|
Cerithideopsilla Conica
''Cerithideopsilla conica'' is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Potamididae.WoRMS (2011). ''Potamides conicus'' (Blainville, 1829). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=140846 on 2011-04-10 Taxonomy Reid et al. (2008) moved ''Potamides conicus'' to the genus ''Cerithideopsilla'' based on the molecular phylogeny research. Other subsequent study also confirmed this placement within ''Cerithideopsilla''.Ozawa T., Yin W., Fu C., Claremont M., Smith L. & Reid D. G. (2015). "Allopatry and overlap in a clade of snails from mangroves and mud flats in the Indo-West Pacific and Mediterranean (Gastropoda: Potamididae: ''Cerithideopsilla'')". '' Biological Journal of the Linnean Society'' 114(1): 212-228. . Distribution Distribution of ''Cerithideopsilla conica'' include Mediterranean and Indian Ocean. This species occurs in or around: * European waters * Madagascar * The Red Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod Shell
The gastropod shell is part of the body of a Gastropoda, gastropod or snail, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or in some cases the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within it (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the Aperture (mollusc), aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group. Shell layers The gastropod shell has three major layers secreted by the Mantle (mollusc), mantle. The calcareous central layer, tracum, is typically made of calcium carbonate precipitated into an organic matrix known as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Brettingham Sowerby II
George Brettingham Sowerby II (1812 – 26 July 1884) was a British naturalist, illustrator, and conchologist. Together with his father, George Brettingham Sowerby I, he published the ''Thesaurus Conchyliorum'' and other illustrated works on molluscs. He was an elected a Fellow of the Linnean Society on 7 May 1844. He was the father of George Brettingham Sowerby III, also a malacologist. He died on 26 July 1884 and is buried on the west side of Highgate Cemetery with his father George Brettingham Sowerby I and sister Charlotte Caroline Sowerby. See also *Sowerby family The Sowerby family () was a British family of several generations of naturalists, illustrators, botanists, and zoologists active from the late 18th century to the mid twentieth century. *James Sowerby (1757–1822) **James De Carle Sowerby (178 ... References * H. Crosse & P. Fischer, 1885. ''Nécrologie''. Journal de Conchyliologie 33(1): 80. * K. v. W. Palmer, 1965. ''Who were the Sowerbys?'' Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
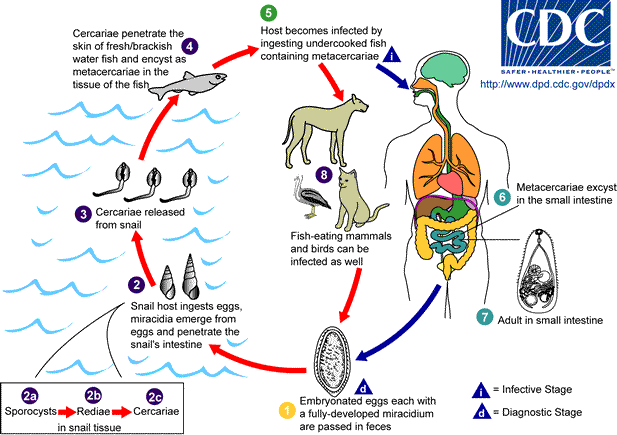
Heterophyes Heterophyes
''Heterophyes heterophyes'' was discovered by Theodor Maximaillian Bilharz in 1851. This parasite was found during an autopsy of an Egyptian mummy. ''H. heterophyes'' is found in the Middle East, West Europe and Africa. They use different species to complete their complex lifestyle. Humans and other mammals are the definitive host, first intermediate host are snails, and second intermediate are fish. Mammals that come in contact with the parasite are dogs, humans, and cats. Snails that are affected by this parasite are the '' Cerithideopsilla conica''. Fish that come in contact with this parasite are ''Mugil cephalus, Tilapia milotica, Aphanius fasciatus,'' and '' Acanthgobius'' sp. Humans and mammals will come in contact with this parasite by the consumption of contaminated or raw fish. This parasite is one of the smallest endoparasite to infect humans. It can cause intestinal infection called heterophyiasis. Distribution This species occurs in Egypt, Sudan, Israel, Brazil, Spai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Journal Of The Linnean Society
The ''Biological Journal of the Linnean Society'' is a direct descendant of the oldest biological journal in the world, the ''Transactions of the Linnean Society''. It succeeded the earlier title in 1969. The journal specializes in evolution, and encompasses work across all taxonomic groups in all five kingdoms of living organisms. It includes all methods, whole-organism or molecular, practical or theoretical. The journal is published by the Linnean Society of London The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript and literature colle .... References External links * Linnean Society of London Biology journals English-language journals Publications with year of establishment missing {{biology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogeny
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the absence of a visible shell. Definition Determining whether some gastropods should be called sea snails is not always easy. Some species that live in brackish water (such as certain neritids) can be listed as either freshwater snails or marine snails, and some species that live at or just above the high tide level (for example species in the genus '' Truncatella'') are sometimes considered to be sea snails and sometimes listed as land snails. Anatomy Sea snails are a very large group of animals and a very diverse one. Most snails that live in salt water respire using a gill or gills; a few species, though, have a lung, are intertidal, and are active only at low tide when they can move around in the air. These air-breathing species includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspard Michaud
Louis André Gaspard MichaudCoan E. V., Kabat A. R. & Petit R. E. (15 February 2009), 830 pp. + 32 pp. nnex of Collations American Malacological Society. (7 December 1795 in Sornac – 4 April 1880 in Lyons) was a French malacologist. He is also known as Gaspard Michaud or as André Louis Gaspard Michaud. Biography Michaud was the son of a teacher who stimulated his son's passion for natural sciences. He signed up for the infantry in 1813. He was injured twice during the siege of Metz (1814–1815). After his recovery in 1815 he became fully interested in natural sciences and began a conchological collection. When his father died in 1817, he decided to stay in the army to support his family. His career went well and he became an officer in 1823. He started to publish his first scientific paper between 1828 and 1831, dealing mainly with Mediterranean molluscs. In 1831 he published his major work, the ''Complément'' to the works of Draparnaud (1805).DRAPARNAUD J. P. R., an XIII ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

