|
Chemical-mechanical Polishing
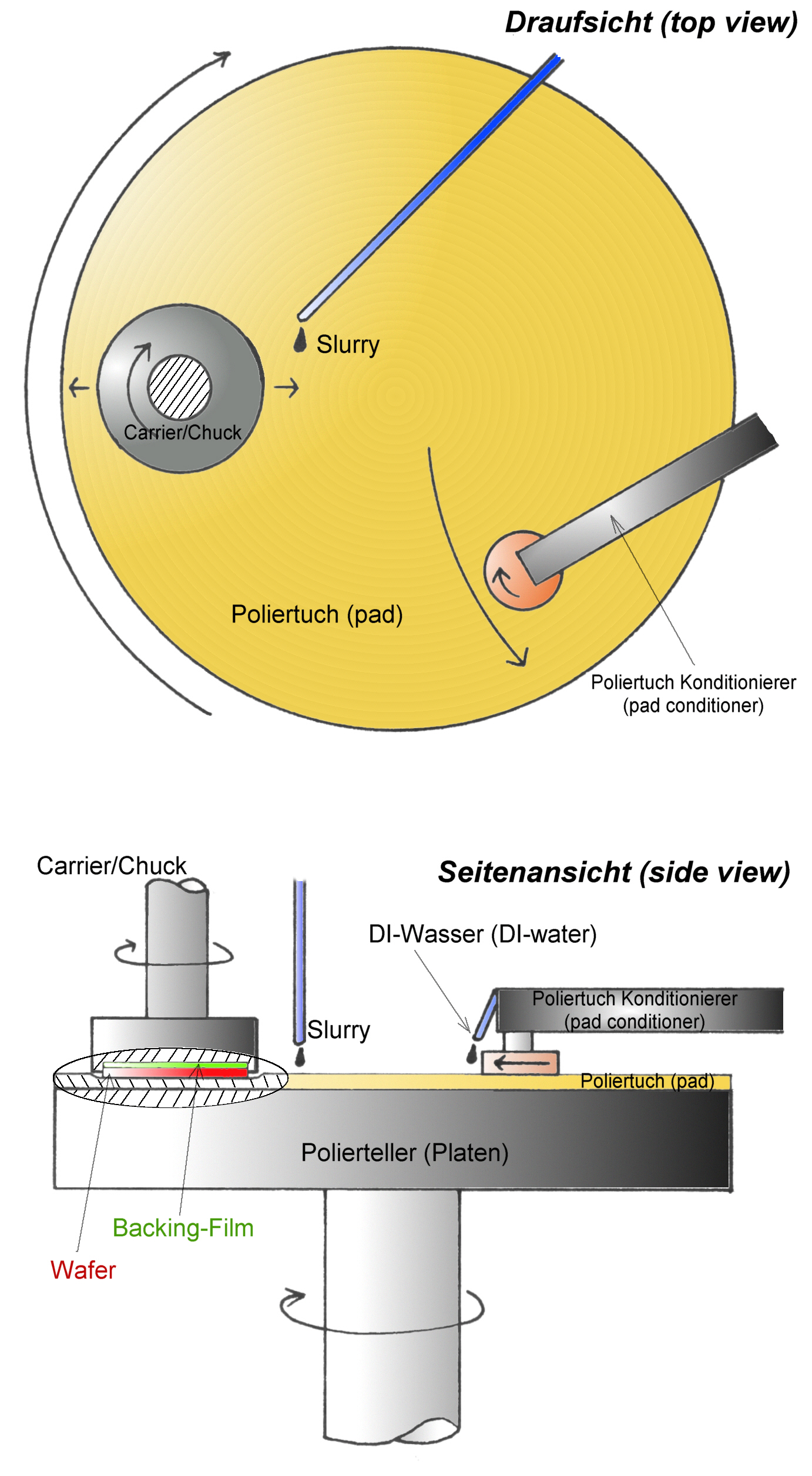
Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) or planarization is a process of smoothing surfaces with the combination of chemical and mechanical forces. It can be thought of as a hybrid of chemical etching and free abrasive polishing. Description The process uses an abrasive and corrosive chemical slurry (commonly a colloid) in conjunction with a polishing pad and retaining ring, typically of a greater diameter than the wafer. The pad and wafer are pressed together by a dynamic polishing head and held in place by a plastic retaining ring. The dynamic polishing head is rotated with different axes of rotation (i.e., not concentric). This removes material and tends to even out any irregular topography, making the wafer flat or planar. This may be necessary to set up the wafer for the formation of additional circuit elements. For example, CMP can bring the entire surface within the depth of field of a photolithography system, or selectively remove material based on its position. Typical depth- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid
Hybrid may refer to: Science * Hybrid (biology), an offspring resulting from cross-breeding ** Hybrid grape, grape varieties produced by cross-breeding two ''Vitis'' species ** Hybridity, the property of a hybrid plant which is a union of two different genetic parent strains * Hybrid (particle physics), a valence quark-antiquark pair and one or more gluons * Hybrid solar eclipse, a rare solar eclipse type Technology Transportation * Hybrid vehicle, a vehicle using more than one power source or an engine sourced from a different chassis ** Hybrid electric vehicle, a vehicle using both internal combustion and electric power sources *** Plug-in hybrid, whose battery can be recharged by a charging cable * Hybrid bicycle, a bicycle with features of road and mountain bikes * Hybrid train, a locomotive, railcar, or train that uses an onboard rechargeable energy storage system * Hybrid motorcycle, a motorcycle built using components from more than one original-manufacturer products, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer
A wafer is a crisp, often sweet, very thin, flat, light and dry biscuit, often used to decorate ice cream, and also used as a garnish on some sweet dishes. Wafers can also be made into cookies with cream flavoring sandwiched between them. They frequently have a waffle surface pattern but may also be patterned with insignia of the food's manufacturer or may be patternless. Some chocolate bars, such as Kit Kat and Coffee Crisp, are wafers with chocolate in and around them. Communion wafers A communion wafer is a type of unleavened bread consumed after transubstantiation as part of the Christian ritual of communion. Spa wafer Special "spa wafers" (Czech: ''lázeňské oplatky'', Slovak: ''kúpeľné oblátky'') are produced in the spa towns of the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic (e.g. Piešťany). The production of the wafers in Karlsbad and Marienbad was traditional to the towns' German-speaking population, who, after the ethnic cleansing of the area, brought the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etching (microfabrication)
Etching is used in microfabrication to chemically remove layers from the surface of a wafer during manufacturing. Etching is a critically important process module, and every wafer undergoes many etching steps before it is complete. For many etch steps, part of the wafer is protected from the etchant by a "masking" material which resists etching. In some cases, the masking material is a photoresist which has been patterned using photolithography. Other situations require a more durable mask, such as silicon nitride. Orientation-Dependent Etching * KOH pellets dissolved in water (self-heating) * Etch Rate > >> ** KOH has a slower etching orientation for the planes ** You cannot use this KOH photoresist as a etching mask, because the oxide attacks too slowly, so this resist will not survive * Photoresist can be used a etching mask, and the best photoresist for etching is nitride * For example, the etch rate of Si in KOH Depends on Crystallographic Plane * At low temperat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Nitride
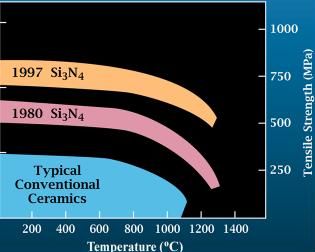
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term "silicon nitride" commonly refers to this specific composition. It is a white, high-melting-point solid that is relatively chemically inert, being attacked by dilute HF and hot . It is very hard (8.5 on the mohs scale). It has a high thermal stability with strong optical nonlinearities for all-optical applications. Production Silicon nitride is prepared by heating powdered silicon between 1300 °C and 1400 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere: :3 Si + 2 → The silicon sample weight increases progressively due to the chemical combination of silicon and nitrogen. Without an iron catalyst, the reaction is complete after several hours (~7), when no further weight increase due to nitrogen absorption (per gram of silicon) is detected. In addition to , several other silicon nitride phases (with chemica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shallow Trench Isolation
Shallow trench isolation (STI), also known as box isolation technique, is an integrated circuit feature which prevents electric current leakage between adjacent semiconductor device components. STI is generally used on CMOS process technology nodes of 250 nanometers and smaller. Older CMOS technologies and non-MOS technologies commonly use isolation based on LOCOS. STI is created early during the semiconductor device fabrication process, before transistors are formed. The key steps of the STI process involve etching a pattern of trenches in the silicon, depositing one or more dielectric materials (such as silicon dioxide) to fill the trenches, and removing the excess dielectric using a technique such as chemical-mechanical planarizationbr> Certain semiconductor fabrication technologies also include deep trench isolation, a related feature often found in analog integrated circuits. The effect of the trench edge has given rise to what has recently been termed the "reverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band or dislocation. Brittle fractures occur with no apparent deformation before fracture. Ductile fractures occur after visible deformation. Fracture strength, or breaking strength, is the stress when a specimen fails or fractures. The detailed understanding of how a fracture occurs and develops in materials is the object of fracture mechanics. Strength Fracture strength, also known as breaking strength, is the stress at which a specimen fails via fracture. This is usually determined for a given specimen by a tensile test, which charts the stress–strain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Interconnects
In semiconductor technology, copper interconnects are interconnects made of copper. They are used in silicon integrated circuits (ICs) to reduce propagation delays and power consumption. Since copper is a better conductor than aluminium, ICs using copper for their interconnects can have interconnects with narrower dimensions, and use less energy to pass electricity through them. Together, these effects lead to ICs with better performance. They were first introduced by IBM, with assistance from Motorola, in 1997. The transition from aluminium to copper required significant developments in fabrication techniques, including radically different methods for patterning the metal as well as the introduction of barrier metal layers to isolate the silicon from potentially damaging copper atoms. Patterning Although some form of volatile copper compound has been known to exist since 1947, with more discovered as the century progressed, none were in industrial use, so copper could not be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity towa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angstrom
The angstromEntry "angstrom" in the Oxford online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/angstrom.Entry "angstrom" in the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/angstrom. (, ; , ) or ångström is a metric unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth ( US) of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre,Entry "angstrom" in the Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1986). Retrieved on 2021-11-22 from https://www.oed.com/oed2/00008552. 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. Its symbol is Å, a letter of the Swedish alphabet. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–1874). The angstrom is often used in the natural sciences and technology to express sizes of atoms, molecules, microscopic biological structures, and lengths of chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms in crystals,Arturas Vailionis (2015):Geometry of Crystals L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrasive
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflective surface, the process can also involve roughening as in satin, matte or beaded finishes. In short, the ceramics which are used to cut, grind and polish other softer materials are known as abrasives. Abrasives are extremely commonplace and are used very extensively in a wide variety of industrial, domestic, and technological applications. This gives rise to a large variation in the physical and chemical composition of abrasives as well as the shape of the abrasive. Some common uses for abrasives include grinding, polishing, buffing, honing, cutting, drilling, sharpening, lapping, and sanding (see abrasive machining). (For simplicity, "mineral" in this article will be used loosely to refer to both minerals and mineral-like substa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)