|
Chinese Corvette Yangwu
''Yangwu'' () was a wooden corvette built for the Imperial Chinese Navy. She was built in 1872 at the Foochow Arsenal, and was the largest ship built there from the shipbuilding programme of 1868–75. During her early career, she was used as a training ship and under the command of English captains. She later saw action in the Battle of Fuzhou in 1884, the opening action of the Sino-French War, where she acted as the flagship of the Fujian Fleet. Shortly after the start of the battle, she was damaged by a spar torpedo, causing a large explosion and the loss of the majority of her crew; she was sunk shortly afterwards by enemy fire. Design ''Yangwu'' was a unique showpiece at the Foochow Arsenal. She was Length overall, long overall, had a Beam (nautical), beam of and an average Draft (hull), draft of .#wright2000, Wright (2000): p. 39 She Displacement (ship), displaced .#FeuerwerkerEt1967, Feuerwerker et al; (1967): p. 113 The propulsion system consisted of a Marine steam engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Gunboat Fuxing
''Fuxing'' () was a wooden gunboat built for the Imperial Chinese Navy. She was built in 1870 at the Foochow Arsenal, the second such gunboat constructed, alongside her sister ship . ''Fuxing'' was based throughout her life at the Foochow Arsenal, and there became involved in the Battle of Fuzhou at the opening of the Sino-French War. She was quickly sunk during the battle by a spar torpedo. Design ''Fuxing'' was the third ship to be constructed at the Foochow Arsenal, after ''Meiyun'' and the troopship, transport ''Wannien Ching''. All the ships of this period were constructed out of wood, mostly teak. She was length overall, long overall. She had a beam (nautical), beam of and a draft (hull), draught of . ''Fuxing'' displaced . She was fully sail rigging, rigged, in addition to her single steam engine powering a single shaft. The engine had an output of , enabling ''Fuxing'' to travel at . She was armed with three Krupp guns; a single and two . Service history file:Bombardme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Overall
__NOTOC__ Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth (for example, £2.50 per metre LOA). LOA is usually measured on the hull alone. For sailing ships, this may ''exclude'' the bowsprit and other fittings added to the hull. This is how some racing boats and tall ships use the term LOA. However, other sources may include bowsprits in LOA. Confusingly, LOA has different meanings. "Sparred length", "Total length including bowsprit", "Mooring length" and "LOA including bowsprit" are other expressions that might indicate the full length of a sailing ship. LOD Often used to distinguish between the length of a vessel including projections (e.g. bow sprits, etc.) from the length of the hull itself, the Length on Deck or LOD is often repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Whitworth
Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd was a major British manufacturing company of the early years of the 20th century. With headquarters in Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Armstrong Whitworth built armaments, ships, locomotives, automobiles and aircraft. The company was founded by William Armstrong in 1847, becoming Armstrong Mitchell and then Armstrong Whitworth through mergers. In 1927, it merged with Vickers Limited to form Vickers-Armstrongs, with its automobile and aircraft interests purchased by J D Siddeley. History In 1847, the engineer William George Armstrong founded the Elswick works at Newcastle, to produce hydraulic machinery, cranes and bridges, soon to be followed by artillery, notably the Armstrong breech-loading gun, with which the British Army was re-equipped after the Crimean War. In 1882, it merged with the shipbuilding firm of Charles Mitchell to form Armstrong Mitchell & Company and at the time its works extended for over a mile (about 2 km) along th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
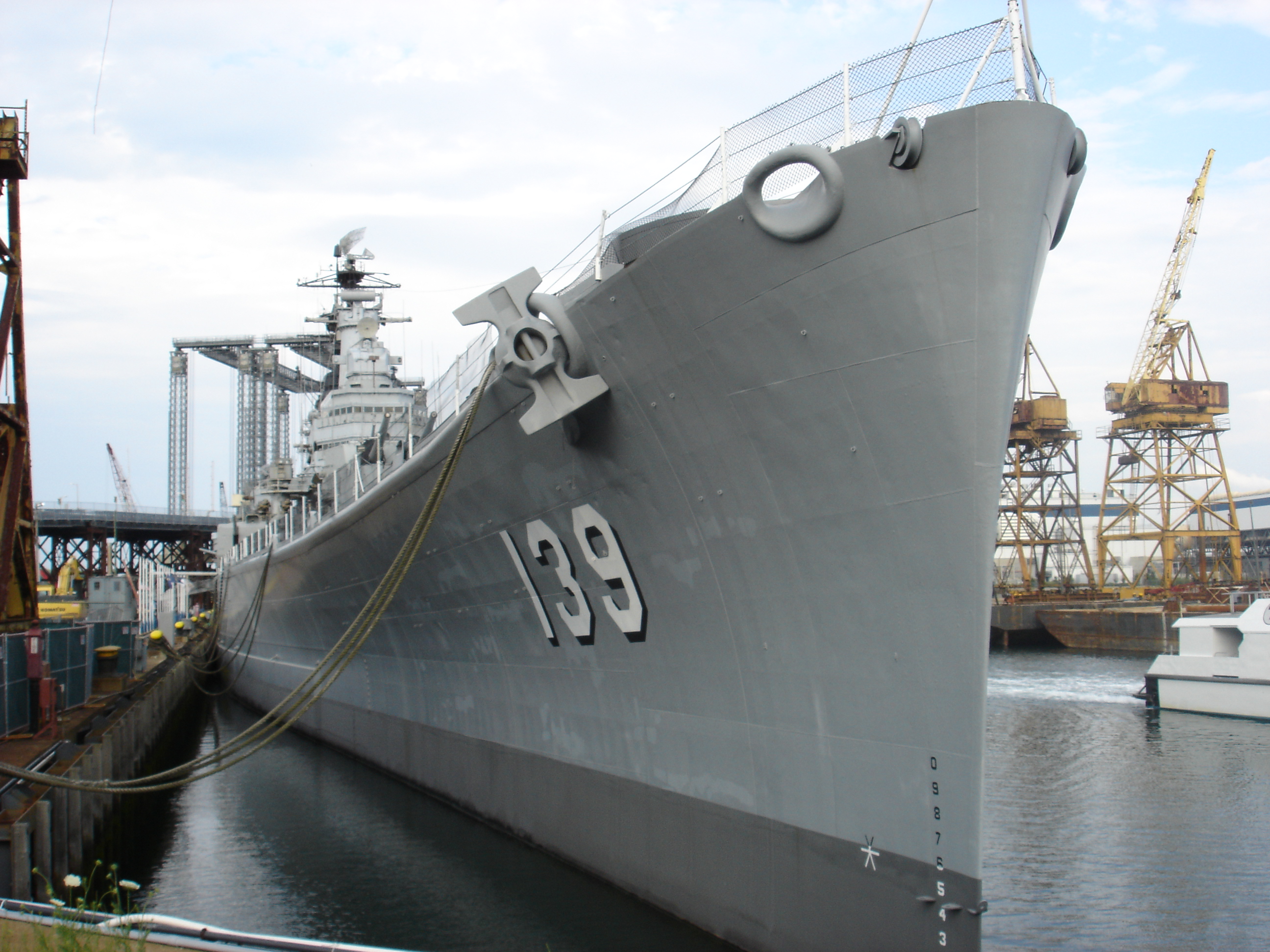
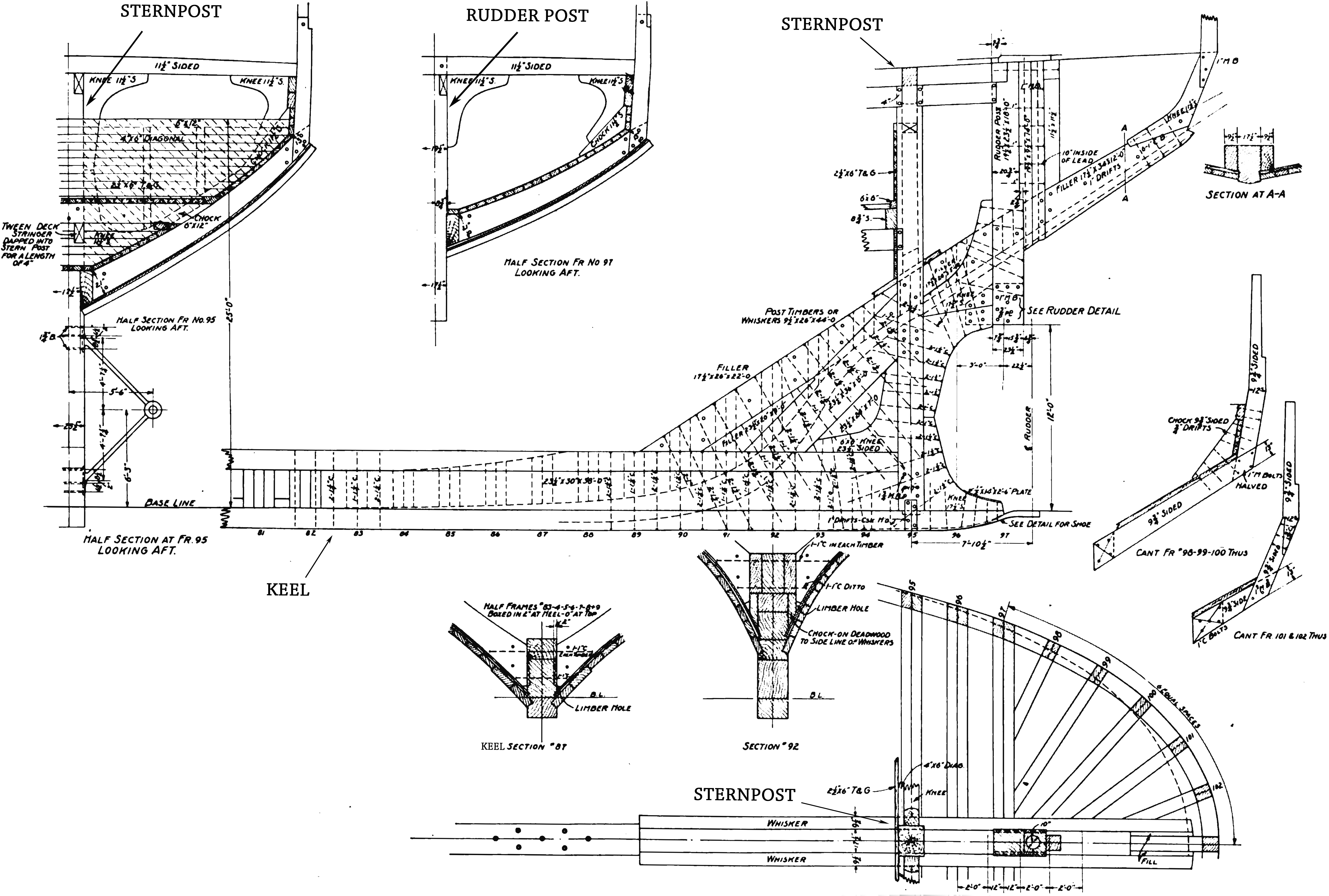
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chase Gun
A chase gun (or chaser), usually distinguished as bow chaser and stern chaser, was a cannon mounted in the bow (aiming forward) or stern (aiming backward) of a sailing ship. They were used to attempt to slow down an enemy ship either chasing (pursuing) or being chased, when the ship's broadside could not be brought to bear. Typically, the chasers were used to attempt to damage the rigging and thereby cause the target to lose performance. Bow chasers could be regular guns brought up from the gundeck and aimed through specially cut-out ports on either side of the bowsprit, or dedicated weapons made with an unusually long bore and a relatively light ball, and mounted in the bow. Stern chasers could also be improvised, or left permanently in the cabins at the stern, covered up and used as part of the furniture. Development In the Age of Sail, shiphandling had been brought to a high art, and chases frequently lasted for hours or sometimes days, as each crew fine-tuned their sail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Battery
In military organizations, an artillery battery is a unit or multiple systems of artillery, mortar systems, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, surface-to-surface missiles, ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, etc., so grouped to facilitate better battlefield communication and command and control, as well as to provide dispersion for its constituent gunnery crews and their systems. The term is also used in a naval context to describe groups of guns on warships. Land usage Historically the term "battery" referred to a cluster of cannon in action as a group, either in a temporary field position during a battle or at the siege of a fortress or a city. Such batteries could be a mixture of cannon, howitzer, or mortar types. A siege could involve many batteries at different sites around the besieged place. The term also came to be used for a group of cannon in a fixed fortification, for coastal or frontier defence. During the 18th century "battery" began to be used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funnel (ship)
A funnel is the smokestack or chimney on a ship used to expel boiler steam and smoke or engine exhaust. They are also commonly referred to as stacks. Purpose The primary purpose of a ship's funnel(s) is to lift the exhaust gases clear of the deck, in order not to foul the ship's structure or decks, and to avoid impairing the ability of the crew to carry out their duties. In steam ships the funnels also served to help induce a convection draught through the boilers. Design Since the introduction of steam-power to ships in the 19th century, the funnel has been a distinctive feature of the silhouette of a vessel, and used for recognition purposes. Funnel area The required funnel cross-sectional area is determined by the volume of exhaust gases produced by the propulsion plant. Often this area is too great for a single funnel. Early steam vessels needed multiple funnels ( had 5 when launched), but as efficiency increased new machinery needed fewer funnels. Merchant ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
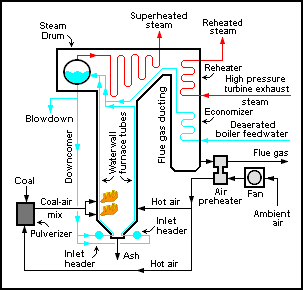
Boiler (power Generation)
An industrial boiler, originally used for supplying steam to a stationary steam engine A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed ''boilers'' and worked at low to medium pressure () but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a ''steam generator''. A boiler or steam generator is used wherever a source of steam is required. The form and size depends on the application: mobile steam engines such as steam locomotives, portable engines and steam-powered road vehicles typically use a smaller boiler that forms an integral part of the vehicle; stationary steam engines, industrial installations and power stations will usually have a larger separate steam generating facility connected to the point-of-use by piping. A notable exception is the steam-powered fireless locomotive, where separately-generated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Inglis And Company
John Inglis and Company was a Canadian manufacturing firm which made weapons for the United Kingdom and British Commonwealth military forces during the World War II era, then later became a major appliance manufacturer. Whirlpool Corporation acquired control of Inglis in 1987 and changed the company's name to Whirlpool Canada in 2001. Today the Inglis name survives as a brand under Whirlpool. History The company traces its roots to John Inglis who was involved in early enterprises in Dundas and Guelph, Ontario. Inglis was born in 1823 in Hawick County, Roxburghshire, Scotland and came to Canada in 1852 setting in first in Dundas and later in Guelph. On 27 July 1859, he, Thomas Mair and Francis Evatt formed Mair, Inglis and Evatt, a machine shop in Guelph, Ontario, that produced machinery for grist and flour mills. In 1864, they added a steam engine to power the machines. Some time after 1864, Daniel Hunter replaced Thomas Mair, and the name of the business was changed to Ingl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p.5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks" (or "load lines"). A mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)

.jpg)