|
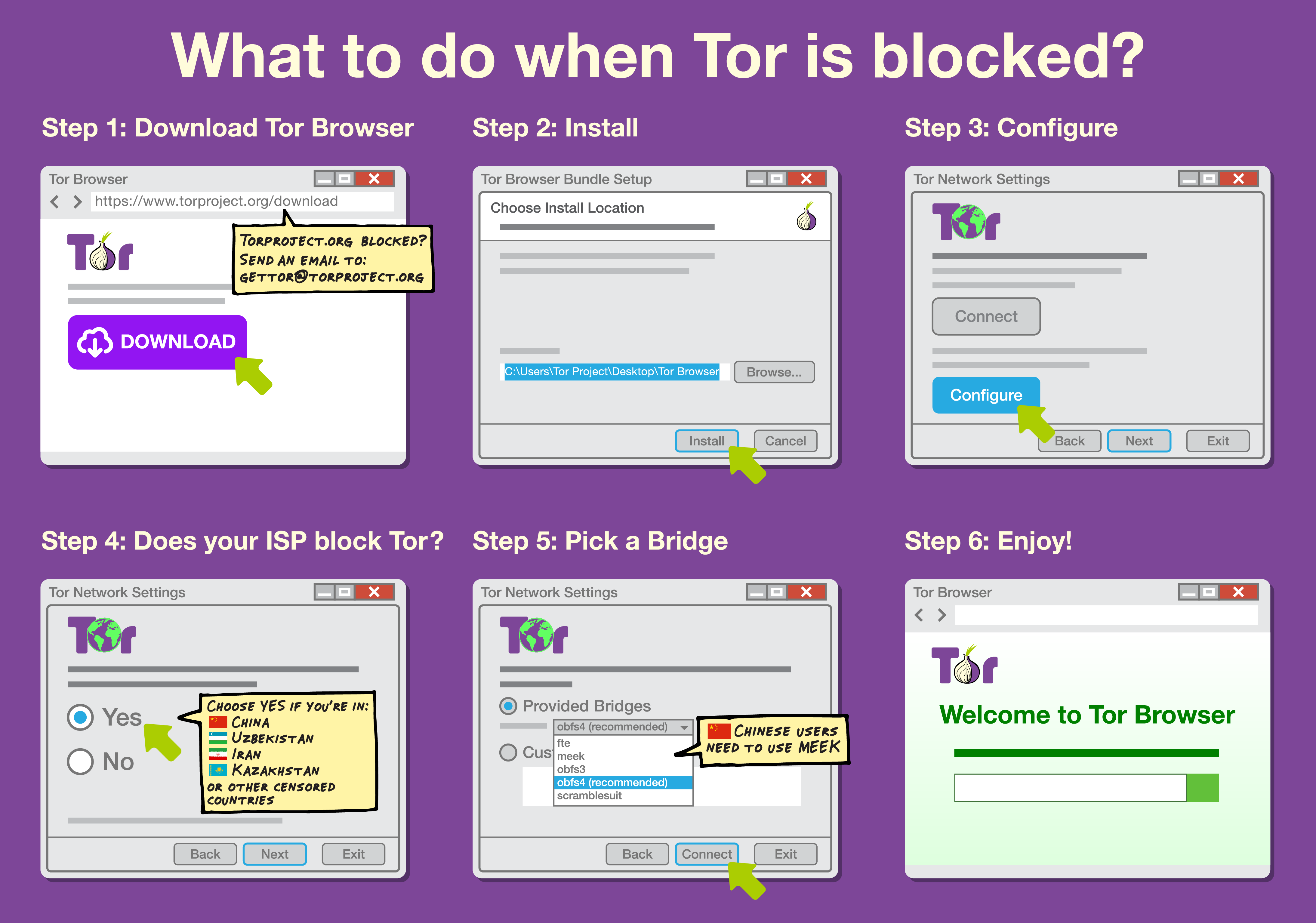
Censorship Circumvention
Internet censorship circumvention is the use of various methods and tools to bypass internet censorship. Various techniques and methods are used to bypass Internet censorship, and have differing ease of use, speed, security, and risks. Some methods, such as the use of alternate DNS servers, evade blocking by using an alternate address or address lookup system to access the site. Techniques using website mirrors or archive sites rely on other copies of the site being available at different locations. Additionally, there are solutions that rely on gaining access to an Internet connection that is not subject to filtering, often in a different jurisdiction not subject to the same censorship laws, using technologies such as proxying, virtual private networks, or anonymization networks. An arms race has developed between censors and developers of circumvention software, resulting in more sophisticated blocking techniques by censors and the development of harder-to-detect tools by re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Censorship
Internet censorship is the legal control or suppression of what can be accessed, published, or viewed on the Internet. Censorship is most often applied to specific internet domains (such as Wikipedia.org) but exceptionally may extend to all Internet resources located outside the jurisdiction of the censoring state. Internet censorship may also put restrictions on what information can be made internet accessible. Organizations providing internet accesssuch as schools and libraries may choose to preclude access to material that they consider undesirable, offensive, age-inappropriate or even illegal, and regard this as ethical behaviour rather than censorship. Individuals and organizations may engage in self-censorship of material they publish, for moral, religious, or business reasons, to conform to societal norms, political views, due to intimidation, or out of fear of legal or other consequences. The extent of Internet censorship varies on a country-to-country basis. While so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archive
An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials – in any medium – or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the function of that person or organization. Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism", and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity. In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value. Archival records are normally unpublished and almost alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Hash Table
A distributed hash table (DHT) is a distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table: key–value pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key. The main advantage of a DHT is that nodes can be added or removed with minimum work around re-distributing keys. ''Keys'' are unique identifiers which map to particular ''values'', which in turn can be anything from addresses, to documents, to arbitrary data. Responsibility for maintaining the mapping from keys to values is distributed among the nodes, in such a way that a change in the set of participants causes a minimal amount of disruption. This allows a DHT to scale to extremely large numbers of nodes and to handle continual node arrivals, departures, and failures. DHTs form an infrastructure that can be used to build more complex services, such as anycast, cooperative web caching, distributed file systems, domain name services, instant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZeroNet
ZeroNet is a decentralized web-like network of peer-to-peer users, created by Tamas Kocsis in 2015, programming for the network was based in Budapest, Hungary; is built in Python; and is fully open source. Instead of having an IP address, sites are identified by a public key (specifically a bitcoin address). The private key allows the owner of a site to sign and publish changes, which propagate through the network. Sites can be accessed through an ordinary web browser when using the ZeroNet application, which acts as a local webhost for such pages. In addition to using bitcoin cryptography, ZeroNet uses trackers from the BitTorrent network to negotiate connections between peers. ZeroNet is not anonymous by default, but it supports routing traffic through the Tor network. The ZeroNet website and bittorrent tracker are blocked in mainland China. Despite the censorship, however, it's still possible to access ZeroNet from behind the Great Firewall of China, even over Tor, by bootstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
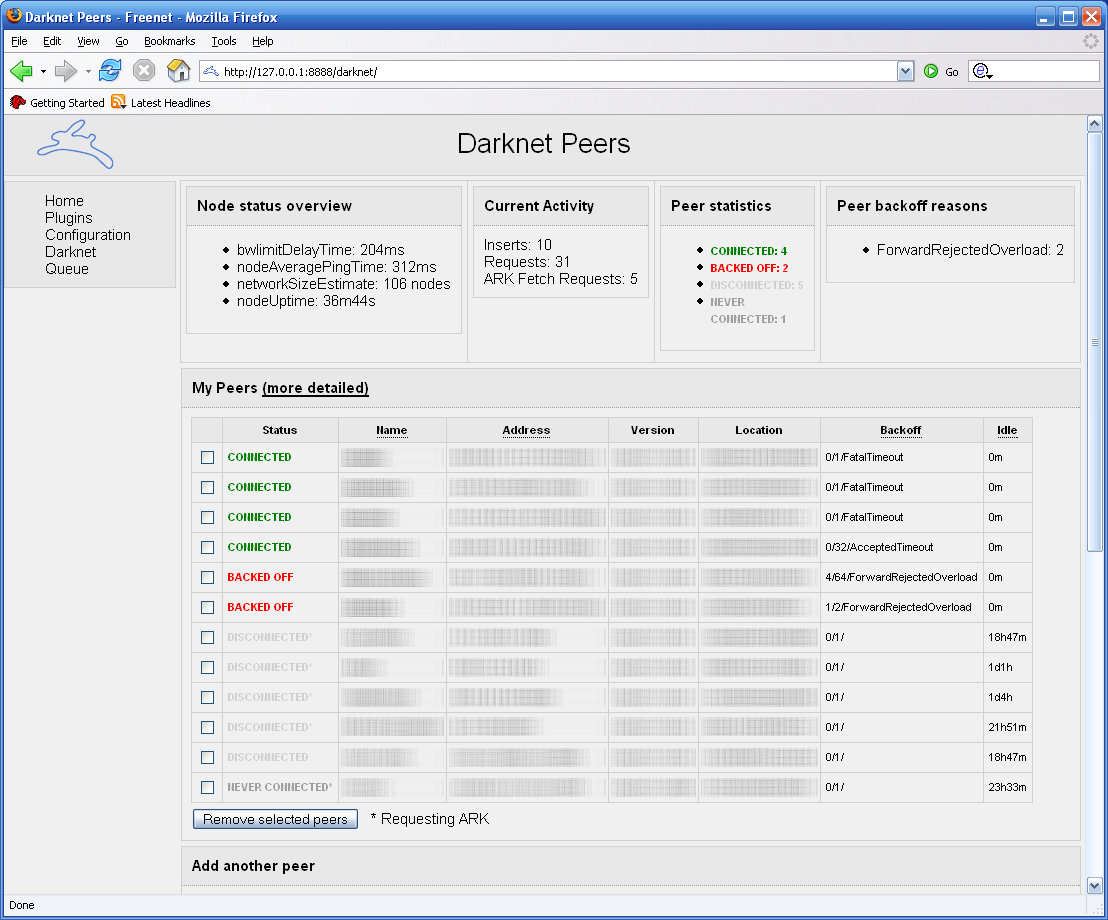
Freenet
Freenet is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship.What is Freenet? , ''Freenet: The Free network official website''.Taylor, Ian J. ''From P2P to Web Services and Grids: Peers in a Client/Server World''. London: Springer, 2005. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing |
Gnutella
Gnutella is a peer-to-peer network protocol. Founded in 2000, it was the first decentralized peer-to-peer network of its kind, leading to other, later networks adopting the model. In June 2005, Gnutella's population was 1.81 million computers increasing to over three million nodes by January 2006.On the Long-term Evolution of the Two-Tier Gnutella Overlay Rasti, Stutzbach, Rejaie, 2006. See Figure 2a. In late 2007, it was the most popular file-sharing network on the Internet with an estimated market share of more than 40%. History The first client (also called Gnutella) from which the network got its name was developed by Justin Frankel and Tom Pepper of Nullsoft in early 2000, soon after the company's acquisition by AOL. On March 14, the program was ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napster
Napster was a peer-to-peer file sharing application. It originally launched on June 1, 1999, with an emphasis on digital audio file distribution. Audio songs shared on the service were typically encoded in the MP3 format. It was founded by Shawn Fanning, Sean Parker, and Hugo Sáez Contreras. As the software became popular, the company ran into legal difficulties over copyright infringement. It ceased operations in 2001 after losing a wave of lawsuits and filed for bankruptcy in June 2002. Later, more decentralized projects followed Napster's P2P file-sharing example, such as Gnutella, Freenet, FastTrack, and Soulseek. Some services and software, like AudioGalaxy, LimeWire, Scour, Kazaa / Grokster, Madster, and eDonkey2000, were also brought down or changed due to copyright issues. Napster's assets were eventually acquired by Roxio, and it re-emerged as an online music store. Best Buy later purchased the service and merged it with its Rhapsody service on December 1, 2011, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feedly
Feedly is a news aggregator application for various web browsers and mobile devices running iOS and Android. It is also available as a cloud-based service. It compiles news feeds from a variety of online sources for the user to customize and share with others. Feedly was first released by DevHD in 2008. History DevHD’s first project, Streets, which aggregates updates from a variety of online sources is the basis of Feedly. Originally called ''Feeddo'', Feedly was first released as a web extension before moving onto mobile platforms. On March 15, 2013, Feedly announced 500,000 new users in 48 hours due to the closure announcement of Google Reader. By April 2, 2013, the total number of new users was up to 3 million. At the end of May 2013, the total user number was up to 12 million. Mobile app The Feedly mobile application is available for iOS and Android devices. All versions of the app run on Streets (DevHD's other project), which allows for the application to run on the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifest File
A manifest file in computing is a file containing metadata for a group of accompanying files that are part of a set or coherent unit. For example, the files of a computer program may have a manifest describing the name, version number, license and the constituent files of the program. The term is borrowed from a cargo shipping procedure, where a ship manifest would list the crew and/or cargo of a vessel. Package manifest Linux distributions rely heavily on package management systems for distributing software. In this scheme, a package is an archive file containing a manifest file. The primary purpose is to enumerate the files which are included in the distribution, either for processing by various packaging tools or for human consumption. Manifests may contain additional information; for example, in JAR (a package format for delivering software written in Java programming language), they can specify a version number and an entry point for execution. The manifest may optionally cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P2P Network
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the file sharing system Napster, originally released in 1999. The concept has inspired new structures and philosophies in many areas of human interaction. In such social contexts, peer-to-peer as a meme refers to the egalitarian soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Network
A telecommunications network is a group of nodes interconnected by telecommunications links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching, to pass messages and signals. Multiple nodes may cooperate to pass the message from an originating node to the destination node, via multiple network hops. For this routing function, each node in the network is assigned a network address for identification and locating it on the network. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space of the network. Examples of telecommunications networks include computer networks, the Internet, the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the global Telex network, the aeronautical ACARS network, and the wireless radio networks of cell phone telecommunication providers. Network structure In general, every telecommunications network conceptually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |