|
Champin (communal Section)
Champin is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located on the Nancowry Island, around 10 km from the Tapong village, and comes under the administration of the Nancowry tehsil. History During the British Raj, the British Indian government bestowed the title of "Rani" ("Queen") on a local woman named Islon, for the services rendered by her to the government. Even after India became independent in 1947, Islon and her only daughter Lachmi were treated as queens by the local villagers, although the government did not recognize them as such. After Lachmi's death in 1989, her only daughter Fathima became the village leader. She had eight children, including five daughters and three sons; her family of 42 lived in three buildings, locally known as Rani Ghat ("Queen's Palace"). After the village was devastated by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, 72-year old Fathima and her family were evacuated by the Indian authorities to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancowry Island
Nancowry (Nancowry language: ''Mūöt'', Hindi: नन्कोव्री ''Nankovrī'') is an island in the central part of the Nicobar Islands chain, located in the northeast Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. History In 1755, the government of Denmark formally claimed sovereignty over Nicobars, under the name of ''Frederiksøerne'' ("Frederik Islands") and encouraged a mission established by the Moravian Brethren of Herrnhut. The Danes established a short-lived colony on the island which they named ''Ny Sjælland'' ("New Zealand"). Along with Kamorta Island, which lies just to the north, Nancowry Island forms the "magnificent land-locked" Nancowry Harbour, used by European sailors since at least the 17th century and described as "one of the safest natural harbours in the world". The harbour was apparently used as a base for piracy; in 1868, the British Navy entered the harbour in some force, destroying suspected pirate ships. 2004 tsunami The island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Caste
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes. In modern literature, the ''Scheduled Castes'' are sometimes referred to as Dalit, meaning "broken" or "dispersed", having been popularised by B. R. Ambedkar (1891–1956), a Dalit himself, an economist, reformer, chairman of the Constituent Assembly of India, and Dalit leader during the independence struggle. Ambedkar preferred the term Dalit to Gandhi's term, Harijan, meaning "person of Hari/Vishnu" (or Man of God). In September 2018, the government "issued an advisory to all private satellite channels asking them to 'refrain' from using the nomenclature 'Dalit'", though "rights groups and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Census Of India
The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information for National Population Register (NPR) was also collected in the first phase, which will be used to issue a 12-digit unique identification number to all registered Indian residents by Unique Identification Authority of India. The second population enumeration phase was conducted between 9 and 28 February 2011. Census has been conducted in India since 1872 and 2011 marks the first time biometric information was collected. According to the provisional reports released on 31 March 2011, the Indian population increased to 1.21 billion with a decadal growth of 17.70%. Adult literacy rate increased to 74.04% with a decadal growth of 9.21%. The motto of the census was 'Our Census, Our future'. Spread across 28 states and 8 union territories, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Census Of India
The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information for National Population Register (NPR) was also collected in the first phase, which will be used to issue a 12-digit unique identification number to all registered Indian residents by Unique Identification Authority of India. The second population enumeration phase was conducted between 9 and 28 February 2011. Census has been conducted in India since 1872 and 2011 marks the first time biometric information was collected. According to the provisional reports released on 31 March 2011, the Indian population increased to 1.21 billion with a decadal growth of 17.70%. Adult literacy rate increased to 74.04% with a decadal growth of 9.21%. The motto of the census was 'Our Census, Our future'. Spread across 28 states and 8 union territories, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katchal Island
Katchal (Hindi: कत्चल, Nicobarese: तिहन्यु, ''Tihnyu'') is one of the Nicobar Islands, India. History Katchal Island was previously known as Tihanyu. Due to the remote location and lack of exposure with the rest of the world, outsiders economically exploited the innocent islanders for a long time. To stop their economic exploitation, the Government of India declared the Nicobar Islands an Aboriginal Tribal Reserve Area (ATRA) on 2 April 1957. This made the Nicobar Islands inaccessible to outsiders and currently even Indian nationals need a special tribal pass to visit the islands. Only Government Servants (outsiders) posted to Katchal Islands are allowed to stay in the island. Nicobar Islands have experienced all kinds of external influences for centuries, because they are located along an ancient international sea trade route and have been known to voyagers and scholars since ancient times. Due to this, the islands have been receiving external influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Blair
Port Blair () is the capital city of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a union territory of India in the Bay of Bengal. It is also the local administrative sub-division (''tehsil'') of the islands, the headquarters for the district of South Andaman and is the territory's only notified town. Port Blair serves as the entry point for visiting the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Port Blair is connected with mainland India by both air and sea. It is a two to three-hour flight from mainland India to Port Blair's Veer Savarkar International Airport, and three to four days by sea to reach Kolkata, Chennai, or Visakhapatnam from Haddo Wharf in Port Blair. It is home to several museums and a major naval base INS Jarawa of the Indian Navy, along with sea and air bases of the Indian Coast Guard, Andaman and Nicobar Police, Andaman and Nicobar Command, the first integrated tri-command of the Indian Armed Forces and the Indian Air Force. Port Blair is also famous for the historic Cellular Jail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
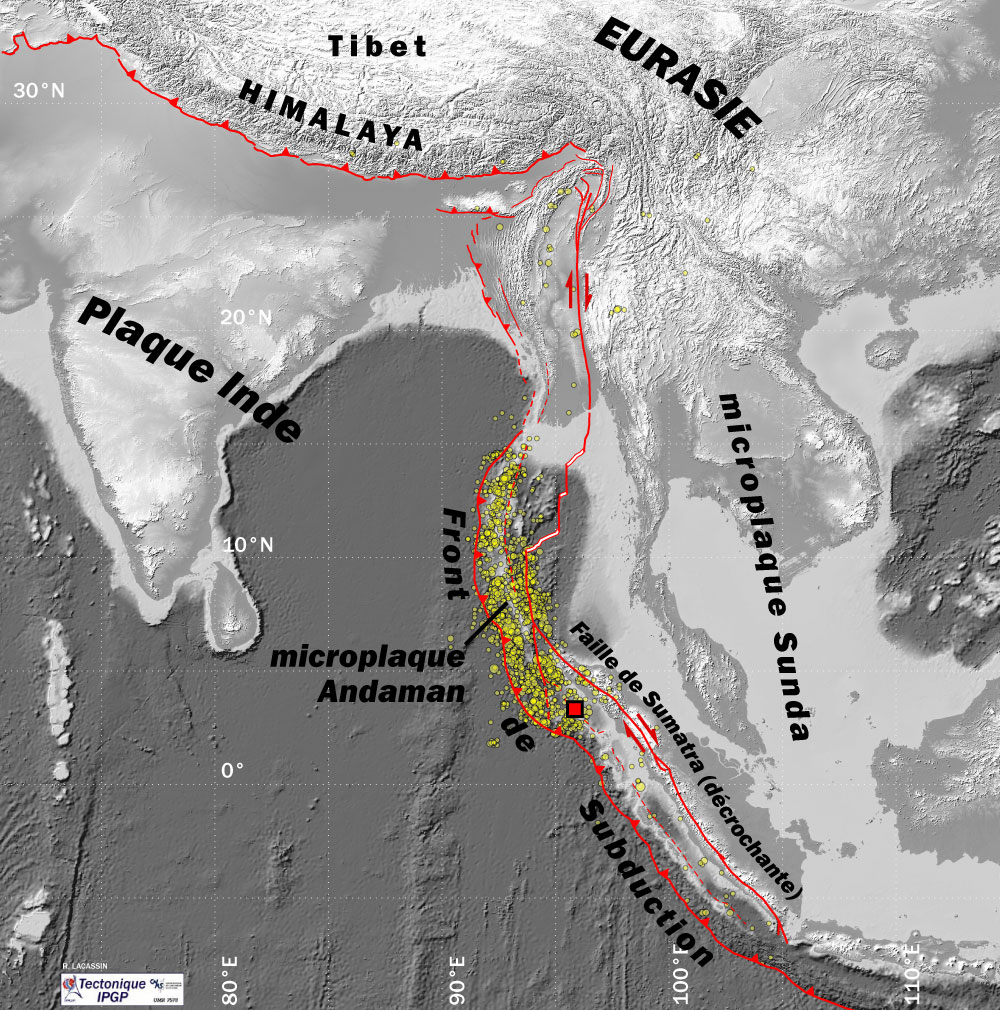
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake And Tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, including Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administrative centre, with possible additional towns, and usually a number of villages. The terms in India have replaced earlier terms, such as '' pargana'' (''pergunnah'') and ''thana''. In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, a newer unit called mandal (circle) has come to replace the system of tehsils. It is generally smaller than a tehsil, and is meant for facilitating local self-government in the panchayat system. In West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, community development blocks are the empowered grassroots administrative unit, replacing tehsils. As an entity of local government, the tehsil office (panchayat samiti) exercises certain fiscal and administrative power over the villages and municipalities within its jurisdiction. It is the ultimate execu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapong
Tapong is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located on the Nancowry Island, around 10 km from the Champin village, and comes under the administration of the Nancowry tehsil. Demographics A census taken by a research team after the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami recorded a population of 296 in Tapong: the tsunami did not cause any deaths in the village. The 2011 census of India The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information ... recorded the population of Tapong (including Kabila settlement) as 270, and the number of households as 62. The effective literacy rate (i.e. the literacy rate of population excluding children aged 6 and below) was 83.41%. References {{coord missing, Andaman and Nicobar Islands Villages in Nancowry teh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census Of India
The decennial Census of India has been conducted 16 times, as of 2021. While it has been undertaken every 10 years, beginning in 1872 under British Viceroy Lord Mayo, the first complete census was taken in 1881. Post 1949, it has been conducted by the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. All the censuses since 1951 were conducted under the 1948 Census of India Act. The last census was held in 2011, whilst the next was to be held in 2021. But it has been postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Historically, there has been a long time between collection of data and dissemination of data. Census of India during British Rule List of censuses conducted in India before independence: * 1872 Census of india *1881 Census of India *1891 Census of India * 1901 Census of India *1911 Census of India * 1921 Census of India * 1931 Census of India *1941 Census of India Census of Republic of India List of censuses conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |