|
Archive
An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials – in any medium – or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the function of that person or organization. Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism", and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity. In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value. Archival records are normally unpublished and almost alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a virtual space, or both. A library's collection can include printed materials and other physical resources in many formats such as DVD, CD and cassette as well as access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. A library, which may vary widely in size, may be organized for use and maintained by a public body such as a government; an institution such as a school or museum; a corporation; or a private individual. In addition to providing materials, libraries also provide the services of librarians who are trained and experts at finding, selecting, circulating and organizing information and at interpreting information needs, navigating and analyzing very large amounts of information with a variety of resources. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archivist
An archivist is an information professional who assesses, collects, organizes, preserves, maintains control over, and provides access to Document, records and archives determined to have long-term value. The records maintained by an archivist can consist of a variety of forms, including letters, diaries, logs, other personal documents, government documents, sound and/or picture recordings, digital files, or other physical objects. Description As Richard Pearce-Moses wrote: Determining what records have enduring value can be challenging. Archivists must also select records valuable enough to justify the costs of storage and preservation, plus the labor-intensive expenses of arrangement, description, and reference service. The theory and scholarly work underpinning archives practices is called archival science. The most common related occupations are librarians, Curator, museum curators, and records managers. The occupation of archivist is distinct from that of librarian. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French National Archives
The Archives nationales (, "National Archives" in English; abbreviated AN) are the national archives of France. They preserve the archives of the French state, apart from the archives of the Ministry of Armed Forces and Ministry of Foreign Affairs, as these two ministries have their own archive services, the Defence Historical Service (SHD) and respectively. The National Archives of France also keep the archives of local secular and religious institutions from the Paris Region seized at the time of the French Revolution (such as local royal courts of Paris, suburban abbeys and monasteries, etc), as well as the archives produced by the notaries of Paris during five centuries, and many private archives donated or placed in the custody of the National Archives by prominent aristocratic families, industrialists, and historical figures. The National Archives have one of the largest and oldest archival collections in the world. As of 2020, they held of physical records (the total l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Archive
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an Discipline (academia), academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the historiography, nature of history as an end in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assembly, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archival Science
Archival science, or archival studies, is the study and theory of building and curating archives, which are collections of documents, recordings and data storage devices. To build and curate an archive, one must acquire and evaluate recorded materials, and be able to access them later. To this end, archival science seeks to improve methods for appraising, storing, preserving, and cataloging recorded materials. An archival record preserves data that is not intended to change. In order to be of value to society, archives must be trustworthy. Therefore, an archivist has a responsibility to authenticate archival materials, such as historical documents, and to ensure their reliability, integrity, and usability. Archival records must be what they claim to be; accurately represent the activity they were created for; present a coherent picture through an array of content; and be in usable condition in an accessible location. An archive curator is called an ''archivist''; the curatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription, for representing the spoken word, and combinations of both. Transcription methods can be subdivided into ''phonemic transcription'', which records the phonemes or units of semantic meaning in speech, and more strict ''phonetic transcription'', which records speech sounds with precision. Methods There are many consistent or standardized romanization systems. They can be classified by their characteristics. A particular system’s characteristics may make it better-suited for various, sometimes contradictory applications, including document retrieval, linguistic analysis, easy readability, faithful representation of pronunciation. * Source, or donor language – A system may be tailored to romanize text from a particular lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
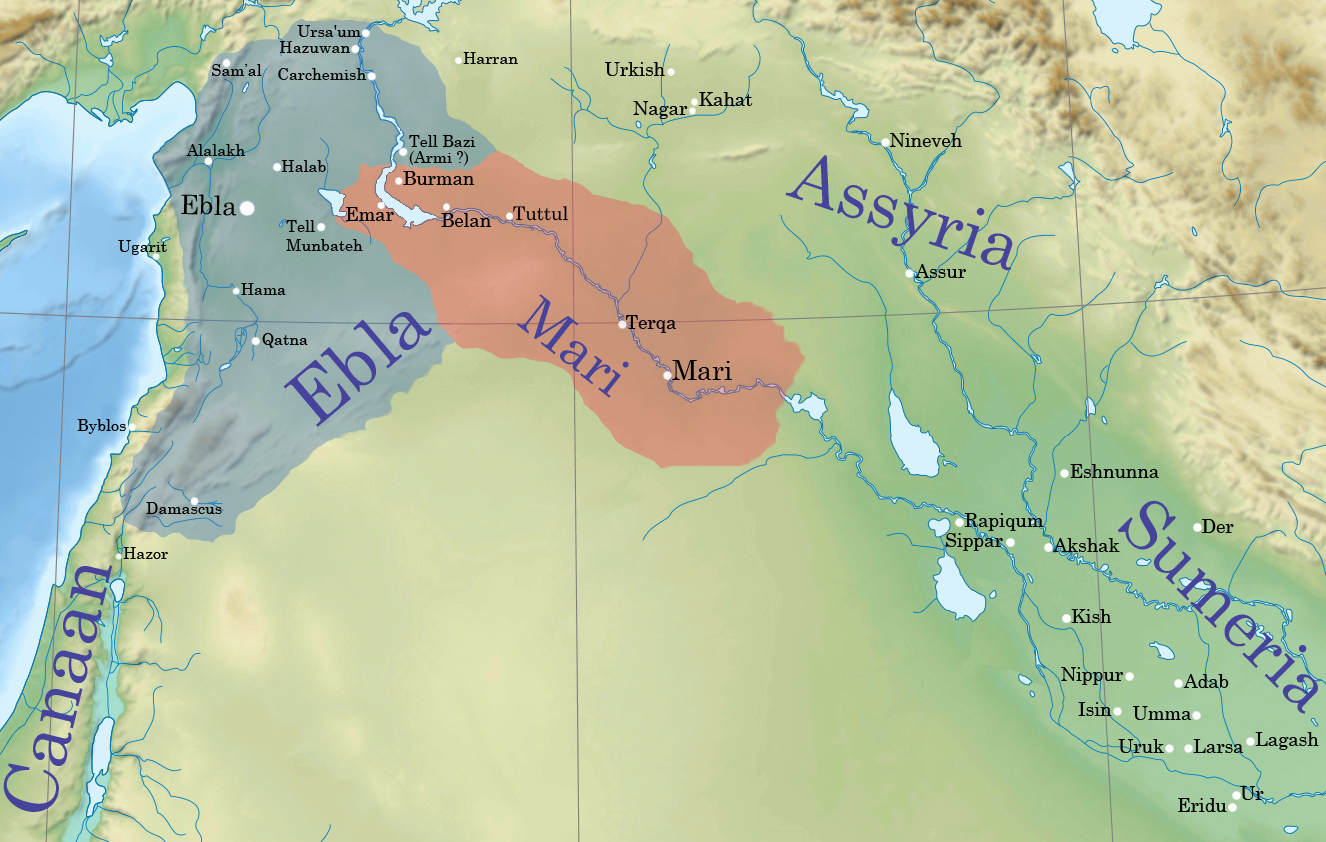
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)