|
Chevalier De Lorraine
Philippe of Lorraine (1643 – 8 December 1702), known as the Chevalier de Lorraine, was a French nobleman and member of the House of Guise, cadet of the Ducal House of Lorraine. He was the renowned lover of Philippe I, Duke of Orléans, brother of Louis XIV. Biography Philippe was the second son of the Count and Countess of Harcourt. His father, Henri of Lorraine, was created the Count of Harcourt in 1605, aged 4. Henri was also the Grand Squire of France, a prestigious charge of the royal stables, the transport of the king, and his ceremonial entourage. He was known as ''Monsieur le Grand''. His mother, Marguerite-Philippe du Cambout, was a member of the old House of Cambout, who traced their ancestry back to the Sovereign Dukes of Brittany (11th century–1547). His oldest brother, Louis, was Count of Armagnac and husband of Catherine de Neufville, the youngest daughter of Nicolas de Neufville de Villeroy, governor of a young Louis XIV. She was a sister of François de Neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Guise
The House of Guise (pronunciation: �ɥiz Dutch: ''Wieze, German: Wiese'') was a prominent French noble family, that was involved heavily in the French Wars of Religion. The House of Guise was the founding house of the Principality of Joinville. Origin The House of Guise was founded as a cadet branch of the House of Lorraine by Claude of Lorraine (1496–1550), who entered French service and was made the first Duke of Guise by King Francis I in 1527. The family's high rank was due not to possession of the Guise dukedom but to their membership in a sovereign dynasty, which procured for them the rank of ''prince étranger'' at the royal court of France. Claude's daughter Mary of Guise (1515–1560) married King James V of Scotland and was mother of Mary, Queen of Scots. Claude's eldest son, Francis, became the second Duke of Guise at his father's death on 12 April 1550 and became a military hero thanks to his defense of Metz in 1552 and the capture of Calais from the English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Benoît-sur-Loire
Saint-Benoît-sur-Loire (, literally ''Saint-Benoît on Loire'') is a commune in the Loiret department in north-central France. Monastery This town hosts the '' Abbaye de Fleury'', also known as the ''Abbaye de Saint Benoît'' (Saint Benedict Abbey). Founded around 630, it is one of the oldest abbeys of the Benedictine rule. In 660, the remains of Saint Benedict of Nursia were transferred to Saint Benoît from Monte Cassino by Mommolin of Fleury. The monastery, known for the ''Fleury Playbook'', was pillaged and damaged multiple times over the course of history, including during the Norman conquests and the French Revolution. The current abbey church is in the Romanesque style and dates from the eleventh century. A community of approximately 40 monks currently resides in the monastery. See also * Communes of the Loiret department The following is the list of the 325 communes of the Loiret department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Charlotte Of The Palatinate
Princess Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate (german: Prinzessin Elisabeth Charlotte von der Pfalz), (french: Princesse Élisabeth-Charlotte du Palatinat); known as Liselotte von der Pfalz, 27 May 1652 – 8 December 1722) was a German member of the House of Wittelsbach and, as ''Madame'' (''Duchesse d'Orléans''), the second wife of Philippe I, Duke of Orléans (younger brother of Louis XIV of France), and mother of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, France's ruler during the Regency. She gained literary and historical importance primarily through preservation of her correspondence, which is of great cultural and historical value due to her sometimes very blunt descriptions of French court life and is today one of the best-known German-language texts of the Baroque period. Although she had only two surviving children, she not only became the ancestress of the House of Orléans, which came to the French throne with Louis Philippe I, the so-called "Citizen King" from 1830 to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
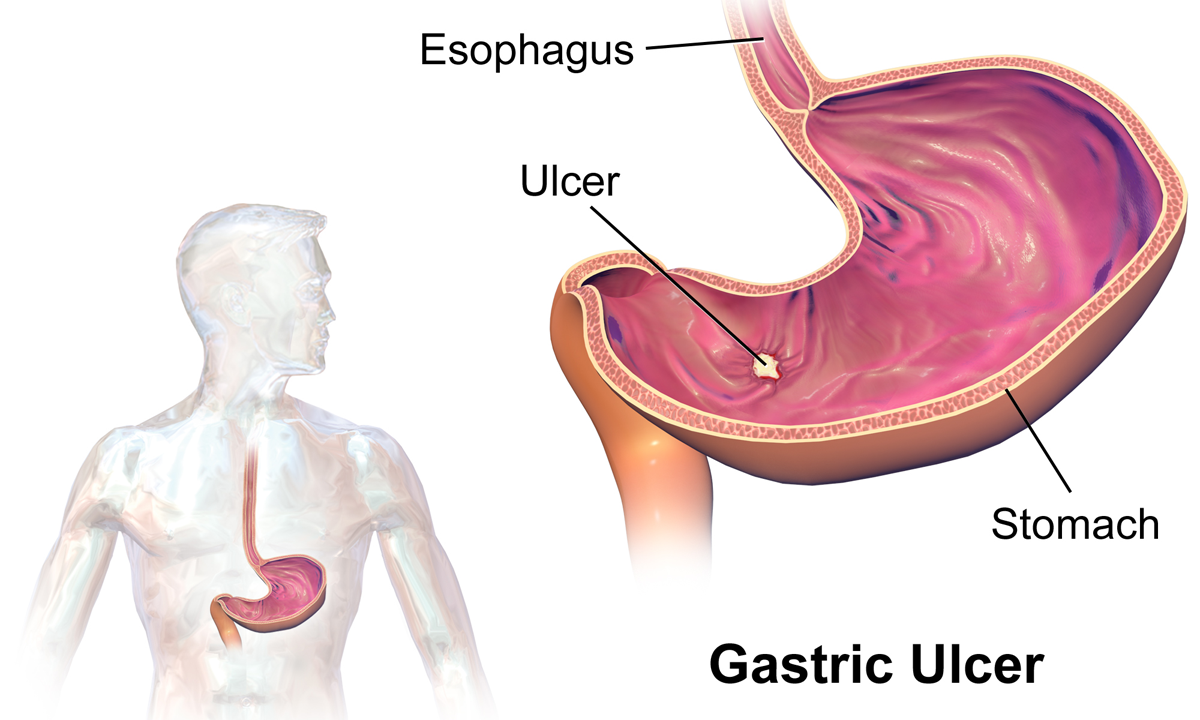
Peptic Ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or the entire abdomen may be tender. Complications may include shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Causes include perforation of the intestinal tract, pancreatitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, stomach ulcer, cirrhosis, or a ruptured appendix. Risk factors include ascites (the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen) and peritoneal dialysis. Diagnosis is generally based on examination, blood tests, and medical imaging. Treatment often includes antibiotics, intravenous fluids, pain medication, and surgery. Other measures may include a nasogastric tube or blood transfusion. Without treatment death may occur within a few days. About 20% of people with cirrhosis who are hospitalized have peritonitis. Signs and symptoms Abd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château De Saint-Cloud
The Château de Saint-Cloud was a château in France, built on a site overlooking the Seine at Saint-Cloud in Hauts-de-Seine, about west of Paris. On the site of the former palace is the state-owned Parc de Saint-Cloud. The château was expanded by Phillipe of France, Duke of Orléans in the 17th century, and by Marie Antoinette in the 1780s. After occupation by Napoleon I and Napoleon III, it was destroyed in 1870 during the Franco-Prussian War. History Hôtel d'Aulnay The Hôtel d'Aulnay on the site was expanded into a château in the 16th century by the Gondi banking family. The Gondis stemmed from a family of Florentine bankers established at Lyon in the first years of the 16th century, who had arrived at the court of France in 1543 in the train of Catherine de' Medici. In the 1570s, the Queen offered Jérôme de Gondi a dwelling at Saint-Cloud, the ''Hôtel d'Aulnay'', which became the nucleus of the château with a right-angled wing that looked out on a terrace. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Strong Mayor–Council , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Capitoline Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château D'If
The Château d'If () is a fortress located on the Île d'If, the smallest island in the Frioul archipelago, situated about offshore from Marseille in southeastern France. Built in the 16th century, it later served as a prison until the end of the 19th century. The fortress was demilitarized and open to the public in 1890. It is famous for being one of the settings of Alexandre Dumas's adventure novel ''The Count of Monte Cristo''. Island The Île d'If measures and is located west of the Old Port of Marseille. The entire island is heavily fortified; high ramparts with gun platforms surmount the cliffs, which rise steeply from the surrounding ocean. Apart from the fortress, the island is uninhabited. Fortress The "château" is a square, three-story building long on each side, flanked by three towers with large gun embrasures. It was built from 1524–31 on the orders of King Francis I, who, during a visit in 1516, saw the island as a strategically important location for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, northeast of Saint-Étienne. The City of Lyon proper had a population of 522,969 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , but together with its suburbs and exurbs the Lyon metropolitan area had a population of 2,280,845 that same year, the second most populated in France. Lyon and 58 suburban municipalities have formed since 2015 the Metropolis of Lyon, a directly elected metropolitan authority now in charge of most urban issues, with a population of 1,411,571 in 2019. Lyon is the prefecture of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region and seat of the Departmental Council of Rhône (whose jurisdiction, however, no longer extends over the Metropolis of Lyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of religious freedom. It was part of the wider Wars of the Three Kingdoms. The first (1642–1646) and second (1648–1649) wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third (1649–1651) saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The wars also involved the Scottish Covenanters and Irish Confederates. The war ended with Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651. Unlike other civil wars in England, which were mainly fought over who should rule, these conflicts were also concerned with how the three Kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland should be governed. The outcome was threefold: the trial of and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henrietta Maria Of France
Henrietta Maria (french: link=no, Henriette Marie; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland from her marriage to King Charles I on 13 June 1625 until Charles was executed on 30 January 1649. She was mother of his sons Charles II and James II and VII. Contemporaneously, by a decree of her husband, she was known in England as Queen Mary, but she did not like this name and signed her letters "Henriette R" or "Henriette Marie R" (the "R" standing for ''regina'', Latin for "queen".) Henrietta Maria's Roman Catholicism made her unpopular in England, and also prohibited her from being crowned in a Church of England service; therefore, she never had a coronation. She immersed herself in national affairs as civil war loomed, and in 1644, following the birth of her youngest daughter, Henrietta, during the height of the First English Civil War, was compelled to seek refuge in France. The execution of Charles I in 1649 left her impoverished. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

