|
Chameria
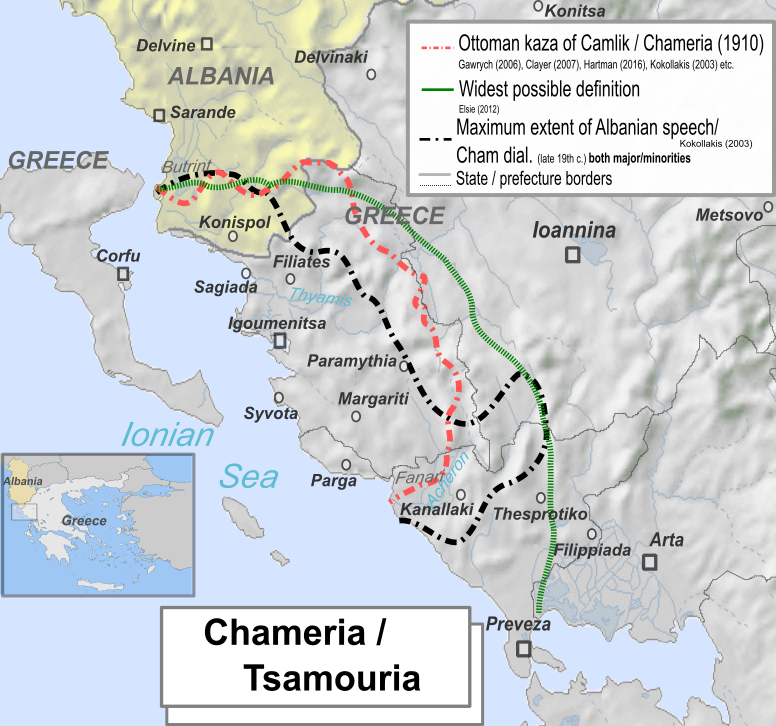
Chameria ( sq, Çamëria; el, Τσαμουριά, ''Tsamouriá''; tr, Çamlık) is a term used today mostly by Albanians to refer to parts of the coastal region of Epirus in southern Albania and Greece, traditionally associated with the Albanian ethnic subgroup of the Chams.Elsie, Robert and Bejtullah D. Destani (2012). ''The Cham Albanians of Greece: A Documentary History''. IB Tauris. . p. XXIX. "Chameria is a mountainous region of the southwestern Balkan Peninsula that now straddles the Greek-Albanian border. Most of Chameria is in the Greek Province of Epirus, corresponding largely to the prefectures of Thesprotia and Preveza, but it also includes the southernmost part of Albania, the area around Konispol. It is approximately 10,000 square kilometres in size and has a current, mostly Greek-speaking population of about 150,000. As an historical region, Chameria, also spelled Chamuria, Chamouria or Tsiamouria, is sometimes confused with Epirus which is in fact a much larger a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cham Albanians
Cham Albanians or Chams ( sq, Çamë; el, Τσάμηδες, ''Tsámidhes''), are a sub-group of Albanians who originally resided in the western part of the region of Epirus in northwestern Greece, an area known among Albanians as Chameria. The Chams have their own particular cultural identity, which is a mixture of Albanian and Greek influences as well as many specifically Cham elements.See Hasluk, 'Christianity and Islam under the Sultans', London, 1927. A number of Chams contributed to the Albanian national identity and played an important role in starting the renaissance of the Albanian culture in the 19th century. The Chams speak their own dialect of the Albanian language, the Cham Albanian dialect, which is a Southern Tosk Albanian dialect and one of the two most conservative ones; the other being Arvanitika. During the late 1930s Chams suffered from intimidation and persecution under the dictatorship of General Metaxas. Following the Italian occupation of Albania in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Irredentism
Greater Albania is an irredentist and nationalist concept that seeks to unify the lands that many Albanians consider to form their national homeland. It is based on claims on the present-day or historical presence of Albanian populations in those areas. In addition to the existing Albania, the term incorporates claims to regions in the neighbouring states, the areas include Kosovo, the Preševo Valley of Serbia, territories in southern Montenegro, northwestern Greece (the Greek regional units of Thesprotia and Preveza, referred by Albanians as Chameria, and other territories that were part of the Vilayet of Yanina during the Ottoman Empire),. and a western part of North Macedonia. The unification of an even larger area into a single territory under Albanian authority had been theoretically conceived by the League of Prizren, an organization of the 19th century whose goal was to unify the Albanian inhabited lands (and other regions, mostly from the regions of Macedonia and Epir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thesprotia
Thesprotia (; el, Θεσπρωτία, ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital and largest town is Igoumenitsa. Thesprotia is named after the Thesprotians, an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited the region in antiquity. History Thesprotia was part of the proto-Greek region in the late Bronze Age in which Greek archaic toponyms are were densely found. In antiquity, the territory of modern Thesprotia was inhabited by the ancient Greek tribe of Thesprotians and was bordered by the neighboring regions of Molossia to the north and Chaonia to the east. Thesprotia was part of the Epirote League before it was annexed by Rome where it became part of the Roman province of Epirus. After the fragmentation of the Roman Empire into East and West, it was part of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire until the late Middle Ages, except for a period of Bulgarian rule in the 9th-11th centuries. In c. 1430 it fell to the Ottomans. From the 8th-9th unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyamis
The Thyamis ( el, Θύαμις), also known as Glykys (Γλυκύς) or Kalamas (Καλαμάς), is a river in the Epirus region of Greece. It flows into the Ionian Sea. It is long, and its drainage area is about , over 99% of which on Greek territory. The names of the Chameria region (''Tsamouria'' in Greek), as well as the Chams, derive from the river's name. Thyamis in ancient Greece was mentioned by Pausanias as forming the boundary between Thesprotis and Kestrine. In addition, Suda and Ptolemaeus mentioned it. Some Renaissance scholars believed that the English River Thames owed its name to the River Thyamis, as early Celtic tribes were thought to have migrated from the Epirus region to England. While this belief influenced the modern spelling of the English river's name, it is no longer regarded as credible. Geography The source of the river is near the village Kalpaki, in the northwestern part of the Ioannina regional unit. It flows south at first, and turns southwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian People
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia as well as in Croatia, Greece, Italy and Turkey. They also constitute a large diaspora with several communities established across Europe, the Americas and Oceania. Albanians have Paleo-Balkanic origins. Exclusively attributing these origins to the Illyrians, Thracians or other Paleo-Balkan people is still a matter of debate among historians and ethnologists. The first certain reference to Albanians as an ethnic group comes from 11th century chronicler Michael Attaleiates who describes them as living in the theme of Dyrrhachium. The Shkumbin River roughly demarcates the Albanian language between Gheg and Tosk dialects. Christianity in Albania was under the jurisdiction of the Bishop of Rome until the 8th century AD. Then, diocese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagenetia
Vagenetia or Vagenitia ( gr, Βαγενετία, Βαγενιτία) was a medieval region on the coast of Epirus, roughly corresponding to modern Thesprotia. The region likely derived its name from the Slavic tribe of the Baiounitai. It is first attested as a ''sclavinia'' under some sort of Byzantine control in the 8th/9th centuries, passed under Bulgarian rule in the late 9th century, and returned to Byzantine rule in the 11th. It passed to the Despotate of Epirus after 1204, where it formed a separate province. Vagenetia came under Albanian rule in the 1360s, until conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1430. History The region's name derives from the Slavic tribe of the Baiounitai, who appear in the early 7th century during the Slavic invasions of the Balkans. Already during the 8th century, the Byzantine Empire tried to re-impose some control over the region, as a seal of office attests the presence of a civil governor ("Theodore, '' basilikos spatharios'' and ''archon'' of Vagen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire. Definition Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on which resided the tribe of the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins or Latians. It was located on the left bank (east and south) of the Tiber, River Tiber, extending northward to the Aniene, River Anio (a left-bank tributary of the Tiber) and southeastward to the Pomptina Palus (Pontine Marshes, now the Pontine Fields) as far south as the Cape Circeo, Circeian promontory. The right bank of the Tiber was occupied by the Etruscan city of Veii, and the other borders were occupied by Ancient Italic people, Italic tribes. Subsequently, Rome defeated Veii and then its Italic neighbours, expanding its dominions over Southern Etruria and to the south, in a partly marshy and partly mountainous region. The latter saw the creation of numerous Roman and Latin co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term toponymy come from grc, τόπος / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional discourse among geographers. Toponym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acheron River
The Acheron (; grc, Ἀχέρων ''Acheron'' or Ἀχερούσιος ''Acherousios''; ell, Αχέροντας ''Acherontas'') is a river located in the Epirus region of northwest Greece. It is long, and its drainage area is . Its source is near the village Zotiko, in the southwestern part of the Ioannina regional unit, and it flows into the Ionian Sea in Ammoudia, near Parga. The Acheron also features prominently in Greek mythology, where it is often depicted as the entrance to the Greek Underworld where souls must be ferried across by Charon (although some later sources, such as Roman poets, assign this role to the river Styx). Mythology Ancient Greek mythology saw the Acheron, sometimes known as the "river of woe", as one of the five rivers of the Greek underworld. The name is of uncertain etymology. Most classical accounts, including Pausanias (10.28) and later Dante's ''Inferno'' (3.78), portray the Acheron as the entrance to the Underworld and depict Charon ferry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
