|
Centrarchids
Centrarchidae, better known as sunfishes, is a family of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the order Perciformes (formerly belonging to the deprecated order Centrarchiformes), native only to North America. There are eight universally included genera within the centrarchid family: ''Lepomis'' (true sunfishes), ''Micropterus'' (black basses), ''Pomoxis'' ( crappies), ''Enneacanthus'' (banded sunfishes), ''Centrarchus'' (type genus, consisting solely of the flier ''C. macropterus''), ''Archoplites'' ( Sacramento perch), ''Ambloplites'' (rock basses), and ''Acantharchus'' (mud sunfish). A genetic study in 2012 suggests that the highly distinct pygmy sunfishes of the genus ''Elassoma'' are also centarchids. The centrarchid family comprises 38 identified species, 34 of which are extant. It includes many popular game fishes familiar to North American anglers, such as the rock bass, largemouth bass, bluegill, pumpkinseed, green sunfish and crappies. Most sunfish are high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enneacanthus
''Enneacanthus'' is a genus of freshwater fish in the sunfish family (Centrarchidae) of order Perciformes. The type species is ''E. obesus,'' the banded sunfish, and the species of this genus are known collectively as the banded or little sunfishes. The ''Enneacanthus'' species, all of which grow to a maximum overall length of about 10 cm (4 in), are native to freshwater lakes, ponds, and estuaries along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts of the United States. All three species are kept as aquarium fish by hobbyists. Etymology The generic name ''Enneacanthus'' derives from the Greek Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ... εννέα (nine) and άκανθα (thorn). Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: References Centrarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
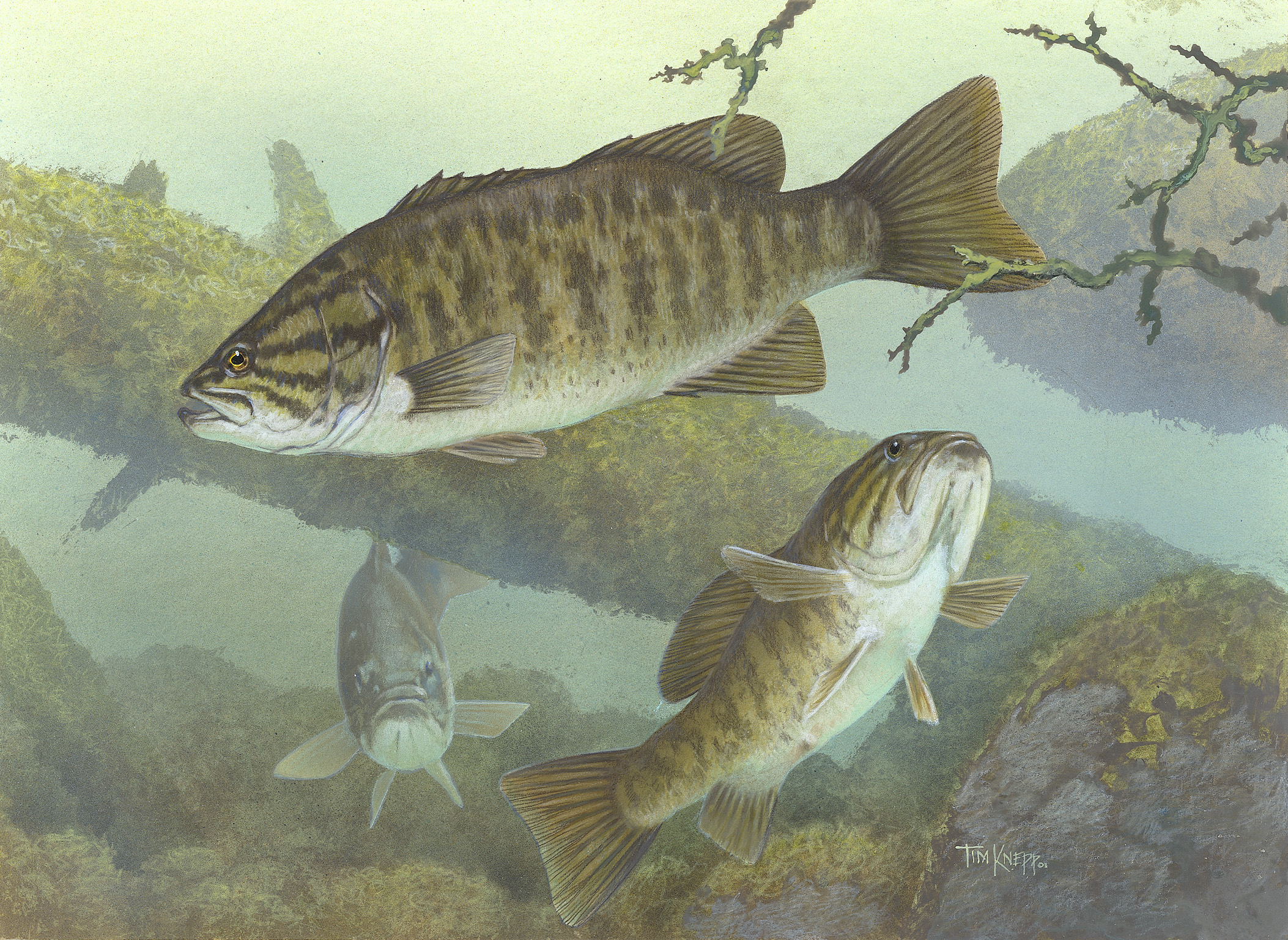
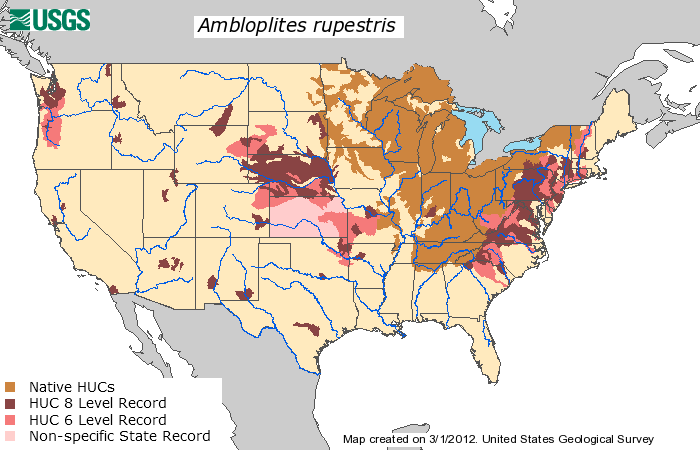
Rock Bass
The rock bass (''Ambloplites rupestris''), also known as the rock perch, goggle-eye, red eye, and black perch, is a freshwater fish native to east-central North America. This red eyed creature is a species of freshwater fish in the sunfish family (Centrarchidae) of order Perciformes and can be distinguished from other similar species by the six spines in the anal fin (other sunfish have only three anal fin spines). Distribution Rock bass are native to the St Lawrence River and Great Lakes system, the upper and middle Mississippi River basin in North America from Québec to Saskatchewan in the north down to Missouri and Arkansas, south to the Savannah River, and throughout the eastern U.S. from New York through Kentucky and Tennessee to the northern portions of Alabama and Georgia and Florida in the south. The rock bass has also been found in the Nueces River system in Texas Description They are similar in appearance to smallmouth bass, but are usually quite a bit smalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angling
Angling is a fishing technique that uses a fish hook or "angle" (from Old English ''angol'') attached to a fishing line to tether individual fish in the mouth. The fishing line is usually manipulated via a fishing rod, although rodless techniques such as handlining and longlining also exist. Modern angling rods are usually fitted with a reel that functions as a cranking device for storing, retrieving and releasing out the line, although Tenkara fishing and cane pole fishing are two rod-angling methods that do not use any reel. The hook itself can be additionally weighted with a dense tackle called a sinker, and is typically dressed with an appetizing bait to attract the fish and enticing it into swallowing the hook, but sometimes an inedible fake bait with multiple attached hooks (known as a lure) is used instead of a single hook with edible bait. A bite indicator, such as a float or a quiver tip, is often used to relay underwater status of the hook to the surface. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Fish
Game fish, sport fish or quarry refer to popular fish pursued by recreational anglers, and can be freshwater or saltwater fish. Game fish can be eaten after being caught, or released after capture. Some game fish are also targeted commercially, particularly salmon and tuna. Specimens of game fish whose measurements (body length and weight) are a lot above the species' average are sometimes known as trophy fish. Examples The species of fish prized by anglers varies with geography and tradition. Some fish are sought for their value as food, while others are pursued for their fighting abilities, or for the difficulty of successfully enticing the fish to bite the hook. * Big-game fish are blue water saltwater bony fish such as tuna, tarpon, grouper and billfish (sailfish, marlin and swordfish). Occasionally other predatory fishes such as sharks, barracuda and dolphinfish are also pursued. * In North America, many anglers fish for common snook, redfish, salmon/trout, bass, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extant Taxon
Neontology is a part of biology that, in contrast to paleontology, deals with living (or, more generally, '' recent'') organisms. It is the study of extant taxa (singular: extant taxon): taxa (such as species, genera and families) with members still alive, as opposed to (all) being extinct. For example: * The moose (''Alces alces'') is an extant species, and the dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct species. * In the group of molluscs known as the cephalopods, there were approximately 600 extant species and 7,500 extinct species. A taxon can be classified as extinct if it is broadly agreed or certified that no members of the group are still alive. Conversely, an extinct taxon can be reclassified as extant if there are new discoveries of living species ("Lazarus species"), or if previously-known extant species are reclassified as members of the taxon. Most biologists, zoologists, and botanists are in practice neontologists, and the term neontologist is used large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elassoma
''Elassoma'' is a genus of freshwater fish, the only member of subfamily Elassomatinae of the sunfish family Centrarchidae in the order Perciformes. It is sometimes classified as a separate family, the Elassomatidae, in a monotypic suborder, Elassomatoidei, in Perciformes. The type species is ''E. zonatum,'' the banded pygmy sunfish. The Elassomatinae are known collectively as pygmy sunfishes, but are considered by some authorities not to be true sunfishes, which are members of family Centrarchidae. Some researchers believe they are related to sticklebacks and pipefishes (order Syngnathiformes) rather than Perciformes, though genetic research strongly implies a close relationship with the centrarchids. Currently the Integrated Taxonomic Information System classifies them in the family Elassomatidae rather than Centrarchidae. The pygmy sunfishes grow to a maximum overall length of . They occur mostly in temperate and subtropical swamps, marshes, and other shallow, slow-moving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pygmy Sunfish
''Elassoma'' is a genus of freshwater fish, the only member of subfamily Elassomatinae of the sunfish family Centrarchidae in the order Perciformes. It is sometimes classified as a separate family, the Elassomatidae, in a monotypic suborder, Elassomatoidei, in Perciformes. The type species is ''E. zonatum,'' the banded pygmy sunfish. The Elassomatinae are known collectively as pygmy sunfishes, but are considered by some authorities not to be true sunfishes, which are members of family Centrarchidae. Some researchers believe they are related to sticklebacks and pipefishes (order Syngnathiformes) rather than Perciformes, though genetic research strongly implies a close relationship with the centrarchids. Currently the Integrated Taxonomic Information System classifies them in the family Elassomatidae rather than Centrarchidae. The pygmy sunfishes grow to a maximum overall length of . They occur mostly in temperate and subtropical swamps, marshes, and other shallow, slow-moving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Study
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the context o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mud Sunfish
The mud sunfish (''Acantharchus pomotis'') is a freshwater ray-finned fish, a sunfish from the family Centrarchidae, which widely distributed in the fresh waters along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from New York to Alabama. It is the only species in the genus ''Acantharchus''. Taxonomy The mud sunfish was first formally described as ''Centrarchus pomotis'' by Spencer Fullerton Baird in 1855 with the type locality given as Cedar Swamp Creek, Beesley's Point, Cape May County, New Jersey and the Hackensack River, Rockland County, New York. In 1864, Theodore Nicholas Gill placed it in its own monospecific genus ''Acantharchus'', the new genus name being a compound of the Greek words meaning "thorn" and meaning "anus". Description The mud sunfish is a small fish which can be distinguished from other members of its family by its possession of 5 or more spines in its anal fin, by having less than 15 gill rakers and in being the only species in its family which has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambloplites
''Ambloplites'' is a genus of North American freshwater fish in the sunfish family (Centrarchidae) of order Perciformes. The type species is ''A. rupestris,'' the rock bass, and the species of this genus are known collectively as the rock basses. The various ''Ambloplites'' species, which grow to a maximum overall length of and a maximum weight of , depending on species, are native to a region extending from the Hudson Bay basin in Canada to the lower Mississippi River basin in the United States. Etymology The generic name ''Ambloplites'' derives from the Greek αμβλύς (blunt) and οπλίτης (bearing a shield). Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: * '' Ambloplites ariommus'' Viosca, 1936 (shadow bass) * '' Ambloplites cavifrons'' Cope, 1868 (Roanoke bass) * '' Ambloplites constellatus'' Cashner & Suttkus, 1977 (Ozark bass) * ''Ambloplites rupestris'' (Rafinesque Constantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz (; October 22, 1783September 18, 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |