|
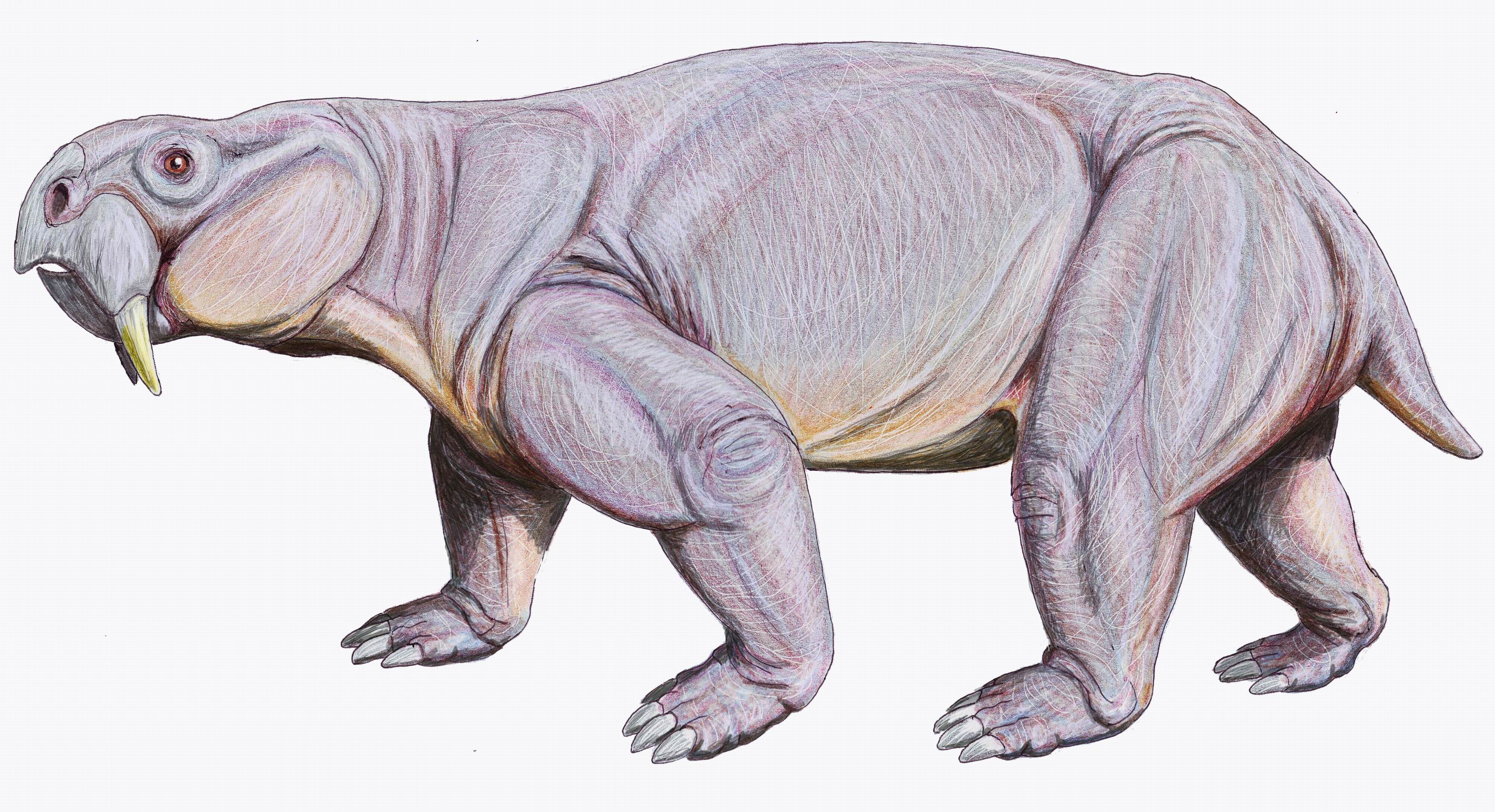
Chiniquodon
''Chiniquodon'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts, which lived during the Late Triassic (Carnian) in South America (Argentina and Brazil) and Africa (Namibia and Madagascar). ''Chiniquodon'' was closely related to the genus '' Aleodon'', and close to the ancestry of mammals. Other contemporaries included early dinosaurs. As both groups filled a similar ecological niche, fairly large therapsid hunters such as ''Chiniquodon'' may have been outcompeted by dinosaurs. Classification ''Chiniquodon theotonicus'', the type species, is from the Santa Maria Formation, Brazil and Chañares Formation, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, northwestern Argentina. This species is known from a number of skulls. The holotype is in the paleontological collection at Tübingen University, Germany. ''Chiniquodon sanjuanensis'' is from the Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, northwestern Argentina. It was originally assigned to the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiniquodon NT Small
''Chiniquodon'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts, which lived during the Late Triassic (Carnian) in South America (Argentina and Brazil) and Africa (Namibia and Madagascar). ''Chiniquodon'' was closely related to the genus ''Aleodon'', and close to the ancestry of mammals. Other contemporaries included early dinosaurs. As both groups filled a similar ecological niche, fairly large therapsid hunters such as ''Chiniquodon'' may have been outcompeted by dinosaurs. Classification ''Chiniquodon theotonicus'', the type species, is from the Santa Maria Formation, Brazil and Chañares Formation, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, northwestern Argentina. This species is known from a number of skulls. The holotype is in the paleontological collection at Tübingen University, Germany. ''Chiniquodon sanjuanensis'' is from the Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, northwestern Argentina. It was originally assigned to the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiniquodon Kalanoro FMNH
''Chiniquodon'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts, which lived during the Late Triassic (Carnian) in South America (Argentina and Brazil) and Africa (Namibia and Madagascar). ''Chiniquodon'' was closely related to the genus ''Aleodon'', and close to the ancestry of mammals. Other contemporaries included early dinosaurs. As both groups filled a similar ecological niche, fairly large therapsid hunters such as ''Chiniquodon'' may have been outcompeted by dinosaurs. Classification ''Chiniquodon theotonicus'', the type species, is from the Santa Maria Formation, Brazil and Chañares Formation, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, northwestern Argentina. This species is known from a number of skulls. The holotype is in the paleontological collection at Tübingen University, Germany. ''Chiniquodon sanjuanensis'' is from the Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, northwestern Argentina. It was originally assigned to the genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chañares Formation
The Chañares Formation is a Carnian-age geologic formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, located in La Rioja Province, Argentina. It is characterized by drab-colored fine-grained volcaniclastic claystones, siltstones, and sandstones which were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment. The formation is most prominently exposed within Talampaya National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site within La Rioja Province. The Chañares formation is the lowermost stratigraphic unit of the Agua de la Peña Group, overlying the Tarjados Formation of the Paganzo Group, and underlying the Los Rastros Formation. Though previously considered Ladinian in age, U-Pb dating has determined that most or all of the Chañares Formation dates to the early Carnian stage of the Late Triassic.Kent et al, 2014, p.7959 The Chañares Formation has provided a diverse and well-preserved faunal assemblage which has been studied intensively since the 1960s. The most common reptiles were pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleodon
''Aleodon'' is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived from the Middle to the Late Triassic. Relatively few analyses have been conducted to identify the phylogenetic placement of ''Aleodon'', however those that have place ''Aleodon'' as a sister taxon to ''Chiniquodon''. Two species of ''Aleodon'' are recognized: ''A. brachyramphus'' which was discovered in Tanzania, and ''A. cromptoni'' which was discovered most recently in Brazil. The name for the genus ''Aleodon'' was created when Alfred W. "Fuzz" Crompton initially discovered the type species, ''Aleodon brachyramphus''. The genus name, "Aleodon" referred to the grinding nature of the postcanine teeth, while "brachyramphus" referred to the relatively short snout of the specimen. The most recently discovered species, ''A. cromptoni'' was named after Crompton. Discovery and Classification In 1955, ''Aleodon'' was initially classified as a gomphodont cynodont based on the partial skull and lower jaw fossils found in 1933 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omingonde Formation
The Omingonde Formation is an Early Triassic, Early to Middle Triassic (Anisian to Ladinian) geologic Formation (geology), formation, part of the Karoo Supergroup, in the western Otjozondjupa Region and northeastern Erongo Region of north-central Namibia. The formation has a maximum thickness of about and comprises sandstones, shales, siltstones and conglomerate (geology), conglomerates, was deposited in a fluvial depositional environment, environment, alternating between a meandering river, meandering and braided river setting. The Omingonde Formation is correlated with a series of formations in northwestern Argentina and the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil, deposited in a larger basinal area, 120 million years before the break-up of Pangea. The formation has provided fossils of several therapsids, amphibians and ichnofossils and belongs to the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone, ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone. The Omingonde Formation preserves the most diverse fauna of Middle Tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isalo II Formation
Isalo II, also known as the Makay Formation, is an informal Triassic geological unit in Madagascar Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa .... It is described as "thick beds of mottled red or green clays associated with soft cross-bedded sandstones, light in colour and much finer-grained than the Isalo I sandstones." It is prominent in the Makay Massif.Brenon, P. (1972). The Geology of Madagascar. In: Battistini, R., Richard-Vindard, G. (eds) ''Biogeography and Ecology in Madagascar''. Monographiae Biologicae, vol 21. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi-org.wikipedialibrary.idm.oclc.org/10.1007/978-94-015-7159-3_2 Fossil content Amphibians Reptiles Synapsids References {{reflist Geologic formations of Madagascar Triassic System of Africa Triassic Madagascar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 In Paleontology
Plants Ferns and fern allies Flowering plants Arthropods Insects Archosauromorphs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Pterosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{DEFAULTSORT:1936 In Paleontology 1930s in paleontology Paleontology 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Maria Formation
The Santa Maria Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is primarily Carnian in age (Late Triassic), and is notable for its fossils of cynodonts, "rauisuchian" pseudosuchians, and early dinosaurs and other dinosauromorphs, including the herrerasaurid '' Staurikosaurus'', the basal sauropodomorphs ''Buriolestes'' and '' Saturnalia,'' and the lagerpetid ''Ixalerpeton''. The formation is named after the city of Santa Maria in the central region of Rio Grande do Sul, where outcrops were first studied. The Santa Maria Formation makes up the majority of the Santa Maria Supersequence, which extends through the entire Late Triassic. The Santa Maria Supersequence is divided into four geological sequences, separated from each other by short unconformities. The first two of these sequences (Pinheiros-Chiniquá and Santa Cruz sequences) lie entirely within the Santa Maria Formation, while the third (the Candelária sequence) is shared with the ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischigualasto Formation
The Ischigualasto Formation is a Late Triassic fossiliferous formation and Lagerstätte in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin of the southwestern La Rioja Province and northeastern San Juan Province in northwestern Argentina. The formation dates to the Carnian and Norian ages and ranges between 231.7 and 225 Ma, based on ash bed dating. The up to thick formation is part of the Agua de la Peña Group, overlies Los Rastros Formation and is overlain by Los Colorados Formation. The formation is subdivided into four members, from old to young; La Peña, Cancha de Bochas, Valle de la Luna and Quebrada de la Sal. The sandstones, mudstones, conglomerates and tuffs of the formation were deposited in a humid alluvial to fluvial floodplain environment, characterized by strongly seasonal rainfall. The Ischigualasto Formation is an important paleontological unit and considered a Lagerstätte, as it preserves several genera of early dinosaurs, other archosaurs, synapsids, and temnospon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynodont
The cynodonts () (clade Cynodontia) are a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian (approximately 260 mya), and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Cynodonts had a wide variety of lifestyles, including carnivory and herbivory. Mammals are cynodonts, as are their extinct ancestors and close relatives, having evolved from advanced probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic. All other cynodont lines went extinct, with the last known non-mammalian cynodont group, the Tritylodontidae, having its youngest records in the Early Cretaceous. Description Early cynodonts have many of the skeletal characteristics of mammals. The teeth were fully differentiated and the braincase bulged at the back of the head. Outside of some crown-group mammals (notably the therians), all cynodonts probably laid eggs. The temporal fenestrae were much larger than those of their ancestors, and the widening of the zygomatic arch in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin
The Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin ( es, Cuenca de Ischigualasto-Villa Unión) is a small sedimentary basin located in the Argentine Northwest, Argentina. It is located in the southwestern part of La Rioja Province and the northeastern part of San Juan Province. The basin borders the Sierras Pampeanas in the east, the western boundary of the basin is formed by the Valle Fértil Fault, bordering the Precordillera, and it is bound in the southeast by the El Alto Fault, separating the basin from the Marayes-El Carrizal Basin. The basin started forming in the Late Permian, with the break-up of Pangea, when extensional tectonics, including rifting, formed several basins in Gondwana; present-day South America, Africa, Antarctica, India and Australia. The accommodation space in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin was filled by an approximately thick succession of volcaniclastic, eolian, alluvial, fluvial and lacustrine deposits in various geologic formations. The Cenozoic ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |