|
Cesium Chloride
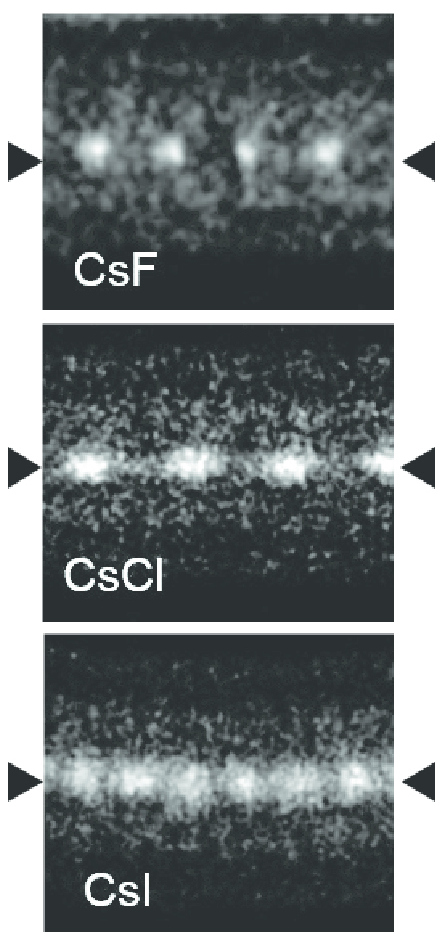
Caesium chloride or cesium chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Cs Cl. This colorless salt is an important source of caesium ions in a variety of niche applications. Its crystal structure forms a major structural type where each caesium ion is coordinated by 8 chloride ions. Caesium chloride dissolves in water. CsCl changes to NaCl structure on heating. Caesium chloride occurs naturally as impurities in carnallite (up to 0.002%), sylvite and kainite. Less than 20 tonnes of CsCl is produced annually worldwide, mostly from a caesium-bearing mineral pollucite. Caesium chloride is widely used medicine structure in isopycnic centrifugation for separating various types of DNA. It is a reagent in analytical chemistry, where it is used to identify ions by the color and morphology of the precipitate. When enriched in radioisotopes, such as 137CsCl or 131CsCl, caesium chloride is used in nuclear medicine applications such as treatment of cancer and diagnosis of myocardial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylvite
Sylvite, or sylvine, is potassium chloride (KCl) in natural mineral form. It forms crystals in the isometric system very similar to normal rock salt, halite ( NaCl). The two are, in fact, isomorphous. Sylvite is colorless to white with shades of yellow and red due to inclusions. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a specific gravity of 1.99. It has a refractive index of 1.4903. Sylvite has a salty taste with a distinct bitterness. Sylvite is one of the last evaporite minerals to precipitate out of solution. As such, it is only found in very dry saline areas. Its principal use is as a potassium fertilizer. Sylvite is found in many evaporite deposits worldwide. Massive bedded deposits occur in New Mexico and western Texas, and in Utah in the US, but the largest world source is in Saskatchewan, Canada. The vast deposits in Saskatchewan, Canada were formed by the evaporation of a Devonian seaway. Sylvite is the official mineral of Saskatchewan. Sylvite was first described in 1832 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, opacity (optics), opacity, and lustre (mineralogy), luster, but may have properties that differ from those of the pure metals, such as increased strength or hardness. In some cases, an alloy may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the mixture imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength. Alloys are defined by a metallic bonding character. The alloy constituents are usually measured by mass percentage for practical applications, and in Atomic ratio, atomic fraction for basic science studies. Alloys are usually classified as substitutional or interstitial alloys, depending on the atomic arrangement that forms the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium Iodide
Caesium iodide or cesium iodide (chemical formula CsI) is the ionic compound of caesium and iodine. It is often used as the input phosphor of an X-ray image intensifier tube found in fluoroscopy equipment. Caesium iodide photocathodes are highly efficient at extreme ultraviolet wavelengths. Synthesis and structure Bulk caesium iodide crystals have the cubic CsCl crystal structure, but the structure type of nanometer-thin CsI films depends on the substrate material – it is CsCl for mica and NaCl for LiF, NaBr and NaCl substrates. Caesium iodide atomic chains can be grown inside double-wall carbon nanotubes. In such chains I atoms appear brighter than Cs atoms in electron micrographs despite having a smaller mass. This difference was explained by the charge difference between Cs atoms (positive), inner nanotube walls (negative) and I atoms (negative). As a result, Cs atoms are attracted to the walls and vibrate more strongly than I atoms, which are pushed toward the nanot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium Bromide
Caesium bromide or cesium bromide is an ionic compound of caesium and bromine with the chemical formula CsBr. It is a white or transparent solid with melting point at 636 °C that readily dissolves in water. Its bulk crystals have the cubic CsCl structure, but the structure changes to the rocksalt type in nanometer-thin film grown on mica, LiF, KBr or NaCl substrates. Synthesis Caesium bromide can be prepared via following reactions: * Neutralization: : CsOH (aq) + HBr (aq) → CsBr (aq) + H2O (l) : Cs2(CO3) (aq) + 2 HBr (aq) → 2 CsBr (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) * Direct synthesis: : 2 Cs (s) + Br2 (g) → 2 CsBr (s) The direct synthesis is a vigorous reaction of caesium with other halogens. Due to its high cost, it is not used for preparation. Uses Caesium bromide is sometimes used in optics as a beamsplitter component in wide-band spectrophotometers Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goiânia Accident
The Goiânia accident was a radioactive contamination accident that occurred on September 13, 1987, in Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil, after a forgotten radiotherapy source was stolen from an abandoned hospital site in the city. It was subsequently handled by many people, resulting in four deaths. About 112,000 people were examined for radioactive contamination and 249 of them were found to have been contaminated. In the consequent cleanup operation, topsoil had to be removed from several sites, and several houses were demolished. All the objects from within those houses, including personal possessions, were seized and incinerated. ''Time'' magazine has identified the accident as one of the world's "worst nuclear disasters" and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) called it "one of the world's worst radiological incidents". Description of the source The radiation source in the Goiânia accident was a small capsule containing about of highly radioactive caesium chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine. Diagnostic medical imaging Diagnostic In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example, through inhalation, intravenously or orally. Then, external detectors (gamma cameras) capture and form images from the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceuticals. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (''t''1/2) for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration. Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemical methods and modern, instrumental methods. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as precipitation, extraction, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Instrumental methods may be used to separate samples using chromatography, electrophoresis or field flow fractionation. Then qualitative and quantitative analysis can be performed, often with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopycnic Centrifugation
An isopycnic surface is a surface of constant density inside a fluid. Isopycnic surfaces contrast with isobaric or isothermal surfaces, which describe surfaces of constant pressure and constant temperature respectively. Isopycnic surfaces are sometimes referred to as "iso-density" surfaces, although this is strictly incorrect. Isopycnic typically describes surfaces, not processes. Unless there is a flux of mass into or out of a control volume, a process which occurs at a constant density also occurs at a constant volume and is called an isochoric process and not an isopycnic process. The term "isopycnic" is commonly encountered in the fluid dynamics of compressible fluids, such as in meteorology and geophysical fluid dynamics, astrophysics, or the fluid dynamics of explosions or high Mach number flows. It may also be applied to other situations where a continuous medium has smoothly varying density, such as in the case of an inhomogeneous colloidal suspension. In general isopycn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |