imesup>2/ istance often expressed in fs2/ mm. Equivalently, group-velocity dispersion can be defined in terms of the medium-dependent wave vector k(\omega) according to : \text(\omega_0) \equiv \left( \frac\right)_, or in terms of the refractive index n(\omega) according to : \text(\omega_0) \equiv \frac \left(\frac\right)_ + \frac\left( \frac\right)_. Applications Group-velocity dispersion is most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical grating with a periodic structure that diffraction, diffracts light, or another type of electromagnetic radiation, into several beams traveling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) Angle of incidence (optics), incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or periodic distance between adjacent diffracting elements (e.g., parallel slits for a transmission grating) on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersion (optics), dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high-precision motion control and wavefront measurement. For typical applications, a reflection (optics), reflective grati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Dispersion
Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency. Sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used to refer to optics specifically, as opposed to wave propagation in general. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium. Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the pulses of light in optical fiber. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refraction of different colors of light, as seen in the spectrum produced by a dispersive prism and in chromatic aberration of lenses. Design of compound achr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirped Pulse Amplification
Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level, with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally, then amplified, and then compressed again. The stretching and compression uses devices that ensure that the different color components of the pulse travel different distances. CPA for lasers was introduced by Donna Strickland and Gérard Mourou at the University of Rochester in the mid-1980s, work for which they received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2018. CPA is the technique used by most high-powered lasers in the world. Background Before the introduction of CPA in the mid-1980s, the peak power of laser pulses was limited because a laser pulse at intensities of gigawatts per square centimeter causes serious damage to the gain medium through nonlinear processes such as self-focusing. For example, some of the most powerful compressed CPA laser beams, even in an unfocused large aperture (afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber-optic Communications
Fiber-optic communication is a form of optical communication for transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. Fiber is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required. This type of communication can transmit voice, video, and telemetry through local area networks or across long distances. Optical fiber is used by many telecommunications companies to transmit telephone signals, internet communication, and cable television signals. Researchers at Bell Labs have reached a record bandwidth–distance product of over kilometers per second using fiber-optic communication. Background First developed in the 1970s, fiber-optics have revolutionized the telecommunications industry and have played a major role in the advent of the Information Age. Becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Bragg Gratings
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical filter to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector. History The first in-fiber Bragg grating was demonstrated by Kenneth O. Hill, Ken Hill in 1978. Initially, the gratings were fabricated using a visible laser propagating along the fiber core. In 1989, Gerald Meltz and colleagues demonstrated the much more flexible transverse holographic inscription technique where the laser illumination came from the side of the fiber. This technique uses the #Interference, interference pattern of ultraviolet laser light to cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |