|
Cavelossim Beach
Cavelossim is a village in South Goa district in the state of Goa, India. The town hosts a well-known beach at the southernmost tip of the Salcete beach stretch that starts from Majorda in the north to Cavelossim in the south. The Sal River flows into the Arabian Sea at the south of this town. History Most of the history of Cavelossim comes from church records and from written statements by clergy originating from the village. The village was referred to as or 'village of the Shudra', as the majority of the burghers belonged to that caste. The Shudra usually worked as fisherman and as labour for the Bhatkars and Zamindars of the neighbouring villages of Assolna and Carmona. The only attraction was a small temple which housed the idol of the Hindu goddess Shantadurga, believed to be located around behind the current location of the church of Santa Cruz. (This temple is not to be confused with the much larger temple to the same deity in Deoolbhat, Quelossim, a simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Goa District
South Goa district is one of two districts that comprises the state of Goa, India, within the region known as the Konkan. It is bounded by North Goa district to the north, the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka state to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its western coast. History The Portuguese established a colony in Goa in 1510 and expanded the colony to its present boundaries during the 17th and 18th centuries. Goa was annexed by India on 19 December 1961. Goa and two other former Portuguese enclaves became the union territory of Goa, Daman and Diu, and Goa was organised into a single district in 1965. On 30 May 1987 Goa attained statehood (while Daman and Diu became a separate union territory), and Goa was reorganised into two districts, North Goa and South Goa. Administration Ruchika Katyal, an officer of the Indian Administrative Service, is the collector and district magistrate of South Goa. There are deputy collectors and ''mamlatdars'' for each sub Divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Conquest Of Goa
The Portuguese conquest of Goa occurred when the governor Afonso de Albuquerque captured the city in 1510 from the Adil Shahis. Goa became the capital of the Portuguese State of India which included possessions such as Fort Manuel, the territory of Bom Bahia, Damann and Chaul. It was not among the places Albuquerque was supposed to conquer. He did so after he was offered the support and guidance of Timoji and his troops. Albuquerque had been given orders by Manuel I of Portugal to capture Ormus, Aden and Malacca only.''Conversions and citizenry: Goa under Portugal, 1510–1610'' Délio de Mendonça pg. 82''ff'/ref> Background On November 4, 1509, Afonso de Albuquerque succeeded Dom Francisco de Almeida as Governor of the Portuguese State of India, after the arrival in India of the Marshal of Portugal Dom Fernando Coutinho, sent by King Manuel to enforce the orderly succession of Albuquerque to office. Unlike Almeida, Albuquerque realized that the Portuguese could take a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter-caste Marriage
Intercaste marriage (ICM), also known as marrying out of caste, is a form of exogamous nuptial union that involve two individuals belonging to different castes. Intercaste marriages are particularly perceived as socially unacceptable and taboo in most parts of South Asia. By region 5.8% of marriages in India is Intercaste marriage. Nepal Nepal has many castes and inter-caste marriage is generally considered taboo. However, this kind of marriage has been gradually gaining acceptance. In 1854, the Government of Nepal passed the "Muluki Ain" commissioned by Jung Bahadur Rana. This law outlawed marriage between people of a lower caste with those of a higher caste. In 1963, King Mahendra modified the law to abolish the "caste-based unequal citizenship". Since then, inter-caste marriage has been gradually gaining acceptance throughout Nepal. In 2009, the Government of Nepal announced that it would give a sum of रू100,000 Nepalese rupees (roughly US$1,350) away to couples who ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaddo
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they are composed of a nested hierarchy of administrative divisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the ''mandals'' of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana correspond to ''tehsils'' of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states but to ''talukas'' of Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu). The smaller subdivisions (villages and blocks) exist only in rural areas. In urban areas, urban local bodies exist instead of these rural subdivisions. Tiers of India The diagram below outlines the six tiers of government: Zones and regions Zones The states of India have been grouped into six zones having an Advisory Council "to develop the habit of cooperative working" among these States. Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. The North Eastern St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
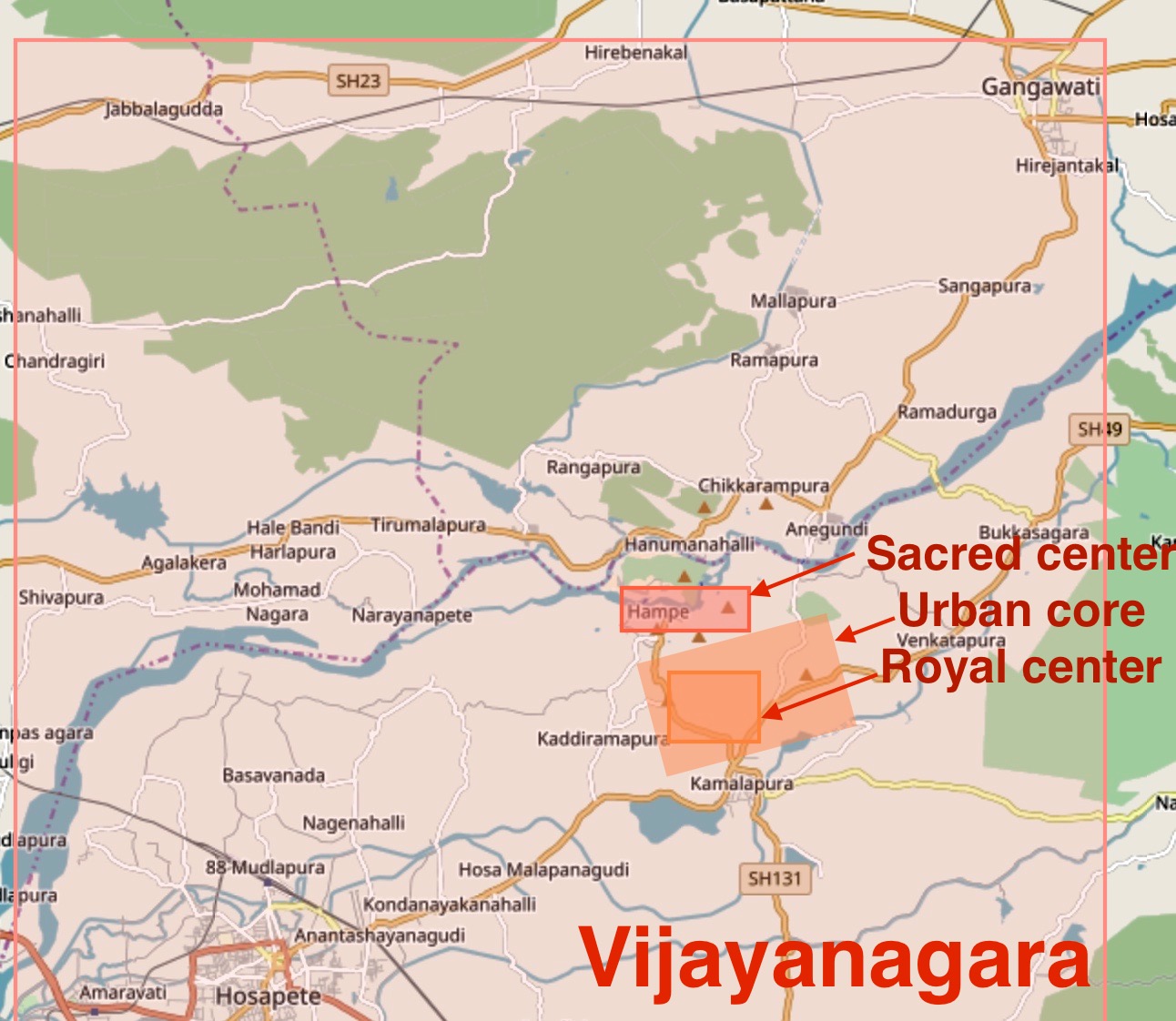
Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara () was the capital city of the historic Vijayanagara Empire. Located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, it spread over a large area and included the modern era Group of Monuments at Hampi site in Vijayanagara district, Bellary district and others in and around these districts in Karnataka, India. A part of Vijayanagara ruins known as Hampi has been designated as a UNESCO world heritage site. Vijayanagara is in the eastern part of central Karnataka, close to the Andhra Pradesh border.Vijayanagara Encyclopaedia Britannica Hampi is an ancient human settlement, mentioned in Hindu texts and has pre-Vijayanagara temples and monuments. In early 14th century, the Deccan region including the dominant Kakatiya Dynasty, Kakatiyas, Yadavas of Devagiri, Seuna Yadavas, Hoysala Empire, Hoysalas and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nayakas Of Keladi
Nayakas of Keladi (1499–1763), also known as Nayakas of Bednore and Ikkeri Nayakas, were an Indian dynasty based in Keladi in present-day Shimoga district of Karnataka, India. They were an important ruling dynasty in post-medieval Karnataka. They initially ruled as a vassal of the famous Vijayanagar Empire. After the fall of the empire in 1565, they gained independence and ruled significant parts of Malnad region of the Western Ghats in present-day Karnataka, most areas in the coastal regions of Karnataka, and parts of northern Kerala, Malabar and the central plains along the Tungabhadra river. In 1763 AD, with their defeat to Hyder Ali, they were absorbed into the Kingdom of Mysore. They played an important part in the history of Karnataka, during a time of confusion and fragmentation that generally prevailed in South India after the fall of the Vijayanagar Empire. The Keladi rulers were of the Vokkaliga:”Venkatappa. ruled from 1504 to 1551. His son Bhadrappa died b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nayaka Dynasties
Nayaka dynasties emerged during the Kakatiya dynasty and the Vijayanagara Empire period. The Nayakas were originally military governors under the Vijayanagara Empire. After the battle of Talikota, several of them declared themselves independent. Major Nayaka kingdoms The Nayaka kingdoms included the following: *Musunuri Nayakas, 14th century Kamma warrior-kings from Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. *Pemmasani Nayaks, 15th–17th century Kamma ruling clan from Andhra Pradesh. * Madurai Nayak, 16th–18th century Telugu rulers. * Thanjavur Nayak, 16th–17th century Telugu rules of Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu. * Nayaks of Gingee (Senji), 16th–17th century Telugu rulers from Tamil Nadu, previously governors of the Vijayanagara Empire. * Nayakas of Chitradurga, 16th–18th century from Karnataka, previously feudatory chiefs of Hoysala and Vijayanagara Empire. * Nayakas of Keladi, 16th–18th century ruling dynasty from Keladi, Karnataka. * Nayaks of Vellore, 16th century Telugu chieftains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested from the Rigveda, where a ' is a ruler, see for example the ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the Indian salute states (those granted a gun salute by the British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the Raja of Pindrawal * the Raja of Morni * the Raja of Rajouri * the Raja of Ali Rajpur * the Raja of Bilaspur * the Raja of Chamba * the Raja of Faridkot * the Raja of Jhabua * the Raja of Mandi * the Raja of Manipur * the Raja of Narsinghgarh * the Raja of Pudukkottai * the Raja of Rajgarh * the Raja of Sangli * the Raja of Sailana * the Raj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salcete
Salcete ( Konkani: ''Saxtti''/''Xaxtti''; pt, Salcette) is a sub-division of the district of South Goa, in the state of Goa, situated by the west coast of India. The Sal river and its backwaters dominate the landscape of Salcete. Historically, the sixty-six settlements south of the River Zuari formed the original Salcette territory. Salcete forms a part of the bigger Konkan region that stretches along the western shoreline of peninsular India. In erstwhile Portuguese Goa, the Salcette ''concelho'' (county) located in the ''Velhas Conquistas'' (Old Conquests) was co-terminous with the undivided Salcette territory (Salcete and Mormugaõ ''talukas''). In 1917, the ''concelho'' was bifurcated into the present-day ''talukas'' of Mormugao and Salcette. The contemporary Salcete ''taluka'' has been classified as a rurban area. Margao serves as the administrative headquarters of both Salcete ''taluka'' and the South Goa district. Etymology "Salcete" is the modern angli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormugao
Mormugao is a seaport city situated in the eponymous Mormugao taluka (municipality) of the South Goa district, South district, in the Goa state, India. It has a deep natural harbour and remains Goa's chief port. Towards the end of the Indo-Portuguese era in 1917, thirty-one settlements were carved out of the Salcette area, to form Morumugão with Mormugao seaport as its headquarters. The remaining thirty-five settlements were retained in Salcette which encompass the present-day Salcete ''taluka'' with Margao as its headquarters. Geography Mormugao is located at . It has an average elevation of 2 metres (7 feet). Demographics and Healthcare India census, Mormugao had a population of 97,085. Males constitute 53% of the population and females 47%. Mormugao has an average literacy rate of 75%, higher than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 80%, and female literacy is 70%. In Mormugão, 11% of the population is under 6 years of age. Konkani being the stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quelossim
Quelossim is a village in Mormugao taluka, South Goa, India. This village was known as ''Kardalipura'' in ancient times and had a beautiful temple dedicated to the Mother-Goddess Shri Shantadurga and Shri Kavale Math which was shifted to Kavale 450 years ago when the Portuguese demolished the shrine as a part of the inquisition. The original temple was built by a Goud Saraswat Brahman trader Anu Shenvi Mone, but was destroyed during the religious persecution period around 1566 AD. Today the exact location can be accessed from NH66 via Kesarval Spring en route to Rassaim or Loutolim, where one can see a few architectural ruins, in the form of the original temple lake. A small modern day shrine is seen under a huge banyan tree, at the end of this route property owned and maintained by Shree Shantadurga Saunsthan, Kavale and this area is protected by the Directorate of Archives and Archaeology, Government of Goa. The Konkani poet Krishnadas Shama Krishnadas Shama, a Gaud Saraswa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)