|
Cecil Ffrench Salkeld
Cecil Ffrench Salkeld (9 July 1904 – 11 May 1969) was an Irish painter, printmaker, critic and writer. Early life and family Cecil Ffrench Salkeld was born in Assam, India on 9 July 1904. His parents were Henry Lyde Salkeld, a member of the Indian civil service, and Blanaid Salkeld (née Mullen), a poet. He returned to Ireland with his mother in 1910 after the death of his father in 1909. He attended Mount St Benedict's, Gorey, County Wexford, and the Dragon School, Oxford. Salkeld did win a scholarship to Oundle but returned to Dublin where he entered the Dublin Metropolitan School of Art in 1919 to study under Seán Keating and James Sleator. He married Irma Taesler in Germany in 1922. They had two daughters, Beatrice and Celia. Career Salkeld worked in tempera and oil, as well as etching and wood engraving. In 1921 he travelled to Germany to study under Ewald Dulberg at the Kassell Kunstschule. He attended the Union of Progressive International Artists in Düsseldorf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Gray (artist)
Reginald Gray (1930 – 29 March 2013) was an Irish portrait artist. He studied at The National College of Art (1953) and then moved to London, becoming part of the School of London led by Francis Bacon, Lucian Freud and Frank Auerbach. In 1960, he painted a portrait of Bacon which now hangs in the permanent collection of the National Portrait Gallery in London.Reginald Gray page at the National Portrait Gallery He subsequently painted portraits from life of writers, musicians and artists such as , , |
Radical Club
The Radical Club was formed in Dublin, Ireland in the 1925 by Liam O'Flaherty. The group held meetings and exhibitions, and ceased activity by 1930. History The Radical Club was founded by Liam O'Flaherty with a circle of artistic and literary figures in Dublin in 1925. O'Flaherty with Cecil Ffrench Salkeld sent out invitations proposing this new club and its inaugural meeting during the summer of 1925. It adopted its constitution in October 1925 with F. R. Higgins as its first chair. The group was composed of artists, poets, and writers who met weekly for conversations, meetings and other events. The Club's stated aims were "to provide a centre of intercourse for Irish intellectual workers; to encourage all forms of progressive cultural activity in Ireland; to fight for the freedom of cultural expression in Ireland; to promote solidarity among artists, writers, scientists, and all people engaged in intellectual pursuits in Ireland". In the beginning the Club was organised into 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Gallery Of Ireland
The National Gallery of Ireland ( ga, Gailearaí Náisiúnta na hÉireann) houses the national collection of Irish and European art. It is located in the centre of Dublin with one entrance on Merrion Square, beside Leinster House, and another on Clare Street. It was founded in 1854 and opened its doors ten years later. The gallery has an extensive, representative collection of Irish paintings and is also notable for its Italian Baroque and Dutch masters painting. The current director is Caroline Campbell. History In 1853 an exhibition, the Great Industrial Exhibition, was held on the lawns of Leinster House in Dublin. Among the most popular exhibits was a substantial display of works of art organised and underwritten by the railway magnate William Dargan. The enthusiasm of the visiting crowds demonstrated a public for art, and it was decided to establish a permanent public art collection as a lasting monument of gratitude to Dargan. The moving spirit behind the proposal was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Tóstal
An Tóstal (, meaning "The Gathering") was the name for a series of festivals held in Ireland in the 20th century. Inaugurated in 1953 as a celebration of Irish life, it continued on until 1958 when it died out in most centres except Drumshanbo. After seeing the 1951 Festival of Britain the President of Pan Am Airlines thought of the idea of an Irish version. The original purpose of the festival was a celebration of Irish culture, with an emphasis upon drawing tourists into the country during the Easter off-season. It was marked by a series of regional parades, arts and sporting events. Many towns began a clean-up plan, thus starting off the National Tidy Town Awards, which is running still in Ireland. In 1953, a set of commemorative stamps designed by Limerick artist Fergus O'Ryan, were issued by the Irish Post Office. Chess competitions Chess competitions were held as part of An Tóstal by the Irish Chess Union from 1953 to 1957, from 1954, 1955 and 1956 it included Internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTÉ Radio
RTÉ Radio is a division of the Irish national broadcasting organisation Raidió Teilifís Éireann. RTÉ Radio broadcasts four analogue channels and five digital channels nationwide. Founded in January 1926 as 2RN, the first broadcaster in the Irish Free State, in 1933 the service became Radio Athlone (Irish ''Raidió Áth Luain'') and in 1938 was renamed as Radio Éireann. In 1966, after launching a television service, it became Raidió Teilifís Éireann, or RTÉ. RTÉ Radio is, like its television parent, a statutory body, overseen by a board appointed by the Government of Ireland, with general management in the hands of the RTÉ Executive Board, headed by the Director-General. RTÉ Radio is regulated by the Broadcasting Authority of Ireland. Channels and availability History The first voice broadcast of 2RN, the original radio callsign for what would eventually become RTÉ Radio 1, took place on 14 November 1925 when Seamus Clandillon, the station director, announc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish National Ballet School
Irish may refer to: Common meanings * Someone or something of, from, or related to: ** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe *** Éire, Irish language name for the isle ** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland ** Republic of Ireland, a sovereign state * Irish language, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family spoken in Ireland * Irish people, people of Irish ethnicity, people born in Ireland and people who hold Irish citizenship Places * Irish Creek (Kansas), a stream in Kansas * Irish Creek (South Dakota), a stream in South Dakota * Irish Lake, Watonwan County, Minnesota * Irish Sea, the body of water which separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain People * Irish (surname), a list of people * William Irish, pseudonym of American writer Cornell Woolrich (1903–1968) * Irish Bob Murphy, Irish-American boxer Edwin Lee Conarty (1922–1961) * Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davy Byrne's Pub
Davy Byrne's pub is a public house located at 21 Duke Street, Dublin. It was made famous by its appearance in Chapter 8 ('Lestrygonians') of James Joyce's 1922 modernist novel ''Ulysses'', set on Thursday 16 June 1904. The main character, advertising canvasser Leopold Bloom, stops at around 1 p.m. for a gorgonzola cheese sandwich and a glass of burgundy while wandering through Dublin. The pub has since become a pilgrimage point for fans of the novel, who, like Bloom, stop and have a cheese sandwich and a glass of wine. The pub is particularly popular on Bloomsday, an annual 16 June celebration of both the book and James Joyce. Joyce also mentioned the pub in the short story "Counterparts" in ''Dubliners ''Dubliners'' is a collection of fifteen short stories by James Joyce, first published in 1914. It presents a naturalistic depiction of Irish middle class life in and around Dublin in the early years of the 20th century. The stories were writt ...'' as a bar visited by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolmen Press
Dolmen Press was founded by Liam and Josephine Miller in 1951. History In 1951 Liam acquired an Adana hand press from Blanaid and Cecil Ffrench Salkeld on loan which they had used for their Gayfield Press, with a case of Bodoni type. Some accounts state that the first publication of the press was 500 copies of a collection of four ballads, ''Travelling Tinkers,'' by Sigerson Clifford. Others believe that the first publication printed was Thomas Kinsella’s ''The Starlit Eye''. The Press took printing jobs from publishers as well as theatres, art galleries, businesses and individuals. The Press later printed using an Albion flat bed press and Caslon type. Founded to provide a publishing outlet for Irish poetry, the Press published the work of Irish artists. The scope of the press grew to include prose literature by Irish authors as well as a broad range of critical works about Irish literature and theatre. The Press published a variety of works by W.B. Yeats, as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liam O'Flaherty
Liam O'Flaherty ( ; 28 August 1896 – 7 September 1984) was an Irish novelist and short-story writer, and one of the foremost socialist writers in the first part of the 20th century, writing about the common people's experience and from their perspective. Liam O'Flaherty served on the Western Front as a soldier in the British army's Irish Guards regiment from 1916 and was badly injured in 1917. After the war, he was a founding member of the Communist Party of Ireland. His brother Tom Maidhc O'Flaherty (also a writer) was also involved in radical politics and their father, Maidhc Ó Flaithearta, was before them. A native Irish-speaker from the Gaeltacht, O'Flaherty wrote almost exclusively in English, except for a play, a notable collection of short stories and some poems in the Irish language. Early years O'Flaherty was born, a son of Maidhc Ó Flaithearta and Maggie Ganley, at Gort na gCapall, Inishmore. Baptised William, he adopted the form 'Liam' in the 1920s. His fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
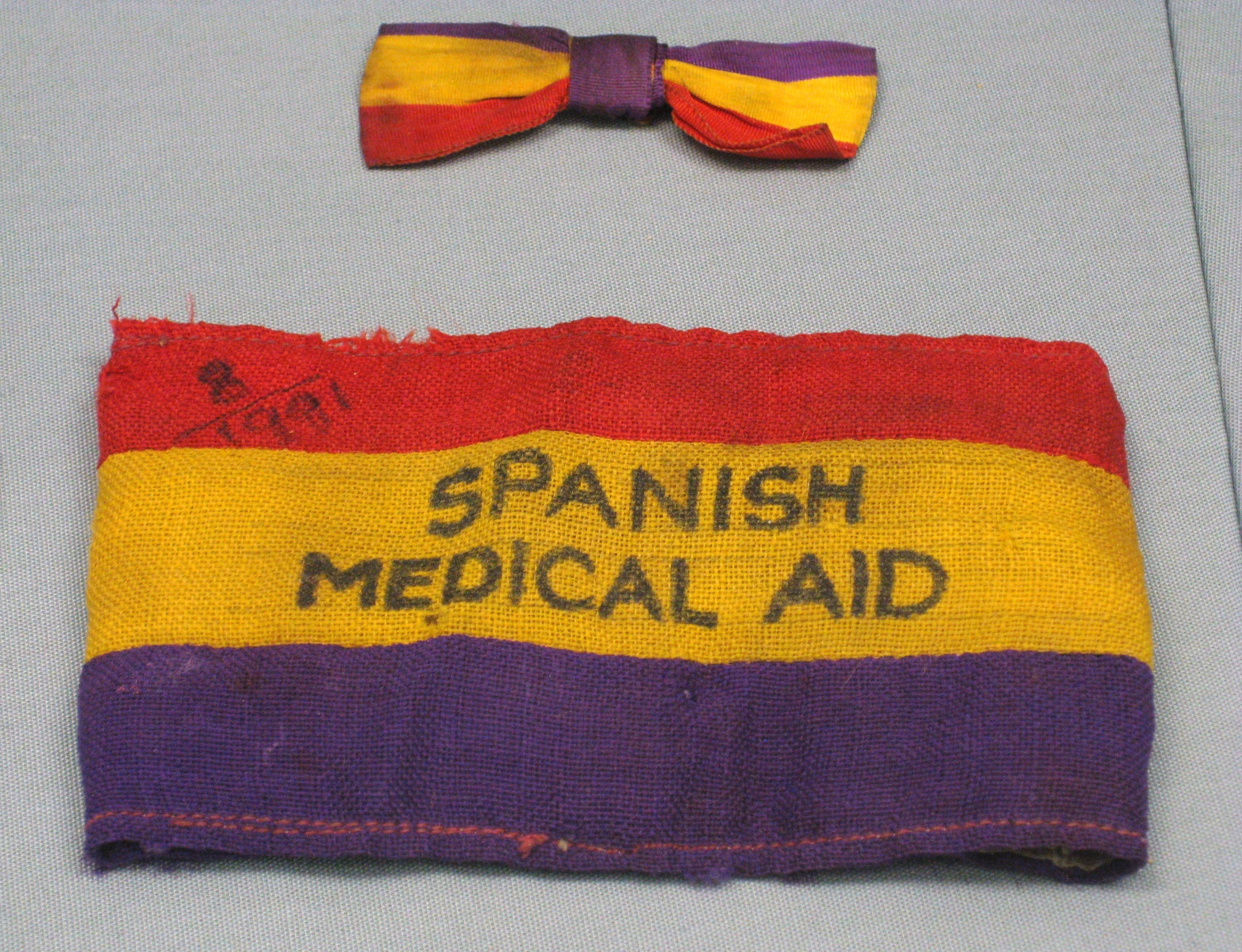
Ewart Milne
Ewart Milne (25 May 1903 – 14 January 1987) was an Irish poet who described himself on various book jackets as "a sailor before the mast, ambulance driver and courier during the Spanish Civil War, a land worker and estate manager in England during and after World War 2" and also "an enthusiast for lost causes – national, political, social and merely human". Life He was born in Dublin, of English and Welsh-Irish parents, and was educated at Christchurch Cathedral Grammar School.Clifford Dyment, Roy Fuller and Montagu Slater (editors), ''New Poems 1952'' (1952), p. 163-4. In 1920 he signed on as a seaman and worked on boats, off and on, until 1935. During the 30s too he began writing and had his first poems published in 1935. That year, Milne was one of the three founders of a duplicated publication called ''Irish Front'', together with two other poets, Charlie Donnelly and Leslie Daiken. The background to the Spanish Civil War contributed to his political awakening and he ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gayfield Press
Gayfield Park, commonly known as Gayfield, is a football stadium in Arbroath, Angus, Scotland. It is the home ground of Scottish Professional Football League team Arbroath F.C. The club have played at Gayfield since 1880, although the pitch has only been on its current alignment since the ground was redeveloped in 1925. The ground has a capacity of , including 861 seats. History Arbroath F.C. was formed in 1878 and played at Woodville Park and Hospitalfield before acquiring a former rubbish tip on the seafront to build Gayfield. The new ground was opened in 1880, with the first match being a Scottish Cup tie against Rob Roy. The original site was very cramped, with no room for spectators on the Dundee Road side; when Rangers lost to Arbroath in the Scottish Cup they protested that the pitch was too small, saying they had been "beaten on a back green", and won the replayed tie. In September 1885, Arbroath played Bon Accord in the Scottish Cup at Gayfield and won 36–0, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flann O'Brien
Brian O'Nolan ( ga, Brian Ó Nualláin; 5 October 1911 – 1 April 1966), better known by his pen name Flann O'Brien, was an Irish civil service official, novelist, playwright and satirist, who is now considered a major figure in twentieth century Irish literature. Born in Strabane, County Tyrone, he is regarded as a key figure in modernist and postmodern literature. His English language novels, such as ''At Swim-Two-Birds'' and ''The Third Policeman'', were written under the O’Brien pen name. His many satirical columns in ''The Irish Times'' and an Irish language novel ''An Béal Bocht'' were written under the name Myles na gCopaleen. O'Brien's novels have attracted a wide following for their unconventional humour and modernist metafiction. As a novelist, O'Brien was influenced by James Joyce. He was nonetheless sceptical of the "cult" of Joyce, saying "I declare to God if I hear that name Joyce one more time I will surely froth at the gob." Biography Family and early life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |