|
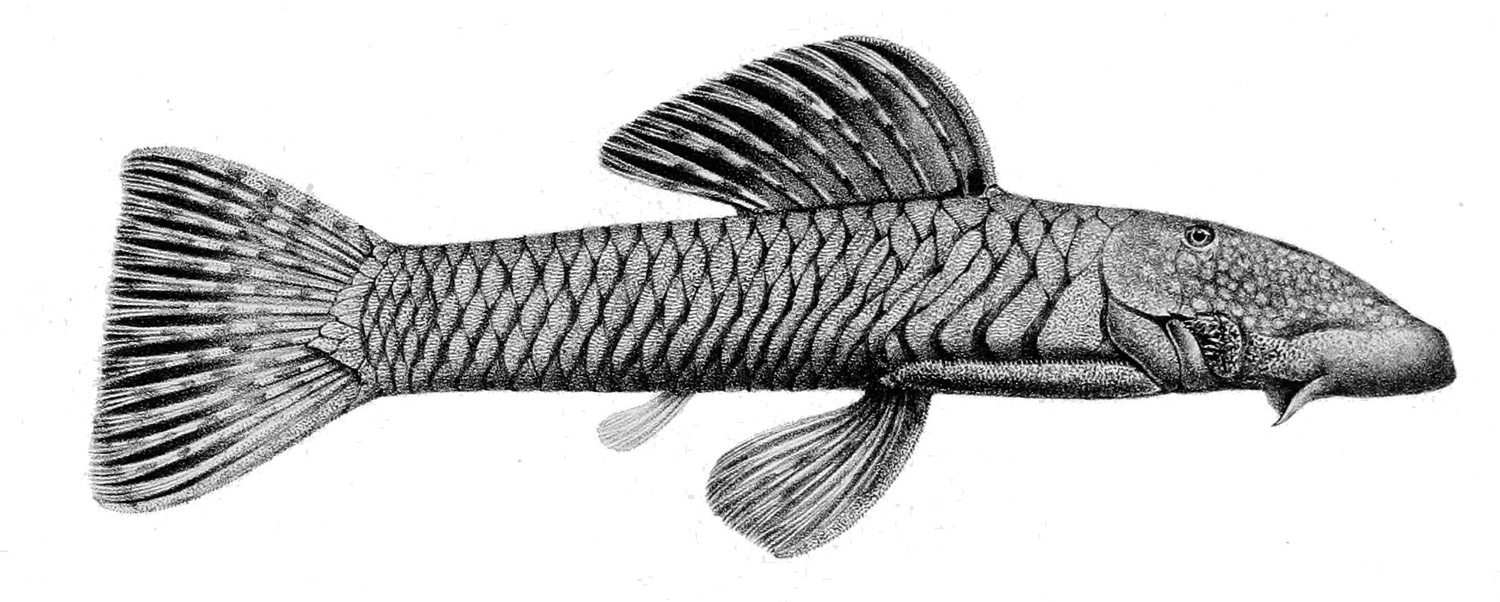
Chaetostoma Loborhynchos
''Chaetostoma loborhynchos'' is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Tambo River basin, which is part of the Ucayali River drainage in Peru. The species reaches 14.2 cm (5.6 inches) SL. It is the type species of the genus ''Chaetostoma ''Chaetostoma'', also known as the bristlemouth catfish, is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes native to South America with one species, '' C. fischeri,'' extending into Panama. Most species inhabit flowing rivers in the lower Andes and it ...''. References loborhynchos Fish described in 1846 Catfish of South America Fish of Peru {{Hypostominae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetostoma Loborhynchos Tschudi Top
''Chaetostoma'', also known as the bristlemouth catfish, is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes native to South America with one species, '' C. fischeri,'' extending into Panama. Most species inhabit flowing rivers in the lower Andes and its foothills. Some species are kept in unheated aquaria. Species These are the currently recognized species in this genus: * ''Chaetostoma aburrensis'' (Posada, 1909) * ''Chaetostoma anale'' ( Fowler, 1943) * ''Chaetostoma anomalum'' Regan, 1903 * ''Chaetostoma bifurcum'' Lujan, Meza-Vargas, Astudillo-Clavijo, Barriga-S. & López-Fernández, 2015Lujan, N.K., Meza-Vargas, V., Astudillo-Clavijo, V., Barriga-Salazar, R. & López-Fernández, H. (2015): A Multilocus Molecular Phylogeny for ''Chaetostoma'' Clade Genera and Species with a Review of ''Chaetostoma'' (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) from the Central Andes. ''Copeia, 103 (3): 664-701.'' * ''Chaetostoma branickii'' Steindachner, 1881 * ''Chaetostoma breve'' Regan, 1904 * ''Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores (species that eat dead material on the bottom), and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, ''Vandellia cirrhosa''. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus ''Corydoras'', are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loricariidae
The Loricariidae is the largest family of catfish (order Siluriformes), with 92 genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South America. These fish are noted for the bony plates covering their bodies and their suckermouths. Several genera are sold as " plecos", notably the suckermouth catfish, ''Hypostomus plecostomus'', and are popular as aquarium fish. Common names Members of the family Loricariidae are commonly referred to as loricariids, suckermouth armoured catfishes, or armoured catfish. The name "plecostomus", and its shortened forms "pleco" and "plec", are used for many Loricariidae, since ''Plecostomus plecostomus'' (now called ''Hypostomus plecostomus'') was one of the first loricariid species imported for the fish-keeping hobby. Some loricariids are not normally considered "plecostomus", such as ''Farlowella'' catfish. In their native range, these fish are known as ''cascudos'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambo River (Peru)
The Tambo River (Spanish: Río Tambo) is a Peruvian river on the eastern slopes of the Andes. The name only refers to a relatively short section; about long. It starts at the confluence of the Ene and Perené Rivers at the town of Puerto Prado. From here the Tambo River flows in an easterly direction and then turns north. When merging with the Urubamba River at the town of Atalaya, it becomes the Ucayali River. The Tambo is part of the headwaters of the Amazon River whose origin is the Mantaro River The Mantaro River ( es, Río Mantaro, qu, Hatunmayu) is a long river running through the central region of Peru. Its Quechua name means "great river". The word "Mantaro" may be a word originally from the Asháninka language, who live downstream a ... at Cordilerra Ruminator Cruz. Tributaries of the Amazon River Rivers of Peru Tributaries of the Ucayali River Rivers of Junín Region Rivers of Ucayali Region {{Peru-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ucayali River
The Ucayali River ( es, Río Ucayali, ) is the main headstream of the Amazon River. It rises about north of Lake Titicaca, in the Arequipa region of Peru and becomes the Amazon at the confluence of the Marañón close to Nauta city. The city of Pucallpa is located on the banks of the Ucayali. Description The Ucayali, together with the Apurímac River, the Ene River and the Tambo River, is today considered the main headwater of the ''Amazon River'', totaling a length of from the source of the ''Apurímac'' at Nevado Mismi to the confluence of the Ucayali and Marañón Rivers: *Apurímac River (total length): *Ene River (total length): *Tambo River (total length): * Ucayali River (confluence with Tambo River to confluence with the Marañón): Exploration The Ucayali was first called ''San Miguel'', then ''Ucayali'', ''Ucayare'', ''Poro'', ''Apu-Poro'', ''Cocama'' and ''Rio de Cuzco''. Peru has organised many costly and ably-conducted expeditions to explore it. One of them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetostoma
''Chaetostoma'', also known as the bristlemouth catfish, is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes native to South America with one species, '' C. fischeri,'' extending into Panama. Most species inhabit flowing rivers in the lower Andes and its foothills. Some species are kept in unheated aquaria. Species These are the currently recognized species in this genus: * '' Chaetostoma aburrensis'' (Posada, 1909) * '' Chaetostoma anale'' ( Fowler, 1943) * '' Chaetostoma anomalum'' Regan, 1903 * ''Chaetostoma bifurcum'' Lujan, Meza-Vargas, Astudillo-Clavijo, Barriga-S. & López-Fernández, 2015Lujan, N.K., Meza-Vargas, V., Astudillo-Clavijo, V., Barriga-Salazar, R. & López-Fernández, H. (2015): A Multilocus Molecular Phylogeny for ''Chaetostoma'' Clade Genera and Species with a Review of ''Chaetostoma'' (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) from the Central Andes. ''Copeia, 103 (3): 664-701.'' * ''Chaetostoma branickii'' Steindachner, 1881 * '' Chaetostoma breve'' Regan, 1904 * ''Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1846
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Most fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish Of South America
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores (species that eat dead material on the bottom), and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, ''Vandellia cirrhosa''. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus ''Corydoras'', are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(2).jpg)


