|
Chemical Modification
Chemical modification refers to a number of various processes involving the alteration of the chemical constitution or structure of molecules. In chemistry Chemical modification describes the conversion of macromolecules through a chemical reaction or series of reactions. Chemically modified electrodes Chemically modified electrodes are electrodes that have their surfaces chemically converted to change the electrode's properties, such as its physical, chemical, electrochemical, optical, electrical, and transport characteristics. These electrodes are used for advanced purposes in research and investigation.Durst, R., Baumner, A., Murray, R., Buck, R., & Andrieux, C.,Chemically modified electrodes: Recommended terminology and definitions (PDF), IUPAC, 1997, pp 1317–1323. In biochemistry In biochemistry, chemical modification is the technique of anatomically reacting a protein or nucleic acid Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemically Modified Electrode
A chemically modified electrode is an electrical conductor that has its surface modified for different electrochemical functions. Chemically modified electrodes are made using advanced approaches to electrode systems by adding a thin film or layer of certain chemicals to change properties of the conductor according to its targeted function.Alkire, R., Kolb, D., & Lipkowski, J., Chemically modified electrodes, Germany: Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2009 At a modified electrode, an oxidation-reduction substance accomplishes electrocatalysis by transferring electrons from the electrode to a reactant, or a reaction substrate.Murray R. W.,Goodenough J. B. and Albery W. J., Modified Electrodes: Chemically Modified Electrodes for Electrocatalysis, The Royal Society, 1981, pp. 253-265, https://www.jstor.org/stable/36940 Modifying electrodes' surfaces has been one of the most active areas of research interest in electrochemistry since 1979, providing control over how electrodes interacts with their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodoacetamide
2-Iodoacetamide is an alkylating agent used for peptide mapping purposes. Its actions are similar to those of iodoacetate. It is commonly used to bind covalently with the thiol group of cysteine so the protein cannot form disulfide bonds. Also used in ubiquitin studies as an inhibitor of deubiquitinase enzymes (DUBs) because it alkylates the cysteine residues at the DUB active site. Peptidase inhibitor Iodoacetamide is an irreversible inhibitor of all cysteine peptidases, with the mechanism of inhibition occurring from alkylation of the catalytic cysteine residue (see schematic). In comparison with its acid derivative, iodoacetate, iodoacetamide reacts substantially faster. This observation appears contradictory to standard chemical reactivity, however the presence of a favourable interaction between the positive imidazolium ion of the catalytic histidine and the negatively charged carboxyl-group of the iodoacetate is the reason for the increased relative activity of iodoacetamide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Methanethiosulfonate
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
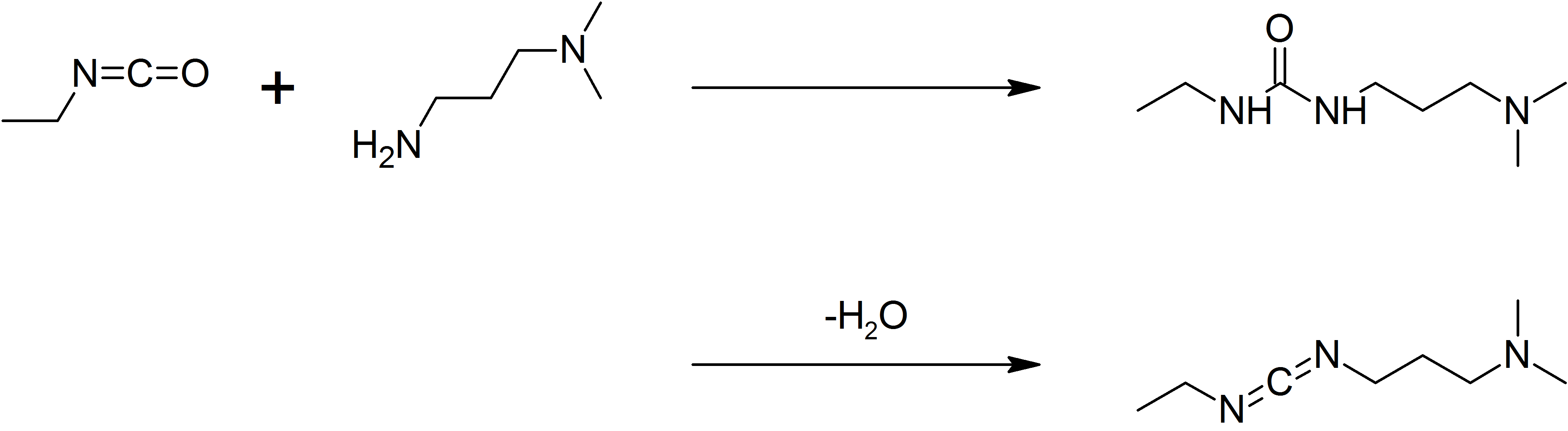
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, EDAC or EDCI) is a water-soluble carbodiimide usually handled as the hydrochloride. It is typically employed in the 4.0-6.0 pH range. It is generally used as a carboxyl activating agent for the coupling of primary amines to yield amide bonds. While other carbodiimides like dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC) are also employed for this purpose, EDC has the advantage that the urea byproduct formed (often challenging to remove in the case of DCC or DIC) can be washed away from the amide product using dilute acid. Additionally, EDC can also be used to activate phosphate groups in order to form phosphomonoesters and phosphodiesters. Common uses for this carbodiimide include peptide synthesis, protein crosslinking to nucleic acids, but also in the preparation of immunoconjugates. EDC is often used in combination with ''N''-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) for the immobilisation of large biomolecules. Recent wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEGylation
PEGylation (or pegylation) is the process of both covalent and non-covalent attachment or amalgamation of polyethylene glycol (PEG, in pharmacy called macrogol) polymer chains to molecules and macrostructures, such as a drug, therapeutic protein or vesicle, which is then described as PEGylated. PEGylation affects the resulting derivatives or aggregates interactions, which typically slows down their coalescence and degradation as well as elimination in vivo. PEGylation is routinely achieved by the incubation of a reactive derivative of PEG with the target molecule. The covalent attachment of PEG to a drug or therapeutic protein can "mask" the agent from the host's immune system (reducing immunogenicity and antigenicity), and increase its hydrodynamic size (size in solution), which prolongs its circulatory time by reducing renal clearance. PEGylation can also provide water solubility to hydrophobic drugs and proteins. Having proven its pharmacological advantages and acceptability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodoacetic Acid
Iodoacetic acid is a derivative of acetic acid. It is a toxic compound, because, like many alkyl halides, it is an alkylating agent. It reacts with cysteine residues in proteins. It is often used to modify SH-groups to prevent the re-formation of disulfide bonds after the reduction of cystine residues to cysteine during protein sequencing. Peptidase inhibitor Iodoacetate is an irreversible inhibitor of all cysteine peptidases, with the mechanism of inhibition occurring from alkylation of the catalytic cysteine residue (see schematic). In comparison with its amide derivative, iodoacetamide, iodoacetate reacts substantially slower. This observation appears contradictory to standard chemical reactivity, however the presence of a favourable interaction between the positive imidazolium ion of the catalytic histidine and the negatively charged carboxyl-group of the iodoacetic acid is the reason for the increased activity of iodoacetamide. Possible cancer therapy Several studies ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells and make up the genetic material. Nucleic acids are found in abundance in all living things, where they create, encode, and then store information of every living cell of every life-form on Earth. In turn, they function to transmit and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus to the interior operations of the cell and ultimately to the next generation of each living organism. The encoded informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Property
A physical property is any Property (philosophy), property that is Measurement, measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. Physical properties are often referred to as observables. They are not modal properties. A Quantity, quantifiable physical property is called physical quantity. Physical properties are often characterized as intensive and extensive properties. An intensive property does not depend on the size or extent of the system, nor on the amount of matter in the object, while an extensive property shows an additive relationship. These classifications are in general only valid in cases when smaller subdivisions of the sample do not interact in some physical or chemical process when combined. Properties may also be classified with respect to the directionality of their nature. For example, isotropy, isotropic properties do not change with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research.Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs, as well as organism structure and function. Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, which is the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |