|
Caturidae
Caturidae is an extinct family of fishes belonging to the order Amiiformes (which contains the modern bowfin) which ranges from the Jurassic (possibly Triassic) to Cretaceous. Members of the family include ''Caturus ''Caturus'' (from el, κατω , 'down' and el, οὐρά 'tail') is an extinct genus of fishes in the family Caturidae in the order Amiiformes, related to modern bowfin. Fossils of this genus range from 200 to 109 mya. It has been suggested ...'', '' Strobilodus, Amblysemius,'' and '' Catutoichthys''. References Biolib Amiiformes Prehistoric ray-finned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amiiformes
The Amiiformes order of fish has only one extant species, the bowfin (''Amia calva''). These Amiiformes are found in the freshwater systems of North America, in the United States and parts of southern Canada. They live in freshwater streams, rivers, and swamps. Bowfins are not on the endangered list. They have the ability to go to the surface to breathe air if the water level is too low. Characteristics of Amiiformes are a cylindrical body with a long dorsal fin, single gular plate, heterocercal caudal fin, 10 to 13 flattened branchiostegal rays, maxilla included in gape, and prominent ocellus near upper base of caudal fin. Evolution and diversity The extinct species of the Amiiformes can be found as fossils in Asia and Europe, but the bowfin is the last living species in the order. Amiiformes is therefore the last surviving order of Halecomorphi, the clade to which the bowfin and its fossil relatives belong. Other orders, such as the Parasemionotiformes, are all extinct. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caturus
''Caturus'' (from el, κατω , 'down' and el, οὐρά 'tail') is an extinct genus of fishes in the family Caturidae in the order Amiiformes, related to modern bowfin. Fossils of this genus range from 200 to 109 mya. It has been suggested that the genus is non- monophyletic with respect to other caturid genera. Species * '' Caturus agassizi'' * '' Caturus chaperi'' * '' Caturus chirotes'' * '' Caturus dartoni'' * '' Caturus ferox'' * '' Caturus furcatus'' * '' Caturus heterurus'' * '' Caturus insignis'' * '' Caturus latipennis'' * '' Caturus porteri'' * '' Caturus retrodorsalis'' * '' Caturus stenospondylus'' * ''Caturus stenoura'' * '' Caturus velifer'' Distribution This genus is present in the Cretaceous of Germany, Japan, Spain, Tunisia, the United Kingdom, from the Jurassic to Cretaceous of France and the Permian The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
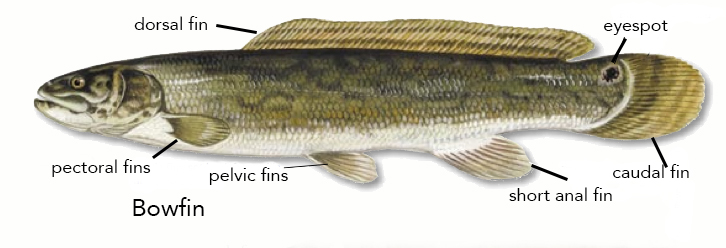
Bowfin
The bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a bony fish, native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being the sole surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "primitive fish" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. Now, their range is limited to much of the eastern United States and adjacent southern Canada, including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Ray-finned Fish Families
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)