|
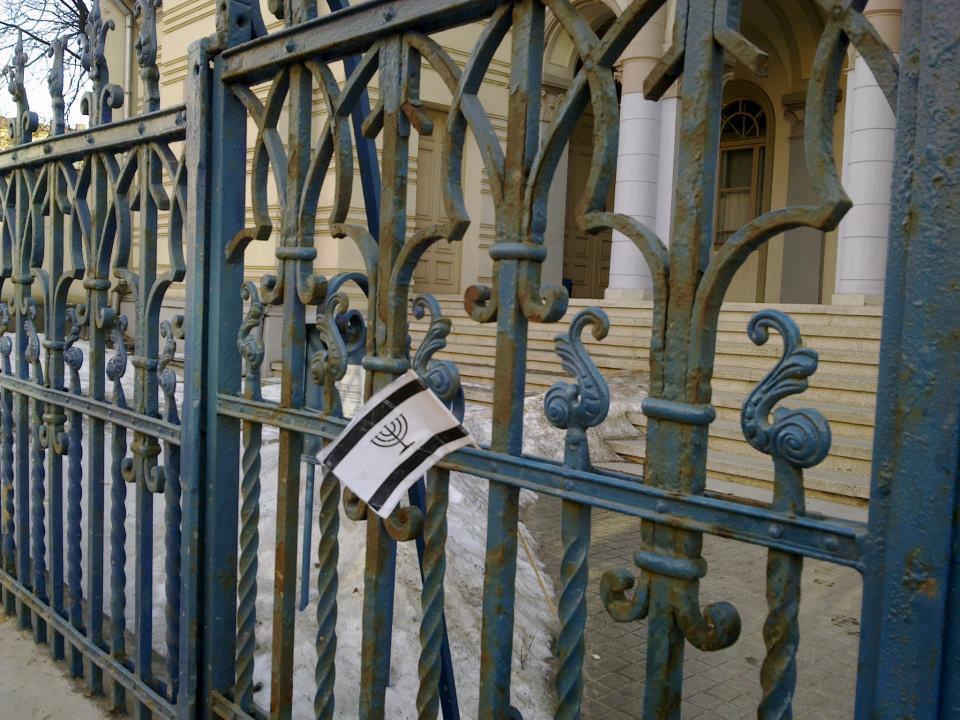
Choral Synagogue (Vilnius)
The Choral Synagogue of Vilnius ( lt, Vilniaus choralinė sinagoga) is the only synagogue in Vilnius that is still in use. The other synagogues were destroyed partly during World War II, when Lithuania was occupied by Nazi Germany, and partly by the Soviet authorities after the war. The Choral Synagogue of Vilnius was built in 1903. The synagogue is built in a Romanesque-Moorish style. It is the only active synagogue that survived both the Holocaust and Soviet rule in this city that once had over 100 synagogues. During the occupation of Lithuania by the Soviet Union the synagogue was nationalised and turned into a metal factory. Resulting from this usage the building suffered considerable damage. It was restored in 2010 and opened again as a synagogue shortly thereafter. International donations and a small community of Jews in Vilnius support the synagogue. The synagogue holds services and is open to visitors. In 2019, the synagogue along with the Jewish community headquar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilnius' Old Town
The Old Town of Vilnius ( lt, Vilniaus senamiestis, pl, Stare Miasto w Wilnie, be, Стары горад у Вільнюсе, russian: Старый город в Вильнюсe), one of the largest surviving medieval old towns in both Northern and Central Europe, has an area of 3.59 square kilometres (887 acres). It encompasses 74 quarters, with 70 streets and lanes numbering 1487 buildings with a total floor area of 1,497,000 square meters. According to the archaeological research, the first traces of a city are found in Vilnius during the reign of Traidenis and Vytenis rule. There is some scientific debate whether Vilnius was already a city at the times of king of Lithuania Mindaugas. It was first mentioned in the written sources in the letters of Gediminas. The Magdeburg rights were granted by the Lithuanian Grand Duke and King of Poland Jogaila in 1387. It is the oldest part of the Lithuanian capital of Vilnius, it had been developed over the course of many centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-wing
Right-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that view certain social orders and hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position on the basis of natural law, economics, authority, property or tradition.T. Alexander Smith, Raymond Tatalovich. ''Cultures at war: moral conflicts in western democracies''. Toronto, Canada: Broadview Press, Ltd, 2003. p. 30. "That viewpoint is held by contemporary sociologists, for whom 'right-wing movements' are conceptualized as 'social movements whose stated goals are to maintain structures of order, status, honor, or traditional social differences or values' as compared to left-wing movements which seek 'greater equality or political participation.' In other words, the sociological perspective sees preservationist politics as a right-wing attempt to defend privilege within the ''social hierarchy''."''Left and right: the significance of a political distinction'', Norberto Bobbio and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaism In Vilnius
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions. Judaism is considered by religious Jews to be the expression of the covenant that God established with the Israelites, their ancestors. It encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization. The Torah, as it is commonly understood by Jews, is part of the larger text known as the ''Tanakh''. The ''Tanakh'' is also known to secular scholars of religion as the Hebrew Bible, and to Christians as the "Old Testament". The Torah's supplemental oral tradition is represented by later texts such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synagogues Completed In 1903
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish language, Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino language, Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Judaism, Jewish house of worship. Synagogues have a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller Chapel, chapels), where Jews attend religious Services or special ceremonies (including Wedding, Weddings, Bar Mitzvah, Bar Mitzvahs or Bat Mitzvah, Bat Mitzvahs, Confirmation, Confirmations, choir performances, or even children's plays), have Beth midrash, rooms for study, social hall(s), administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious school and Hebrew school, sometimes Jewish preschool, preschools, and often have many places to sit and congregate; display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork throughout; and sometimes have items of some Jewish historical significance or history about the Synagog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synagogues In Vilnius
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worship. Synagogues have a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels), where Jews attend religious Services or special ceremonies (including Weddings, Bar Mitzvahs or Bat Mitzvahs, Confirmations, choir performances, or even children's plays), have rooms for study, social hall(s), administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious school and Hebrew school, sometimes Jewish preschools, and often have many places to sit and congregate; display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork throughout; and sometimes have items of some Jewish historical significance or history about the Synagogue itself, on display. Synagogues are consecrated spaces used for the purpose of Jewish prayer, study, assembly, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodox Synagogues
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to: Religion * Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-paganism or Hinduism Christian Traditional Christian denominations * Eastern Orthodox Church, the world's second largest Christian church, that accepts seven Ecumenical Councils *Oriental Orthodox Churches, a Christian communion that accepts three Ecumenical Councils Modern denominations * True Orthodox Churches, also called Old Calendarists, a movement that separated from the mainstream Eastern Orthodox Church in the 1920s over issues of ecumenism and calendar reform * Reformed Orthodoxy (16th–18th century), a systematized, institutionalized and codified Reformed theology * Neo-orthodoxy, a theological position also known as ''dialectical theology'' * Paleo-orthodoxy, (20th–21st century), a movement in the United States focusing on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodox Judaism In Lithuania
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to: Religion * Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-paganism or Hinduism Christian Traditional Christian denominations * Eastern Orthodox Church, the world's second largest Christian church, that accepts seven Ecumenical Councils * Oriental Orthodox Churches, a Christian communion that accepts three Ecumenical Councils Modern denominations * True Orthodox Churches, also called Old Calendarists, a movement that separated from the mainstream Eastern Orthodox Church in the 1920s over issues of ecumenism and calendar reform * Reformed Orthodoxy (16th–18th century), a systematized, institutionalized and codified Reformed theology * Neo-orthodoxy, a theological position also known as ''dialectical theology'' * Paleo-orthodoxy, (20th–21st century), a movement in the United States focusin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkenazi Synagogues
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who Coalescent theory, coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is Yiddish (a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language with Jewish linguistic elements, including the Hebrew alphabet), which developed during the Middle Ages after they had moved from Germany in the Middle Ages, Germany and France in the Middle Ages, France into Northern Europe#UN geoscheme classification, Northern Europe and Eastern Europe. For centuries, Ashkenazim in Europe used Hebrew only as a sacred language until Revival of the Hebrew language, the revival of Hebrew as a common language in 20th-century Israel. Throughout their numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkenazi Jewish Culture In Lithuania
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is Yiddish (a West Germanic language with Jewish linguistic elements, including the Hebrew alphabet), which developed during the Middle Ages after they had moved from Germany and France into Northern Europe and Eastern Europe. For centuries, Ashkenazim in Europe used Hebrew only as a sacred language until the revival of Hebrew as a common language in 20th-century Israel. Throughout their numerous centuries living in Europe, Ashkenazim have made many important contributions to its philosophy, scholarship, literature, art, music, and science. The rabbinical term '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Synagogue Of Vilna
The Great Synagogue of Vilna, which once stood at the end of Jewish Street (I-2), Vilnius, Lithuania, was built between 1630 and 1633 after permission was granted to construct a synagogue from stone. Standing on the spot of an existing synagogue built in 1572, the site had first been used to house a Jewish house of prayer in 1440. Damaged in World War II, it was demolished in 1955–1957 and replaced by a kindergarten and a primary school. Structure The synagogue had a number of entrances. One, at street level, consisted of a pair of iron gates that had been donated by a tailors' society in 1640. The other entrance on the western side, added in 1800, was a bit more imposing: it had an elevated two-tiered wooden gable with a portal and wrought iron posts. There was a heavy iron door with an original Hebrew inscription indicating it was a gift of a "society of Psalm reciters" in 1642. At the time of its building, ecclesiastical regulations all through Europe specified that a synagog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamelis Synagogue
The Zamelis Synagogue ( lt, Zamelio sinagoga) is a former synagogue in Vilnius, Lithuania Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania .... History The Synagogue was built at the beginning of the 19th century, between 1817 and 1833. It was actively used until 1940. After World War II it was used as a warehouse and apartment complex. At the end of the 20th century, the building was abandoned. Current state In 2015 the reconstruction works in the abandoned synagogue started. Currently the building is not used for religious activities, but hosts various cultural events. See also * Lithuanian Jews References External links 2020 reconstruction gallery Synagogues in Vilnius {{Lithuania-synagogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Jews
Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks () are Jews with roots in the territory of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania (covering present-day Lithuania, Belarus, Latvia, the northeastern Suwałki and Białystok regions of Poland, as well as adjacent areas of modern-day Russia and Ukraine). The term is sometimes used to cover all Haredi Jews who follow a " Lithuanian" ( Ashkenazi, non- Hasidic) style of life and learning, whatever their ethnic background. The area where Lithuanian Jews lived is referred to in Yiddish as , hence the Hebrew term (). No other famous Jew is more closely linked to a specifically Lithuanian city than Vilna Gaon (in Yiddish, "the genius of Vilna"). Rabbi Elijah ben Solomon Zalman (1720–1797) to give his rarely used full name, helped make Vilna (modern-day Vilnius) a world center for Talmudic learning. Chaim Grade (1910–1982) was born in Vilna, the city about which he would write. The inter-war Republic of Lithuania was home to a large and influential Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)