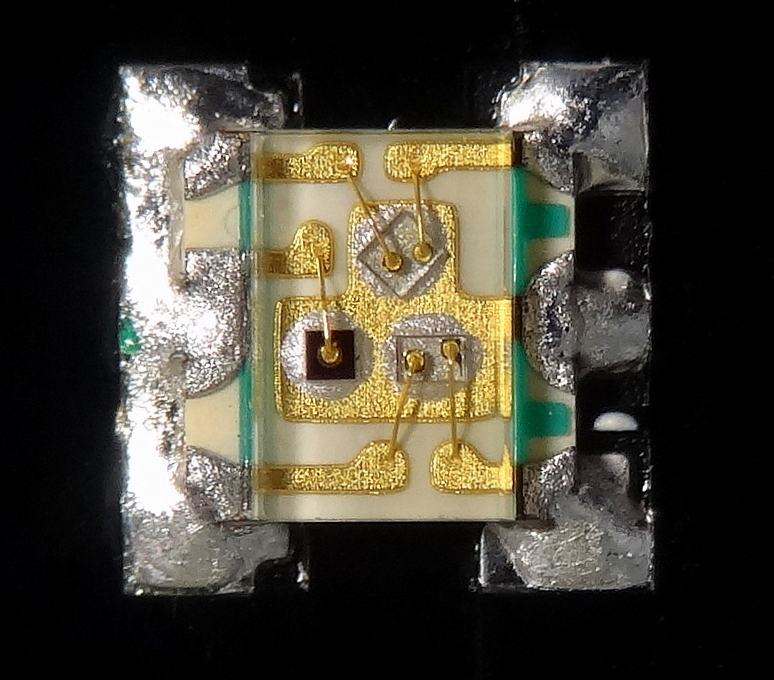
|
Chip On Board
Chip on board (COB) is a method of circuit board manufacturing in which the integrated circuits (e.g. microprocessors) are attached (wired, bonded directly) to a printed circuit board, and covered by a blob of epoxy. By eliminating the packaging of individual semiconductor devices, the completed product can be more compact, lighter, and less costly. In some cases, COB construction improves the operation of radio frequency systems by reducing the inductance and capacitance of integrated circuit leads. COB effectively merges two levels of electronic packaging: level 1 (components) and level 2 (wiring boards), and may be referred to as "level 1.5".John H. Lau, ''Chip On Board: Technology for Multichip Modules'', Springer Science & Business Media, 1994 pages 1-3 Construction A finished semiconductor wafer is cut into dies. Each die is then physically bonded to the PCB. Three different methods are used to connect the terminal pads of the integrated circuit (or other semicond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two High Power COB-LEDs With 20W And 10W
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Evolution Arabic digit The digit used in the modern Western world to represent the number 2 traces its roots back to the Indic Brahmic script, where "2" was written as two horizontal lines. The modern Chinese and Japanese languages (and Korean Hanja) still use this method. The Gupta script rotated the two lines 45 degrees, making them diagonal. The top line was sometimes also shortened and had its bottom end curve towards the center of the bottom line. In the Nagari script, the top line was written more like a curve connecting to the bottom line. In the Arabic Ghubar writing, the bottom line was completely vertical, and the digit looked like a dotless closing question mark. Restoring the bottom line to its original horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip Chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to external circuitry with solder bumps that have been deposited onto the chip pads. The technique was developed by General Electric's Light Military Electronics Department, Utica, New York. The solder bumps are deposited on the chip pads on the top side of the wafer during the final wafer processing step. In order to mount the chip to external circuitry (e.g., a circuit board or another chip or wafer), it is flipped over so that its top side faces down, and aligned so that its pads align with matching pads on the external circuit, and then the solder is reflowed to complete the interconnect. This is in contrast to wire bonding, in which the chip is mounted upright and fine wires are welded onto the chip pads and lead frame contacts to interconnect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blob Top
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection from mechanical damage, cooling, radio frequency noise emission and electrostatic discharge. Product safety standards may dictate particular features of a consumer product, for example, external case temperature or grounding of exposed metal parts. Prototypes and industrial equipment made in small quantities may use standardized commercially available enclosures such as card cages or prefabricated boxes. Mass-market consumer devices may have highly specialized packaging to increase consumer appeal. Electronic packaging is a major discipline within the field of mechanical engineering. Design Electronic packaging can be organized by levels: * Level 0 - "Chip", protecting a bare semiconductor die from contamination and damage. * Level 1 - C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium Aluminium Garnet
Yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG, Y3 Al5 O12) is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group. It is a cubic yttrium aluminium oxide phase, with other examples being YAlO3 (YAP) in a hexagonal or an orthorhombic, perovskite-like form, and the monoclinic Y4Al2O9 (YAM). Due to its broad optical transparency, low internal stress, high hardness, chemical and heat resistance, YAG is used for a variety of optics. Its lack of birefringence (unlike sapphire) makes it an interesting material for high-energy/high-power laser systems. Laser damage levels of YAG ranged from 1.1 to 2.2 kJ/cm² (1064 nm, 10 ns). YAG, like garnet and sapphire, has no uses as a laser medium when pure. However, after being doped with an appropriate ion, YAG is commonly used as a host material in various solid-state lasers. Rare earth elements such as neodymium and erbium can be doped into YAG as active laser ions, yielding Nd:YAG and Er:YAG lasers, respectively. Cerium-doped YAG (Ce:YAG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, silicone rubber, silicone resin, and silicone caulk. Chemistry More precisely called polymerized siloxanes or polysiloxanes, silicones consist of an inorganic silicon–oxygen backbone chain (⋯−Si−O−Si−O−Si−O−⋯) with two organic groups attached to each silicon center. Commonly, the organic groups are methyl. The materials can be cyclic or polymeric. By varying the −Si−O− chain lengths, side groups, and crosslinking, silicones can be synthesized with a wide variety of properties and compositions. They can vary in consistency from liquid to gel to rubber to hard plastic. The most common siloxan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Lighting
Solid-state lighting (SSL) is a type of lighting that uses semiconductor light-emitting diodes (LEDs), organic light-emitting diodes (OLED), or polymer light-emitting diodes (PLED) as sources of illumination rather than electrical filaments, plasma (used in arc lamps such as fluorescent lamps), or gas. Solid state electroluminescence is used in SSL as opposed to incandescent bulbs (which use thermal radiation) or fluorescent tubes. Compared to incandescent lighting, SSL creates visible light with reduced heat generation and less energy dissipation. Most common "white LEDs” convert blue light from a solid-state device to an (approximate) white light spectrum using photoluminescence, the same principle used in conventional fluorescent tubes. The typically small mass of a solid-state electronic lighting device provides for greater resistance to shock and vibration compared to brittle glass tubes/bulbs and long, thin filament wires. They also eliminate filament evaporation, poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Led Flood Outdoor Lamp
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape-automated Bonding
Tape-automated bonding (TAB) is a process that places bare semiconductor chips (dies) like integrated circuits onto a flexible circuit board (FPC) by attaching them to fine conductors in a polyamide or polyimide (like trade names Kapton or UPILEX) film carrier. This FPC with the die(s) (TAB inner lead bonding, ILB) can be mounted on the system or module board or assembled inside a package (TAB outer lead bonding, OLB). Typically the FPC includes from one to three conductive layers and all inputs and outputs of the semiconductor die are connected simultaneously during the TAB bonding. Tape automated bonding is one of the methods needed for achieving chip-on-flex (COF) assembly and it is one of the first roll-to-roll processing (also called R2R, reel-to-reel) type methods in the electronics manufacturing. Process The TAB mounting is done such that the bonding sites of the die, usually in the form of bumps or balls made of gold, solder or anisotropic conductive material, are connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Bonding
Wire bonding is the method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its packaging during semiconductor device fabrication. Although less common, wire bonding can be used to connect an IC to other electronics or to connect from one printed circuit board (PCB) to another. Wire bonding is generally considered the most cost-effective and flexible interconnect technology and is used to assemble the vast majority of semiconductor packages. Wire bonding can be used at frequencies above 100 GHz. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solder
Solder (; NA: ) is a fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces after cooling. Metals or alloys suitable for use as solder should have a lower melting point than the pieces to be joined. The solder should also be resistant to oxidative and corrosive effects that would degrade the joint over time. Solder used in making electrical connections also needs to have favorable electrical characteristics. Soft solder typically has a melting point range of , and is commonly used in electronics, plumbing, and sheet metal work. Alloys that melt between are the most commonly used. Soldering performed using alloys with a melting point above is called "hard soldering", "silver soldering", or brazing. In specific proportions, some alloys are eutectic — that is, the alloy's melting point is the lowest possible for a mixture of those components, and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die (integrated Circuit)
A die, in the context of integrated circuits, is a small block of semiconducting material on which a given functional circuit is fabricated. Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer of electronic-grade silicon (EGS) or other semiconductor (such as GaAs) through processes such as photolithography. The wafer is cut (diced) into many pieces, each containing one copy of the circuit. Each of these pieces is called a die. There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a printed circuit board, most dies are packaged in various forms. Manufacturing process Most dies are composed of silicon and used for integrated circuits. The process begins with the production of monocrystalline silicon ingots. These ingots are then sliced into disks with a diameter of up to 300 mm. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |