|
Charles Levert
Charles-Alphonse Levert (11 June 1825 – 6 April 1899) was a French public servant and politician. During the Second French Empire he was a prefect of various departments. During the French Third Republic he served as deputy for Pas-de-Calais between 1872 and 1889. He held right-wing Bonapartist views and consistently voted against the republican governments. Early years Charles-Alphonse Levert was born on 11 June 1825 in Sens, Yonne. His parents were Antoine Levert (1793–1865) and Caroline Colombe Tarbé (1800–1847). He studied at the Collège Sainte-Barbe in Paris. In the French Revolution of 1848 he declared for the republicans. He joined the administration as secretary of Émile Ollivier, Commissioner General of the Provisional Government in Bouches-du-Rhône. He was adviser to the prefecture of Arras in 1850–51. He joined the cause of Prince Louis-Napoleon Bonaparte. Second Empire After the coup d'état of 2 December 1951 Levert was named sub-prefect of Saint-Om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sens
Sens () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yonne Departments of France, department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France, 120 km from Paris. Sens is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture and the second city of the department, the sixth in the region. It is crossed by the Yonne (river), Yonne and the Vanne (river), Vanne, which empties into the Yonne here. History The city is said to have been one of the oppidum, oppida of the Senones, one of the oldest Celtic tribes living in Gaul. It is mentioned as Agedincum by Julius Caesar several times in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The Roman city was built during the first century BC and surrounded by walls during the third (notable parts of the walls still remain, with alterations along the centuries). It still retains today the skeleton of its Roman street plan. The site was referred to by Ammianus Marcellinus as ''Senones'' (''oppidum Senonas''), where the future emperor Julian (emperor), Julian f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal Pierre Duprat
Pascal Pierre Duprat (1815–1885) was a French journalist and politician with Republicanism in France, republican beliefs. He was elected as a deputy to the Constituent and Legislative Assemblies during the Second Republic (France), second Republic. He was an opponent of Louis-Napoleon Bonaparte.Biographical note contained in the ''Collected Works of Karl Marx and Frederick Engels: Volume 10'' (International Publishers: New York, 1978) p. 718. Books * Essai historique sur les races anciennes et modernes de l’Afrique septentrionale : leurs origines, leurs mouvements et leurs transformations, depuis l’antiquité la plus reculée jusqu’à nos jours, Paris, Jules Labitte, 1840, 308 p., in-8° * Timon et sa logique : avec une préface, Paris, Labitte, 1845, 72 p., in-32 * Une guerre insensée : expédition contre les Kabyles ou Berbers de l’Algérie (Extrait de la Revue indépendante du 25 mars 1845), Paris, Schneider et Langrand, 1845, 15 p., in-8 * Victoire du peuple sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri-Alexandre Wallon
Henri-Alexandre Wallon (23 December 1812 – 13 November 1904) was a French historian and statesman whose decisive contribution to the creation of the Third Republic led him to be called the "Father of the Republic". He was the grandfather of psychologist and politician Henri Wallon. Early life Wallon was born at Valenciennes, Nord on 23 December 1812. Career Devoting himself to a literary career, in 1840 he became professor at the École Normale Supérieure under the patronage of Guizot, whom he succeeded as professor at the Faculté des Lettres in 1846. His works on slavery in the French colonies (1847) and on slavery in antiquity (1848; new edition in 3 vols., 1879) led to his being placed, after the Revolution of 1848, on a commission for the regulation of labour in the French colonial possessions, and in November 1849 he was elected to the Legislative Assembly by the department of the Nord. He resigned in 1850, disapproving of the measure for the restriction of the suffra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert, 4th Duc De Broglie
Jacques-Victor-Albert, 4th duc de Broglie (; 13 June 182119 January 1901) was a French monarchist politician, diplomat and writer (of historical works and translations). Broglie twice served as Prime Minister of France, first from May 1873 to May 1874, and again from May to November 1877. Biography Albert de Broglie was born in Paris, France, the eldest son of Victor, 3rd duc de Broglie, a liberal statesman of the July Monarchy, and Albertine, baroness Staël von Holstein, the fourth child of Madame de Staël. He was therefore the great-grandson of Jacques Necker. After a brief diplomatic career at Madrid and Rome, upon the revolution of 1848 Albert de Broglie withdrew from public life and devoted himself to literature. He had already published a translation of the religious system of Leibniz (1846). He now at once made his mark by his contributions to the '' Revue des deux mondes'' and the Orleanist and clerical organ '. These, and other contributions, brought him the succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolphe Thiers
Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers ( , ; 15 April 17973 September 1877) was a French statesman and historian. He was the second elected President of France and first President of the French Third Republic. Thiers was a key figure in the July Revolution of 1830, which overthrew King Charles X in favor of the more liberal King Louis Philippe, and the French Revolution of 1848, which overthrew the House of Orléans, Orléans monarchy and established the Second French Republic. He served as a prime minister in 1836 and 1840, dedicated the Arc de Triomphe, and arranged the return to France of the remains of Napoleon from Saint-Helena. He was first a supporter, then a vocal opponent of Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte (who served from 1848 to 1852 as President of the Second Republic and then reigned as Emperor Napoleon III from 1852 to 1871). When Napoleon III seized power, Thiers was arrested and briefly expelled from France. He then returned and became an opponent of the government. Followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appel Au Peuple
The Appel au peuple (Plebiscite) was a Bonapartist parliamentary group during the early years of the French Third Republic. They advocated a plebiscite by which the people would choose the form of government, which they assumed would be a revival of the Second French Empire. They were a significant force in the 1870s and 1880s They were associated with Boulangism and the right-wing Ligue des Patriotes. There was a brief revival of the Appel au peuple in the 1900s. Although the members supported universal suffrage, believed in advancement based on merit rather than birth, and had diverse views on other subjects, they were generally conservative. Many of them believed in the virtues of family, religion, free trade and private property. Foundation "''Appel au Peuple''" was the slogan of the Bonapartist party. The Nantes shipowner Alphonse-Alfred Haentjens founded the Appel au Peuple parliamentary group late in 1871 to restore the Second Empire's ideals of democratic imperialism a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Faidherbe
Louis Léon César Faidherbe (; 3 June 1818 – 29 September 1889) was a French general and colonial administrator. He created the Senegalese Tirailleurs when he was governor of Senegal. Early life Faidherbe was born into a lower-middle-class family in Lille. He was the fifth child of Louis César Joseph Faidherde, a hosier, and his wife, Sophie Monnier. His father died in 1826 when he was seven and he was brought up by his mother. He received his military education at the École Polytechnique and then at the École d'Application in Metz. From 1843 to 1847 he served in Algeria, then for one year in Guadeloupe, and again from 1849 to 1852 in Algeria. West Africa In 1852 he was transferred to Senegal as sub-director of engineers, and in 1854 was promoted ''chef de bataillon'' and appointed governor of the colony on December 16. He held this post with one brief interval (1861–1863) until July 1865. The work he accomplished in French West Africa constitutes his most endurin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
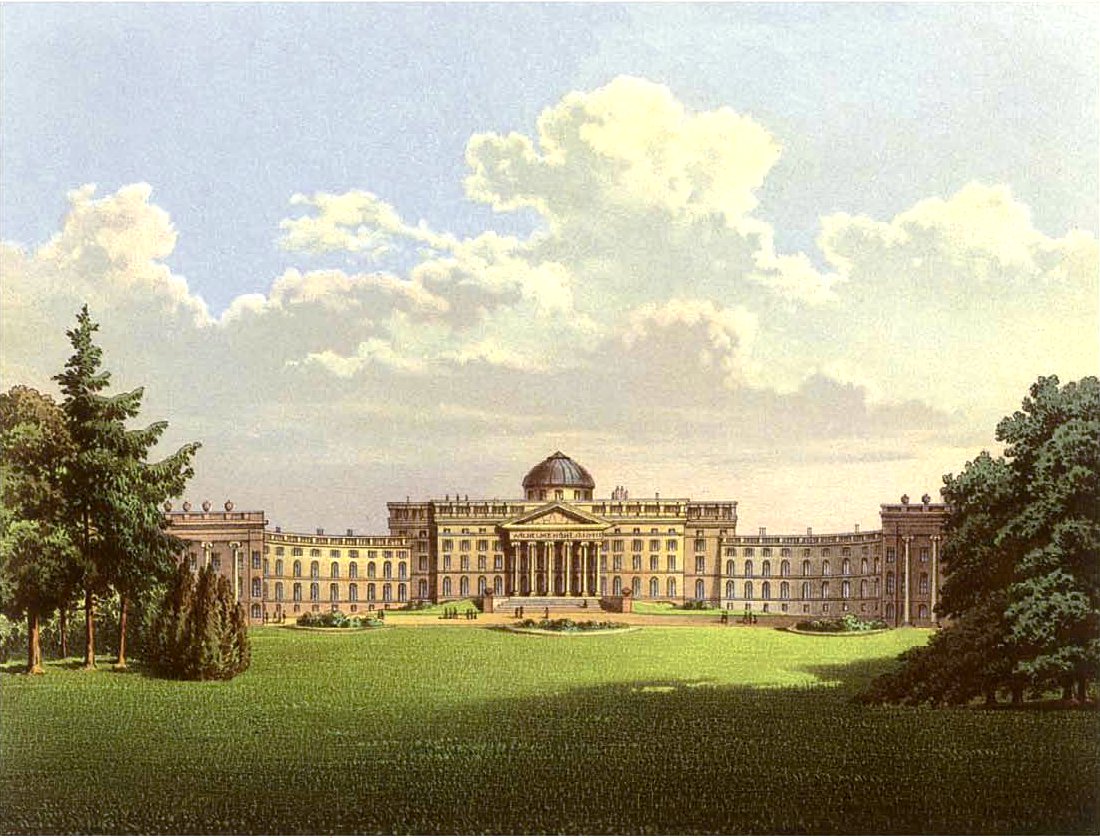
Schloss Wilhelmshöhe
Schloss Wilhelmshöhe is a Neoclassical palace located in , a part of Kassel, Germany. It was built for Landgrave Wilhelm (William) IX of Hesse in the late 18th century. Emperor Wilhelm II made extensive use of it as a summer residence and personal retreat. Today, the palace houses the art gallery Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, part of ''Museumslandschaft Hessen Kassel''. Since 2013, ''Schloss Wilhelmshöhe'' has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site ''Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe'' because of its contribution to Baroque architecture and the outstanding water features that surround the palace. History Beginning in the 12th century the site was used as a monastery. Under Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse 1504-1567 it was secularised and used as a castle. This castle was replaced by a new one from 1606 to 1610 by Landgrave Moritz. The current Neoclassical ''Schloss Wilhelmshöhe'' was designed by architects Simon Louis du Ry and from 1786 to 1798 for Landgrave William IX of Hesse. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern France, it is located on the coast of the Gulf of Lion, part of the Mediterranean Sea, near the mouth of the Rhône river. Its inhabitants are called ''Marseillais''. Marseille is the second most populous city in France, with 870,731 inhabitants in 2019 (Jan. census) over a municipal territory of . Together with its suburbs and exurbs, the Marseille metropolitan area, which extends over , had a population of 1,873,270 at the Jan. 2019 census, the third most populated in France after those of Paris and Lyon. The cities of Marseille, Aix-en-Provence, and 90 suburban municipalities have formed since 2016 the Aix-Marseille-Provence Metropolis, an Indirect election, indirectly elected Métropole, metropolitan authority now in charge of wider metropo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne De Maupas
Charlemagne Émile de Maupas (8 December 1818 – 19 June 1888) was a French lawyer and politician who was head of the Parisian Police during the critical period when Napoleon III seized power in the coup of 2 December 1851. Early years Charlemagne Émile de Maupas was born in Bar-sur-Aube, Aube, on 8 December 1818. He studied law in Paris. He entered the prefectural career as a sub-prefect of Uzès in 1845, then of Beaune in 1847. He returned to private life after the February Revolution of 1848. He attached himself to the Bonapartist party, and soon gained the confidence of Louis Napoleon Bonaparte. De Maupas was named in succession sub-prefect of Boulogne-sur-Mer (1849), prefect of Allier (1849) and prefect of Haute-Garonne (1850). He was noted for his zeal and lack of scruples. When prefect of Haute-Garonne he wanted to arrest enemies of the regime. The magistrate protested that there was no evidence. He replied that evidence would be created. December 1851 coup On 27 Octobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)