Chromo-modal Dispersion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
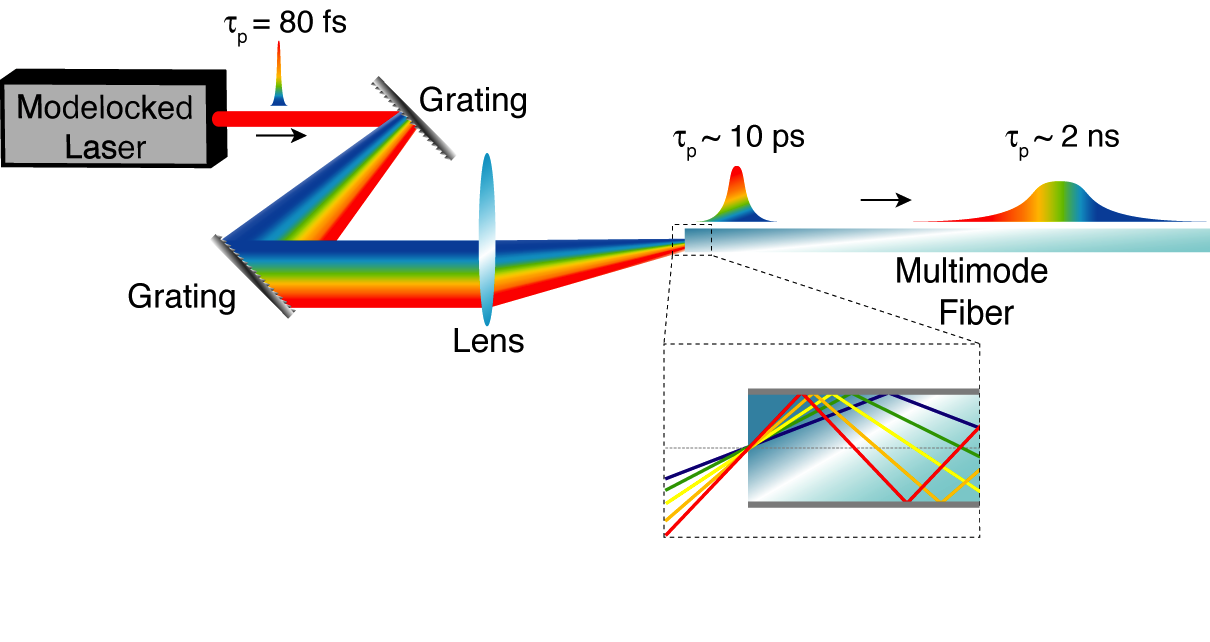 Chromo-modal dispersion (CMD) results from exciting various modes of a multimode
Chromo-modal dispersion (CMD) results from exciting various modes of a multimode
 Chromo-modal dispersion (CMD) results from exciting various modes of a multimode
Chromo-modal dispersion (CMD) results from exciting various modes of a multimode waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Common types of waveguides include acoustic waveguides which direct sound, optical waveguides which direct light, and radio-frequency w ...
with unique spectral components of a broadband optical signal.E.D. Diebold et al., "Giant tunable optical dispersion using chromo-modal excitation of a multimode waveguide," Optics Express 19 (24) 2011. Modal dispersion
Modal dispersion is a distortion mechanism occurring in multimode fibers and other waveguides, in which the signal is spread in time because the propagation velocity of the optical signal is not the same for all modes. Other names for this phen ...
during propagation in the waveguide then provides group velocity dispersion to the signal. The large modal dispersion inherent to multimode waveguides enables the dispersion per unit length of a chromo-modal dispersion device to be several orders of magnitude higher than that of diffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical grating with a periodic structure that diffraction, diffracts light, or another type of electromagnetic radiation, into several beams traveling in different directions (i.e., different diffractio ...
or dispersion compensating fiber-based dispersive elements.
Applications
The ability to controlchromatic dispersion
Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency. Sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used to refer to optics specifically, as opposed to wave propagation in general. A medium having this commo ...
is paramount in applications where the optical pulsewidth is critical, such as chirped pulse amplification
Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level, with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally, then amplified, and then compressed again. The stretching and ...
and fiber-optic communications
Fiber-optic communication is a form of optical communication for transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modulated ...
.
Other devices
Typically, devices used to generate large amounts (>100 ps/nm) of chromatic dispersion are based ondiffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical grating with a periodic structure that diffraction, diffracts light, or another type of electromagnetic radiation, into several beams traveling in different directions (i.e., different diffractio ...
s, chirped fiber Bragg gratings, or dispersion compensating fiber. Unfortunately, these dispersive elements suffer from one or more of the following restrictions:
# Limited operational bandwidth
# Limited total dispersion
# Low peak power handling
# Large spatial footprint.
Construction
The chromo-modal dispersion device is constructed by combining the angular dispersion ofdiffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical grating with a periodic structure that diffraction, diffracts light, or another type of electromagnetic radiation, into several beams traveling in different directions (i.e., different diffractio ...
s with the modal dispersion
Modal dispersion is a distortion mechanism occurring in multimode fibers and other waveguides, in which the signal is spread in time because the propagation velocity of the optical signal is not the same for all modes. Other names for this phen ...
of a multimode waveguide.
Advantages
The large dispersion and small footprint of the device make the chromo-modal dispersion device potentially useful for on-chip dispersion compensation using optical components such as integrated gratings and planar multimode waveguides. The advantage of physical compactness, combined with the magnitude and tunability of its dispersion suggest its potential use as a versatile tool for pulse stretching or compression in a variety of applications in which the capabilities of singlemode fiber or diffraction grating-based dispersive elements will not suffice.References
{{reflist Photonics Fiber optics Telecommunications engineering