|
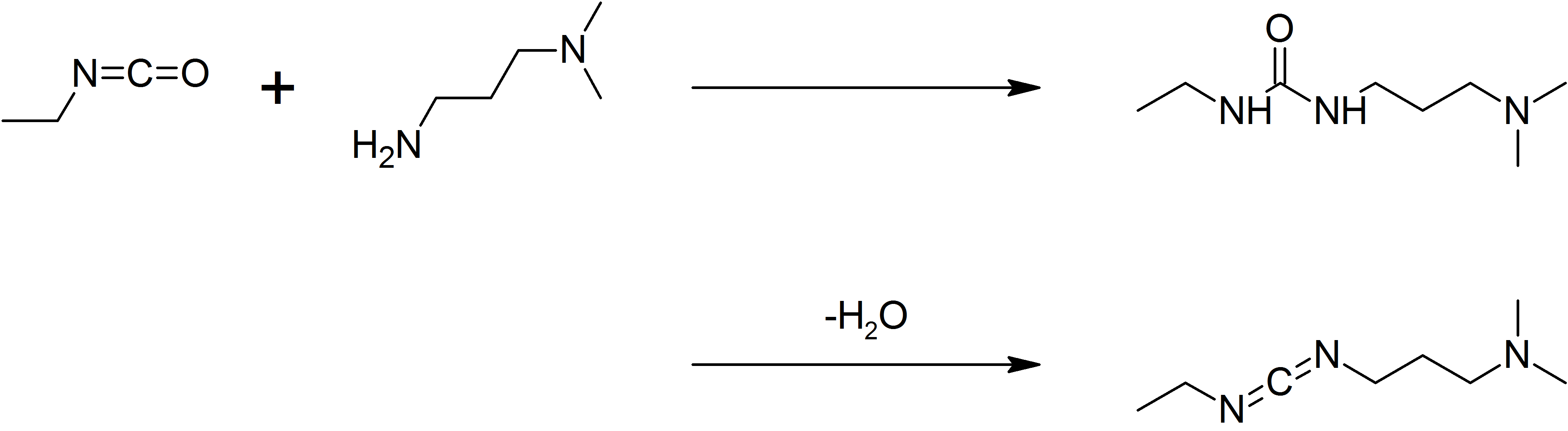
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, EDAC or EDCI) is a water-soluble carbodiimide usually handled as the hydrochloride. It is typically employed in the 4.0-6.0 pH range. It is generally used as a carboxyl activating agent for the coupling of primary amines to yield amide bonds. While other carbodiimides like dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC) are also employed for this purpose, EDC has the advantage that the urea byproduct formed (often challenging to remove in the case of DCC or DIC) can be washed away from the amide product using dilute acid. Additionally, EDC can also be used to activate phosphate groups in order to form phosphomonoesters and phosphodiesters. Common uses for this carbodiimide include peptide synthesis, protein crosslinking to nucleic acids, but also in the preparation of immunoconjugates. EDC is often used in combination with ''N''-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) for the immobilisation of large biomolecules. Recent wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbodiimide
In organic chemistry, a carbodiimide (systematic IUPAC name: methanediimine) is a functional group with the formula RN=C=NR. They are exclusively synthetic. A well known carbodiimide is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, which is used in peptide synthesis. Dialkylcarbodiimides are stable. Some diaryl derivatives tend to convert to dimers and polymers upon standing at room temperature, though this mostly occurs with low melting point carbodiimides that are liquids at room temperature. Solid diaryl carbodiimides are more stable, but can slowly undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water over time. Structure and bonding From the perspective of bonding, carbodiimides are isoelectronic with carbon dioxide. Three principal resonance structures describe carbodiimides: :RN=C=NR ↔ RN+≡C-N−R ↔ RN−-C≡N+R The N=C=N core is relatively linear and the C-N=C angles approach 120°. In the case of C(NCHPh2)2, the central N=C=N angle is 170° and the C-N=C angles are within 1° of 126°. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Synthesis
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Protecting group strategies are usually necessary to prevent undesirable side reactions with the various amino acid side chains. Chemical peptide synthesis most commonly starts at the carboxyl end of the peptide (C-terminus), and proceeds toward the amino-terminus (N-terminus). Protein biosynthesis (long peptides) in living organisms occurs in the opposite direction. The chemical synthesis of peptides can be carried out using classical solution-phase techniques, although these have been replaced in most research and development settings by solid-phase methods (see below). Solution-phase synthesis retains its usefulness in large-scale production of peptides for industrial purposes how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDC Mechanism
EDC or EdC may refer to: Education * East Devon College, in Tiverton, Devon, England * EDC Paris Business School, a French business school * Education Development Center, an American educational organization * Department for Education (South Australia)#Education Development Centre, conference centre run by the South Australian Department for Education Entertainment * ''EDC'', a 1994 album by the band Satchel * Electric Daisy Carnival, a music festival * Entertainment Distribution Company, a music distribution center * Étienne de Crécy (born 1969), a French DJ and producer * Eurovision Dance Contest Government and politics * Christian Democratic Team of the Spanish State (Spanish: '), a defunct political party in Spain * Democratic Left of Catalonia (Catalan: '), a defunct political party in Spain * Dubai Export Development Corporation * Expediency Discernment Council of the Government of Iran * Export Development Canada, Canada's export credit agency * European Defence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbodiimides
In organic chemistry, a carbodiimide (systematic IUPAC name: methanediimine) is a functional group with the formula RN=C=NR. They are exclusively synthetic. A well known carbodiimide is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, which is used in peptide synthesis. Dialkylcarbodiimides are stable. Some diaryl derivatives tend to convert to dimers and polymers upon standing at room temperature, though this mostly occurs with low melting point carbodiimides that are liquids at room temperature. Solid diaryl carbodiimides are more stable, but can slowly undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water over time. Structure and bonding From the perspective of bonding, carbodiimides are isoelectronic with carbon dioxide. Three principal resonance structures describe carbodiimides: :RN=C=NR ↔ RN+≡C-N−R ↔ RN−-C≡N+R The N=C=N core is relatively linear and the C-N=C angles approach 120°. In the case of C(NCHPh2)2, the central N=C=N angle is 170° and the C-N=C angles are within 1° of 126°. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
''N'',''N''′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC or DCCD) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (C6H11N)2C. It is a waxy white solid with a sweet odor. Its primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. The low melting point of this material allows it to be melted for easy handling. It is highly soluble in dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and dimethylformamide, but insoluble in water. Structure and spectroscopy The C−N=C=N−C core of carbodiimides (N=C=N) is linear, being related to the structure of allene. The molecule has idealized C2 symmetry. The N=C=N moiety gives characteristic IR spectroscopic signature at 2117 cm−1. The 15N NMR spectrum shows a characteristic shift of 275 ppm upfield of nitric acid and the 13C NMR spectrum features a peak at about 139 ppm downfield from TMS. Preparation DCC is produced by the decarboxylation of cyclohexyl isocyanate using phosphine oxides as a catalyst: :2 C6H11N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N,N'-Diisopropylcarbodiimide
''N'',''N′''-Diisopropylcarbodiimide is a carbodiimide used in peptide synthesis. As a liquid, it is easier to handle than the commonly used ''N'',''N′''-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, a waxy solid. In addition, ''N'',''N′''-diisopropylurea, its byproduct in many chemical reactions, is soluble in most organic solvents, a property that facilitates work-up In chemistry, work-up refers to the series of manipulations required to isolate and Chemical purity, purify the Product (chemistry), product(s) of a chemical reaction. Typically, these manipulations may include: * quenching a reaction to deactiva .... Further reading * * {{organic-compound-stub Peptide coupling reagents Carbodiimides Reagents for biochemistry Biochemistry Biochemistry methods Isopropyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Crosslinking
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. As with all science, there are overlaps, and the following delineations are a starting point to understanding the subtleties. Polymer chemistry Crosslinking is the general term for the proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells and make up the genetic material. Nucleic acids are found in abundance in all living things, where they create, encode, and then store information of every living cell of every life-form on Earth. In turn, they function to transmit and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus to the interior operations of the cell and ultimately to the next generation of each living organism. The encoded informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoconjugate
Immunoconjugates are antibodies conjugated (joined) to a second molecule, usually a toxin, radioisotope or label. These conjugates are used in immunotherapy and to develop monoclonal antibody therapy as a targeted form of chemotherapy when they are often known as antibody-drug conjugates. When the conjugates include a radioisotope see radioimmunotherapy. When the conjugates include a toxin A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849 ... see immunotoxin. References Further reading Technology Insight: cytotoxic drug immunoconjugates for cancer therapy. 2007looks useful from the abstract. Targeted Therapy of Cancer: New Prospects for Antibodies and Immunoconjugates. 2006full article, 18 pages. Arming antibodies: prospects and challenges for immunoconjugates. 200510 pages. Imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid. Uses Converting amine In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent su ...s into their hydrochlorides is a common way to improve their water solubility, which can be desirable for substances used in medications. The European Pharmacopoeia lists more than 200 hydrochlorides as active ingredients in medications. These hydrochlorides, compared to free bases, may more readily dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract and be absorbed into the bloodstream more quickly. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomolecules
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or development. Biomolecules include large macromolecules (or polyelectrolytes) such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites and natural products. A more general name for this class of material is biological materials. Biomolecules are an important element of living organisms, those biomolecules are often endogenous, produced within the organism but organisms usually need exogenous biomolecules, for example certain nutrients, to survive. Biology and its subfields of biochemistry and molecular biology study biomolecules and their reactions. Most biomolecules are organic compounds, and just four elements—oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen—make up 96% of the human body's mass. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |