|
Cherrydale, Virginia
Cherrydale is a neighborhood in northern Arlington, Virginia. It is centered on the intersection known as the Five Points consisting of Quincy Street, Military Road, and Old Dominion Road being bisected by Lee Highway (U.S. Route 29). Located in the community is Dorothy Hamm Middle School. One of the oldest nonresidential structures in the community is the Cherrydale Volunteer Fire House, built in 1919 to serve as the home of the Cherrydale Volunteer Fire Department. The department supplements the career staff who operate from the Arlington County Fire Department's Station 3, now located west of the Five Points intersection. History In 1893, a branch post office at Lee Highway and Pollard Street was named Cherrydale, with reference to Dorsey Donaldson's large cherry orchard in back of the present firehouse. Quincy Street was then known as Cherry Valley Road. Settlement in this area began after the Civil War and was stimulated in 1906 by the establishment of The Great Falls an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington County, Virginia
Arlington County is a County (United States), county in the Virginia, Commonwealth of Virginia. The county is situated in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from the Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, of which it was District of Columbia retrocession, once a part. The county is coextensive with the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau's census-designated place of Arlington. Arlington County is considered to be the second-largest "principal city" of the Washington metropolitan area, although Arlington County does not have the legal designation of Independent city (Virginia), independent city or incorporated town under Law of Virginia, Virginia state law. In 2020, the county's population was estimated at 238,643, making Arlington the List of cities and counties in Virginia, sixth-largest county in Virginia by population; if it were incorporated as a city, Arlington would be the third most populous city in the state. Wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond; Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's population was over 8.65million, with 36% of them living in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The area's history begins with several indigenous groups, including the Powhatan. In 1607, the London Company established the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English colony in the New World. Virginia's state nickname, the Old Dominion, is a reference to this status. Slave labor and land acquired from displaced native tribes fueled the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Highway
The Lee Highway was a national auto trail in the United States, connecting New York City and San Francisco, California, via the South and Southwest. After receiving a letter on January 15, 1919, from Dr. Samuel Myrtle Johnson of Roswell, New Mexico, David Carlisle Humphreys of Lexington, Virginia, put out a call for a meeting in Roanoke, Virginia, to form a new national highway association. On December 3, 1919, five hundred men from five states met in Roanoke to officially form the Lee Highway Association. The auto trail was named after Robert E. Lee. From the memoirs of Katherine Johnson Balcomb (April 3, 1894 — February 2, 1980), published in The Balcomb Family Tree Book: Routing The route of the Lee Highway is now roughly designated by the following routes: * US 1: New York to Washington, D.C. * US 29: Key Bridge from Washington to Rosslyn, Virginia *US 29: traversing Arlington County, Virginia, where it carries the name Langston Boulevard. In July 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington Public Schools
Arlington Public Schools is a public school division in Arlington County, Virginia. In 2019, student enrollment was 28,020 students, with students coming from more than 146 countries. In 2015, there were 2,166 teachers. There are 24 elementary schools, 6 middle schools, 4 high schools, 1 secondary institution and 4 other educational programs within the school district. ''Forbes'' magazine named the Washington, D.C. and Arlington area as the top place in the nation to educate one's child in 2007. In fiscal year 2019, close to $637.1 million was budgeted for the school district. History The first public schools in Arlington County, Virginia (then known as Alexandria County) were established in 1870: the Columbia and Walker schools, which were for whites only, and the Arlington School for Negroes in Freedman’s Village, which was located on land seized from Robert E. Lee's plantation. In 1932, Hoffman-Boston Junior High School, opened, allowing black students to pursue educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherrydale Volunteer Fire House
The Cherrydale Volunteer Fire House is home to the Cherrydale Volunteer Fire Department in the Cherrydale neighborhood of Arlington, Virginia. Constructed in 1919, it has been a focal point for community attention ever since. The building served as Arlington County Fire Station #3 until a new station opened nearby in July 2011. Early history The Cherrydale Volunteer Fire Department was organized in 1898 by a group of twelve men. It is the oldest volunteer fire department in Arlington County. Since its beginnings, the Cherrydale Volunteer Fire Department has remained active in the community, serving in many ways - from fighting fires and saving lives to sponsoring Christmas and Halloween parties, dances, parades, youth sports activities, and Bingo games. During the first few years after the CVFD was organized, the equipment (consisting of leather buckets, bells, and ladders) stayed out in the open. By 1906, a small shed (later referred to as "House #2") on what is now Taylor Stree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherrydale Sign
Cherrydale is a neighborhood in northern Arlington, Virginia. It is centered on the intersection known as the Five Points consisting of Quincy Street, Military Road, and Old Dominion Road being bisected by Lee Highway (U.S. Route 29). Located in the community is Dorothy Hamm Middle School. One of the oldest nonresidential structures in the community is the Cherrydale Volunteer Fire House, built in 1919 to serve as the home of the Cherrydale Volunteer Fire Department. The department supplements the career staff who operate from the Arlington County Fire Department's Station 3, now located west of the Five Points intersection. History In 1893, a branch post office at Lee Highway and Pollard Street was named Cherrydale, with reference to Dorsey Donaldson's large cherry orchard in back of the present firehouse. Quincy Street was then known as Cherry Valley Road. Settlement in this area began after the Civil War and was stimulated in 1906 by the establishment of The Great Falls and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Falls And Old Dominion Railroad
The Great Falls and Old Dominion Railroad (GF&OD) was an interurban trolley line that ran in Northern Virginia during the early 20th century. History Chartered in 1900 by a group of local landowners and acquired in 1902 by John Roll McLean (owner of ''The Washington Post'') and Senator Stephen Benton Elkins, the 15-mile electrified railroad began operating from Georgetown in Washington, D.C., in 1906. The first scheduled car reached Great Falls Park in Fairfax County, Virginia, on July 3 of that year. From Georgetown, the railroad crossed the Potomac River on a superstructure built on the upstream side of the old Aqueduct Bridge to Rosslyn in Arlington, where it made connections with an older electric trolley line, the Washington, Arlington & Falls Church Railway (see Northern Virginia trolleys). From Rosslyn, the railroad traveled northwest along the north side of Lee Highway (now part of U.S. Route 29) to Cherrydale and then on its own right-of-way (now Old Dominion D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Bridge (Potomac River)
The Chain Bridge is a viaduct which crosses the Potomac River at Little Falls in Washington, D.C. The steel girder bridge carries close to 22,000 cars a day. It connects Washington with affluent sections of Arlington and Fairfax counties in Virginia. On the Washington side, the bridge connects with Canal Road. Left turns onto the Clara Barton Parkway from the Chain Bridge are prohibited, but the reverse is permitted. On the Virginia side, the bridge connects with State Route 123 (Chain Bridge Road), which provides access to the George Washington Memorial Parkway. The Chain Bridge has three lanes (of which the center is reversible) and can be safely accessed by pedestrians and cyclists. The pedestrian sidewalk provides access to the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal towpath via a ramp. The bridge also carries water mains which provides Arlington County with water from the Washington Aqueduct. History The first bridge at the location was opened on July 3, 1797. It was a wooden c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Marcy Park
Fort Marcy was a Union fortification protecting Washington, D.C. during the American Civil War. Its remains are now administered by the National Park Service as part of the George Washington Memorial Parkway in Fairfax County, Virginia. History Fort Marcy is approximately south of the Potomac River on the south side of the Chain Bridge Road leading from Chain Bridge to Langley and McLean, Virginia. By car it can only be reached from the northbound lanes of the George Washington Parkway. The hill on which the fort is located was known as Prospect Hill. It is near the location where the famous but bloodless duel between Henry Clay and John Randolph was fought in 1826. The perimeter of the fort is . When completed, the fort mounted 18 guns, a 10-inch (25 cm) mortar and two 24-pound (10 kg) Coehorn mortars. The batteries were aimed toward the south and west. Originally the fort was called Fort Baldy Smith, after General William Farrar Smith, the troops of whose divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Ethan Allen (Arlington, Virginia)
Fort Ethan Allen was an earthwork fortification that the Union Army built in 1861 on the property of Gilbert Vanderwerken in Alexandria County (now Arlington County), Virginia, as part of the Civil War defenses of Washington (see Washington, D.C., in the American Civil War). The remains of the fort are now within Arlington County's Fort Ethan Allen Park. an''Accompanying two photos'' History The Union Army built Fort Ethan Allen in September 1861, shortly after the Army's rout at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July of that year. The fortification was a large bastion-style fort that was located in the County's highlands near the Potomac River. Before the Army constructed the fort, farmland and forests filled the area. To allow for clear lines of sight toward other fortifications and approaches to Washington, D.C., the Army removed trees and other vegetation that were near the site. Built like other northern Virginia defenses, the fort was constructed followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
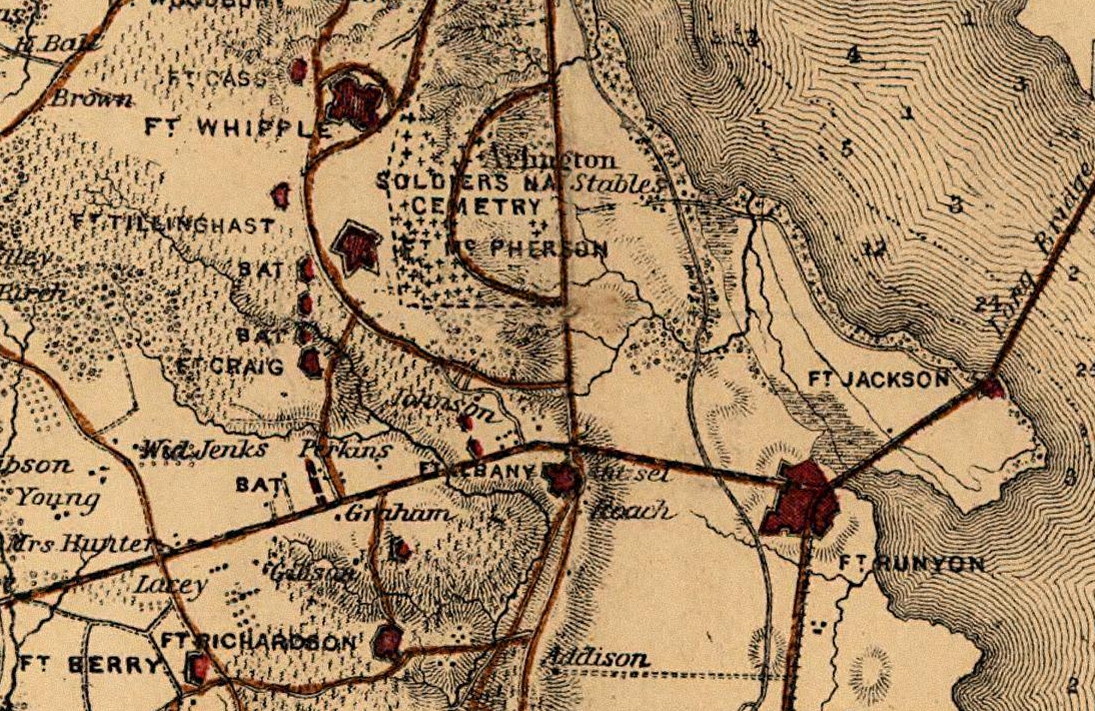
Arlington Line
The Arlington Line was a series of fortifications that the Union Army erected in Alexandria County (now Arlington County), Virginia, to protect the City of Washington during the American Civil War (see Civil War Defenses of Washington and Washington, D.C., in the American Civil War).(1) (2) (3) Just across the Potomac River from the Union capital city, Confederate Virginia was a major Union concern when the war began. In May 1861, federal troops seized much the County and immediately began constructing a group of forts near Washington on the Virginia side of the River to protect the capital city. After the Confederate Army routed the Union Army at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July 1861, the Union Army began construction on a line of breastworks and lunettes to the west of the earlier fortifications. These and larger fortifications later constructed nearby became known as the Arlington Line. They included a lunette (Fort Cass) and Fort Whipple, which beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



_(2).jpg)