|
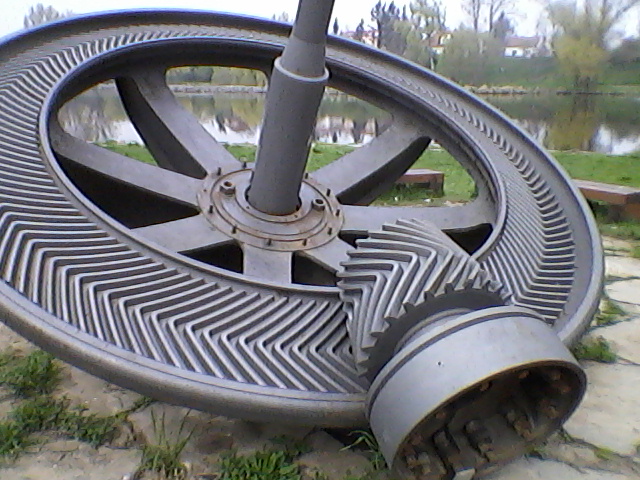
Chevron Gear
A herringbone gear, a specific type of double helical gear, is a special type of gear that is a side-to-side (not face-to-face) combination of two helical gears of opposite hands. From the top, each helical groove of this gear looks like the letter V, and many together form a herringbone pattern (resembling the bones of a fish such as a herring). Unlike helical gears, herringbone gears do not produce an additional axial load. Like helical gears, they have the advantage of transferring power smoothly, because more than two teeth will be enmeshed at any moment in time. Their advantage over the helical gears is that the side-thrust of one half is balanced by that of the other half. This means that herringbone gears can be used in torque gearboxes without requiring a substantial thrust bearing. Because of this, herringbone gears were an important step in the introduction of the steam turbine to marine propulsion. Manufacture Precision herringbone gears are more difficult to manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engrenages - 85
''Spiral'' (french: Engrenages, ) is a French television police procedural and legal drama series following the work and the private lives of Paris police officers and lawyers and judges at the Palais de Justice, Paris. It was created by Alexandra Clert for the TV production company Son et Lumière. The first series of eight episodes started broadcast on Canal+ in France in December 2005. The series was shown in the UK on BBC Four during the summer of 2006. It was the channel's first French language drama series, attracting firm critical approval and a loyal audience of around 200,000. The second series, also eight episodes, was broadcast in France starting in May 2008, and in the UK on BBC Four starting in September 2009. The third series consisted of 12 episodes and was shown from April 2011. The fourth series was broadcast in February 2013. The fifth was broadcast in France in late 2014 and in the UK on BBC Four from January 2015. The sixth series was broadcast in 2017. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuest Type Herringbone Gear
A Wuest type herringbone gear, invented by Swiss engineer Caspar Wüst-Kunz in early 1900s, is a special type of herringbone gear wherein "the teeth on opposite sides of the center line are staggered by an amount equal to one half the circular pitch". By having the teeth of two sides staggered, the gear wears more evenly at the slight cost of strength. References Gears {{mech-engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powertrain
A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components of a motor vehicle that deliver power to the drive wheels. This excludes the engine or motor that generates the power. In marine applications, the drive shaft will drive a propeller, thruster, or waterjet rather than a drive axle, while the actual engine might be similar to an automotive engine. Other machinery, equipment and vehicles may also use a drivetrain to deliver power from the engine(s) to the driven components. In contrast, the powertrain is considered to include both the engine and/or motor(s) as well as the drivetrain. Function The function of the drivetrain is to couple the engine that produces the power to the driving wheels that use this mechanical power to rotate the axle. This connection involves physically linking th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mors (automobile)
The Mors automobile factory was an early French car manufacturer. It was one of the first to take part in automobile racing, beginning in 1897, due to the belief of the company founder, Émile Mors, in racing's technical and promotional benefits. By the turn of the century, automobile racing had become largely a contest between Mors and Panhard et Levassor. Technical achievements Mors was one of the first automobiles to use the V engine configuration. The Mors 60 horsepower Grand Prix car was powered by a 9.2-litre V4 side valve engine, with magneto ignition and dry sump lubrication, which could reach 950 rpm. The car had a steel chassis and a four-speed transmission that drove the rear wheels via chain drive, and rear-wheel brakes. In 1902, Mors added pneumatic shock absorbers to their cars, which represented a great leap forward given the quality of the roads and racetracks at the time. With this car, Henri Fournier was able to win the highly significant Paris-Berl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Citroën
André-Gustave Citroën (; 5 February 1878 – 3 July 1935) was a French industrialist and the founder of French automaker Citroën. He is remembered chiefly for the make of car named after him, but also for his application of double helical gears. Life and career Born in Paris in 1878, André-Gustave Citroën was the fifth and last child of Jewish parents, diamond merchant Levie Citroën and Masza Amelia Kleinman. He was a cousin of the British philosopher Sir A. J. Ayer (the only son of his aunt Reine). The Citroën family moved to Paris in 1873. Upon arrival, the French '' tréma'' was added to the Dutch surname (reputedly by one of André's teachers), changing Citroen to Citroën. Citroen comes from a grandfather in the Netherlands who had been a greengrocer and seller of tropical fruit, and had taken the surname of ''Limoenman'', Dutch for "lime man"; his son however changed it to ''Citroen'', which in Dutch means "lemon". His father died by suicide when André was six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citroën
Citroën () is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded in March 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën is owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 89.95% share in 1976. Citroën's head office is located in the Stellantis Poissy Plant in Saint-Ouen-sur-Seine since 2021 (previously in Rueil-Malmaison) and its offices studies and research in Vélizy-Villacoublay, Poissy (CEMR), Carrières-sous-Poissy and Sochaux-Montbéliard. In 1934, the firm established its reputation for innovative technology with the Traction Avant. This was the world's first car to be mass-produced with front-wheel drive, four-wheel independent suspension, as well as unibody construction, omitting a separate chassis, and instead using the body of the car itself as its main load-bearing structure. In 1954, they produced the world's first hydropneumatic self-levelling suspension system then, in 1955, the revol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herringbone Double-helical Bevel Gears, Citroens Patent (Autocar Handbook, Ninth Edition)
Herringbone may refer to: * Herring-Bone (card game), a game of patience *Herringbone (cloth), a woven pattern of tweed or twill cloth * Herringbone (formation), a type of military formation * Herringbone (horse) (1940–1961), a Thoroughbred racehorse *Herringbone cross-stratification, a sedimentary structure in geology that is formed from back-and-forth tidal water flow *Herringbone gear, a type of gear *Herringbone pattern, a pattern of floor tiling or paving * Herringbone seating, a pattern of airliner seating *A bonding pattern of brickwork, also known as opus spicatum *Herringbone stitch *A type of braided hairstyle, which is also known as a fishtail braid *A distortion pattern from deinterlacing video called mouse teeth *A method of counting used with the unary numeral system *A technique of moving one's skis while cross-country skiing * Herringbone milking shed *Herringbone, another name for the medical condition scintillating scotoma *"Herringbone", a song by Department of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology, whereby the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise impossible to construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Shaper
A gear shaper is a machine tool for cutting the teeth of internal or external gears, it is a specialised application of the more general shaper machine. The name shaper relates to the fact that the cutter engages the part on the forward stroke and pulls away from the part on the return stroke, just like the clapper box on a planer shaper.Woodbury, Robert S. ''Studies in the history of machine'' ''tools''. Cambridge, Mass. :M.I.T. Press, 1972 The cutting tool is also gear shaped having the same pitch as the gear to be cut. However number of cutting teeth must be less than that of the gear to be cut for internal gears. For external gears the number of teeth on the cutter is limited only by the size of the shaping machine. For larger gears the blank is sometimes gashed to the rough shape to make shaping easier. The principal motions involved in rotary gear shaper cutting are of the following : # ''Cutting Motion'': The downward linear motion of the cutter spindle together with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hobbing
Hobbing is a machining process for gear cutting, cutting splines, and cutting sprockets on a hobbing machine, which is a special type of milling machine. The teeth or splines of the gear are progressively cut into the material (a flat, cylindrical piece of metal) by a series of cuts made by a cutting tool called a hob. Hobbing is relatively fast and inexpensive compared to most other gear-forming processes and is used for a broad range of parts and quantities. Hobbing is especially common for machining spur and helical gears. A type of skiving that is analogous to the hobbing of external gears can be applied to the cutting of internal gears, which are skived with a rotary cutter (rather than shaped or broached). Process Hobbing uses a hobbing machine with two skew spindles. One spindle is mounted with a blank workpiece and the other holds the hob. The angle between the hob's spindle (axis) and the workpiece's spindle varies depending on the type part being manufactured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spur Gear
Spur gears or straight-cut gears are the simplest type of gear. They consist of a cylinder or disk with teeth projecting radially. Viewing the gear at 90 degrees from the shaft length (side on) the tooth faces are straight and aligned parallel to the axis of rotation. Looking down the length of the shaft, a tooth's cross section is usually not triangular. Instead of being straight (as in a triangle) the sides of the cross section have a curved form (usually involute and less commonly cycloidal) to achieve a constant drive ratio. Spur gears mesh together correctly only if fitted to parallel shafts. No axial thrust is created by the tooth loads. Spur gears are excellent at moderate speeds but tend to be noisy at high speeds. Spur gear can be classified into two pressure angles, 20° being the current industry standard and 14½° being the former (often found in older equipment). Spur gear teeth are manufactured as either involute profile or cycloidal profile. When two gears a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |