|
Charles Orlando Bridgeman
Vice-Admiral the Hon. Charles Orlando Bridgeman (5 February 1791 – 13 April 1860) was a Royal Navy officer who saw active service in the Napoleonic Wars and the Greek War of Independence. Life Bridgeman was a younger son of Orlando Bridgeman, 1st Earl of Bradford, by his marriage to Lucy Elizabeth Byng, daughter of George Byng, 4th Viscount Torrington and Lady Lucy Boyle, a daughter of John Boyle, 5th Earl of Cork.''Burke's Peerage'', volume 1 (2003), p. 482 His siblings were: George Bridgeman, 2nd Earl of Bradford, Lady Lucy Whitmore, Hon. Orlando Henry Bridgeman, and Reverend Hon. Henry Edmund Bridgeman. He was educated at Harrow. On 18 June 1804, at the age of thirteen, he joined the navy as a first class volunteer on the almost-new HMS ''Repulse''.'Bridgeman, The Honourable Charles Orlando', in William Richard O'Byrne, ''A Naval Biographical Dictionary'' vol. I (1849)p. 123/ref> In 1805, Bridgeman was rated as a Midshipman, and during the Napoleonic Wars, he saw active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old English ' ("shallow"), Modern English ''shoal'', Low German ''schol'', West Frisian ''skol'', and Swedish (obsolete) ''skäll'' ("thin"). Course The headwaters of the Scheldt are in Gouy, in the Aisne department of northern France. It flows north through Cambrai and Valenciennes, and enters Belgium near Tournai. Ghent developed at the confluence of the Lys, one of its main tributaries, and the Scheldt, which then turns east. Near Antwerp, the largest city on its banks, the Scheldt flows west into the Netherlands toward the North Sea. Originally there were two branches from that point: the Oosterschelde (Eastern Scheldt); and the Westerschelde (Western Scheldt). In the 19th century, however, the Dutch built a dyke that cut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
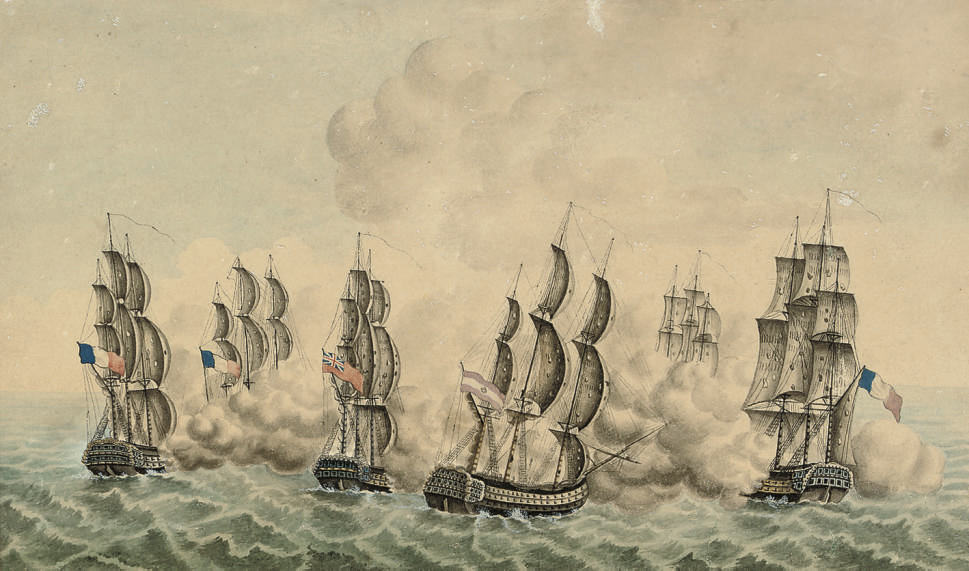
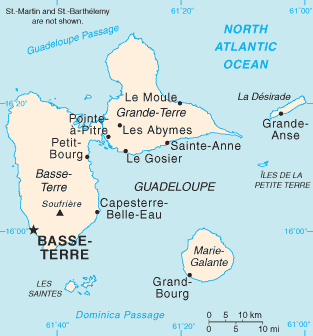
Invasion Of Guadeloupe (1815)
The Invasion of Guadeloupe (8–10 August 1815) was the last conflict between French and British forces during the Napoleonic Wars, and took place after Napoleon's defeat at Waterloo. Background Guadeloupe had been captured by the British twice before, most recently in 1810, but had been returned to the French following Napoleon's first abdication in April 1814. Louis XVIII had appointed Admiral Charles-Alexandre Léon Durand Linois as governor, with General Eugène Édouard Boyer de Peyreleau as his deputy. News of Napoleon's return from exile in Elba in February 1815 eventually reached the island in May, and divided it. Linois remained loyal to the King, while Boyer-Peyreleau led the Bonapartists. On 15 June the schooner ''Argile'' arrived from France with orders to rally Guadeloupe and Martinique to Bonaparte's cause. Boyer-Peyreleau attempted to persuade Linois to declare his support for Bonaparte, but he refused, so on 18 June Boyer-Peyreleau began arresting key officials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee-class Brig-sloop
The ''Cherokee'' class was a class of brig-sloops of the Royal Navy, mounting ten guns. Brig-sloops were sloops-of-war with two masts (a fore mast and a taller main mast) rather than the three masts of '' ship sloops''. Orders for 115 vessels were placed, including five which were cancelled and six for which the orders were replaced by ones for equivalent steam-powered paddle vessels. Many of these sailing vessels served as mail packet ships, and more than eight assisted with exploration and surveys. The best known of the class was , then considerably modified for ''Beagle''s second survey voyage under Robert FitzRoy, with the gentleman naturalist Charles Darwin on board as a self-funded supernumerary. Design The carronade, nicknamed the "smasher" or "devil gun", was significantly smaller and lighter than conventional cannon. It was also found to have a more destructive broadside at close range, so that a smaller (and cheaper) ship could be more effective in naval actions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Royal Sovereign (1804)
HMS ''Royal Sovereign'' was one of the royal yachts of King George III. She was the largest of his yachts and served from 1804 until she was broken up in 1849. Design and construction ''Royal Sovereign'' was one of two, the other being ''William and Mary'', ship-rigged royal yachts designed by Sir John Henslow. ''Royal Sovereign'' was ordered in 1800 to be built at Deptford by Edward Tippett. In March 1803 the master shipwright in charge of construction changed from Tippett to Henry Peake. She was laid down in November 1801 and launched on 12 May 1804 with the following dimensions: along the gun deck, at the keel, with a beam of and a depth in the hold of . She measured 278 tons burthen. She was armed with eight small swivel guns. She was the largest yacht owned by King George III and was known to sail very well at sea. Service From 31 August 1812 to 2 April 1814, she was under the command of William Hotham. On 25 June 1814 a naval review was held at Spithead t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Yacht
A royal yacht is a ship used by a monarch or a royal family. If the monarch is an emperor the proper term is imperial yacht. Most of them are financed by the government of the country of which the monarch is head. The royal yacht is most often crewed by personnel from the navy and used by the monarch and his/her family on both private and official travels. Types of vessels used Some royal yachts have been/are small vessels only used for short trips on rivers or in calm waters, but others have been/are large seaworthy ships. History Depending on how the term is defined royal yachts date back to the days of antiquity with royal barges on the Nile in ancient Egypt. Later the Vikings produced royal vessels. They followed the pattern of longships although highly decorated and fitted with purple sails (purple sails remained standard for royal vessels the next 400 years). In England, Henry V sold off the royal yachts to clear the Crown's debts. The next royal vessels in England were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Bellerophon (1786)
HMS ''Bellerophon'', known to sailors as the "Billy Ruffian", was a ship of the line of the Royal Navy. A third-rate of 74 guns, she was launched in 1786. ''Bellerophon'' served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, mostly on blockades or convoy escort duties. She fought in three fleet actions: the Glorious First of June (1794), the Battle of the Nile (1798) and the Battle of Trafalgar (1805). While the ship was on blockade duty in 1815, Napoleon boarded ''Bellerophon'' so he could surrender to the ship's captain, ending 22 years of almost continuous war between Britain and France. Built at Frindsbury, near Rochester in Kent, ''Bellerophon'' was initially laid up in ordinary, briefly being commissioned during the Spanish and Russian Armaments. She entered service with the Channel Fleet on the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1792, and took part in the Glorious First of June in 1794, the first major fleet action of the wars. ''Bellerophon'' n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Kaye Legge
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more widely believed, is that the name is derived from the Roman clan '' Artorius'' who lived in Roman Britain for centuries. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest datable attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text ''Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th to 6th-century Briton general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Revenge (1805)
HMS ''Revenge'' was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 13 April 1805. Sir John Henslow designed her as one of the large class 74s; she was the only ship built to her draught. As a large 74, she carried 24-pounder guns on her upper gun deck, rather than the 18-pounder guns found on the middling and common class 74s. Career Newly commissioned, and captained by Robert Moorsom, she fought at the Battle of Trafalgar, where she sailed in Collingwood's column. ''Revenge'' was engaged at the Battle of Basque Roads in April 1809 under Captain Alexander Robert Kerr. In October 1810, ''Revenge'' captured the French privateer cutter ''Vauteur'' off Cherbourg after a five-hour chase. ''Vauteur'' had been armed with 16 guns, but she threw 14 of them overboard during the chase. She had been out of Dieppe for 45 hours but had made no captures. She was the former British cutter ''John Bull'', of Plymouth, and was restored to Plymouth on 19 October. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo-class Frigate
The ''Apollo''-class sailing frigates were a series of twenty-seven ships that the British Admiralty commissioned be built to a 1798 design by Sir William Rule. Twenty-five served in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars, two being launched too late. Of the 25 ships that served during the Napoleonic Wars, only one was lost to enemy action. Of the entire class of 27 ships, only two were lost to wrecking, and none to foundering. The Admiralty ordered three frigates in 1798–1800. Following the Peace of Amiens, it ordered a further twenty-four sister-ships to the same design between 1803 and 1812. The last was ordered to a fresh 38-gun design. Initially, the Admiralty split the order for the 24 vessels equally between its yards and commercial yards, but two commercial yards failed to perform and the Admiralty transferred these orders to its own dockyards, making the split 14–10 as between the Admiralty and commercial yards. Ships in class * ** Builder: John Dudman, Deptfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


_2017-08-16.jpg)

