|
Catherine Virginia Baxley
Catherine Virginia Baxley was a Confederate spy during the American Civil War. Baxley worked with infamous spy Rose Greenhow were imprisoned on December 30, 1861, and deported back to the confederate states in 1862. Later, Baxley continued being a blockade runner for the Confederacy during the civil war. She was arrested again while getting off a boat from Baltimore, Maryland and became a union prisoner. She was one of the first women confined in the Old Capital Prison, Washington, D.C. from February 24-July 2, 1865 where she was transferred after originally being held at Fort Greenhow. Like John Surratt, Baxley was a courier and carried letters across the union blockade. Baxley's son, a 17-year-old Confederate soldier, was also imprisoned at Old Capital Prison. The teenager had joined the Confederacy at 16. He arrived at the prison wounded after Baxley had already been captured for quite some time. His wounds were reportedly minor, but he was taken to the hospital infirmary. He e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rose O'Neal Greenhow
Rose O'Neal Greenhow (1813– October 1, 1864) was a renowned Confederate spy during the American Civil War. A socialite in Washington, D.C., during the period before the war, she moved in important political circles and cultivated friendships with presidents, generals, senators, and high-ranking military officers including John C. Calhoun and James Buchanan. She used her connections to pass along key military information to the Confederacy at the start of the war. In early 1861, she was given control of a pro-Southern spy network in Washington, D.C., by her handler, Thomas Jordan, then a captain in the Confederate Army. She was credited by Jefferson Davis, the Confederate president, with ensuring the South's victory at the First Battle of Bull Run in late July 1861. The government found that information was being leaked and the trail led to Rose Greenhow's residence. Greenhow was subject to house arrest; found to have continued her activities, in 1862 after an espionage h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
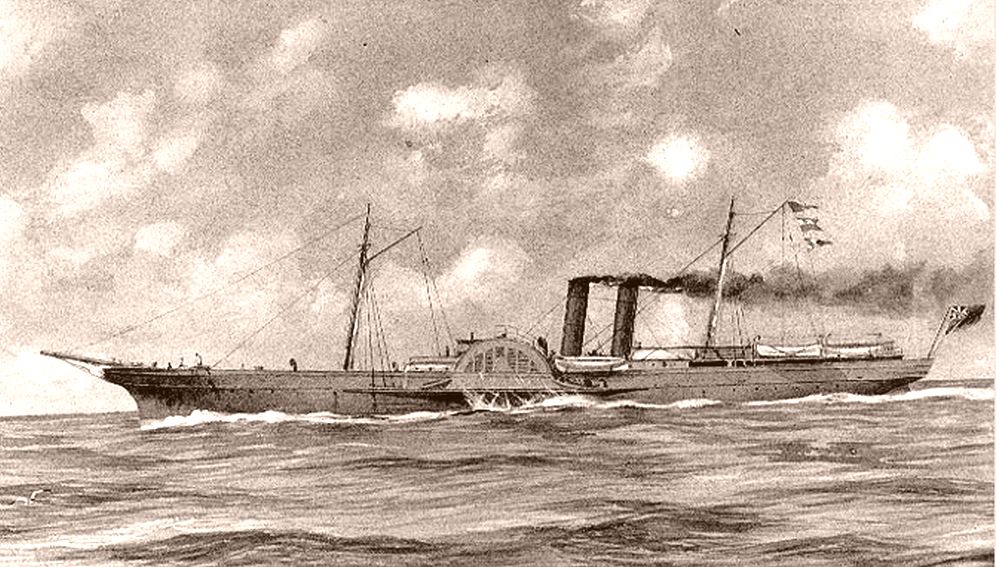
Blockade Runners Of The American Civil War
The blockade runners of the American Civil War were seagoing steam ships that were used to get through the Union blockade that extended some along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coastlines and the lower Mississippi River. The Confederate states were largely without industrial capability and could not provide the quantity of arms and other supplies needed to fight against the industrial north. To meet this need blockade runners were built in Scotland and England and were used to import the guns, ordnance and other supplies that the Confederacy desperately needed, in exchange for cotton that the British textile industry needed greatly. To penetrate the blockade, these relatively lightweight shallow draft ships, mostly built in British ship yards and specially designed for speed, but not suited for transporting large quantities of cotton, had to cruise undetected, usually at night, through the Union blockade. The typical blockade runners were privately owned vessels often operatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky and Missouri also declared secession and had full representation in the Confederate Congress, though their territory was largely controlled by Union forces. The Confederacy was formed on February 8, 1861, by seven slave states: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. All seven were in the Deep South region of the United States, whose economy was heavily dependent upon agriculture—particularly cotton—and a plantation system that relied upon enslaved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Capitol Prison
The Old Brick Capitol in Washington, D.C., served as the temporary Capitol of the United States from 1815 to 1819. The building was a private school, a boarding house, and, during the American Civil War, a prison known as the Old Capitol Prison. It was demolished in 1929, and its site is now occupied by the U.S. Supreme Court building. Site history The site, as with most of Capitol Hill, was part of Jenkins Hill and was acquired from the Carroll family to accommodate the U.S. Capitol. Located at 1st and A streets NE in Washington, D.C., on the eastern slope of Capitol Hill, the site's first building was a red brick tavern and hostel called Stelle's Hotel, built around 1800. It was part of a neighborhood of rooming houses catering to the U.S. Congress. Temporary U.S. Capitol, 1815–1819 In August 1814, during the War of 1812, the British burned the nearby United States Capitol building. The Congress, forced to meet in temporary quarters, pulled down the hostel at 1st and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Surratt
John Harrison Surratt Jr. (April 13, 1844 – April 21, 1916) was an American Confederate spy who was accused of plotting with John Wilkes Booth to kidnap U.S. President Abraham Lincoln; he was also suspected of involvement in the Abraham Lincoln assassination. His mother, Mary Surratt, was convicted of conspiracy by a military tribunal and hanged; she owned the boarding house that the conspirators used as a safe house and to plot the scheme. He avoided arrest immediately after the assassination by fleeing to Canada and then to Europe. He thus avoided the fate of the other conspirators, who were hanged. He served briefly as a Pontifical Zouave but was recognized and arrested. He escaped to Egypt but was eventually arrested and extradited. By the time of his trial, the statute of limitations had expired on most of the potential charges which meant that he was never convicted of anything. Early life He was born in 1844, to John Harrison Surratt Sr. and Mary Elizabeth Jenkins S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Surratt
Mary Elizabeth Jenkins SurrattCashin, p. 287.Steers, 2010, p. 516. (1820 or May 1823 – July 7, 1865) was an American boarding house owner in Washington, D.C., who was convicted of taking part in the conspiracy which led to the assassination of U.S. President Abraham Lincoln in 1865. Sentenced to death, she was hanged and became the first woman executed by the U.S. federal government. She maintained her innocence until her death, and the case against her was and remains controversial. Surratt was the mother of John Surratt, who was later tried, but due to statute of limitations, was not convicted. Born in Maryland in the 1820s, Surratt converted to Catholicism at a young age and remained a practicing Catholic for the rest of her life. She wed John Harrison Surratt in 1840 and had three children with him. An entrepreneur, John became the owner of a tavern, an inn, and a hotel. The Surratts were sympathetic to the Confederate States of America and often hosted fellow Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a member of the Democratic Party before the American Civil War. He had previously served as the United States Secretary of War from 1853 to 1857 under President Franklin Pierce. Davis, the youngest of ten children, was born in Fairview, Kentucky. He grew up in Wilkinson County, Mississippi, and also lived in Louisiana. His eldest brother Joseph Emory Davis secured the younger Davis's appointment to the United States Military Academy. After graduating, Jefferson Davis served six years as a lieutenant in the United States Army. He fought in the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) as the colonel of a volunteer regiment. Before the American Civil War, he operated in Mississippi a large cotton plantation which his brother Joseph had given him, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Missing
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Death Missing
Place may refer to: Geography * Place (United States Census Bureau), defined as any concentration of population ** Census-designated place, a populated area lacking its own municipal government * "Place", a type of street or road name ** Often implies a dead end (street) or cul-de-sac * Place, based on the Cornish word "plas" meaning mansion * Place, a populated place, an area of human settlement ** Incorporated place (see municipal corporation), a populated area with its own municipal government * Location (geography), an area with definite or indefinite boundaries or a portion of space which has a name in an area Placenames * Placé, a commune in Pays de la Loire, Paris, France * Plače, a small settlement in Slovenia * Place (Mysia), a town of ancient Mysia, Anatolia, now in Turkey * Place, New Hampshire, a location in the United States * Place House, a 16th-century mansion largely remodelled in the 19th century, in Fowey, Cornwall * Place House, a 19th-century mansion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Birth Missing
Place may refer to: Geography * Place (United States Census Bureau), defined as any concentration of population ** Census-designated place, a populated area lacking its own municipal government * "Place", a type of street or road name ** Often implies a dead end (street) or cul-de-sac * Place, based on the Cornish word "plas" meaning mansion * Place, a populated place, an area of human settlement ** Incorporated place (see municipal corporation), a populated area with its own municipal government * Location (geography), an area with definite or indefinite boundaries or a portion of space which has a name in an area Placenames * Placé, a commune in Pays de la Loire, Paris, France * Plače, a small settlement in Slovenia * Place (Mysia), a town of ancient Mysia, Anatolia, now in Turkey * Place, New Hampshire, a location in the United States * Place House, a 16th-century mansion largely remodelled in the 19th century, in Fowey, Cornwall * Place House, a 19th-century mansion on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women In The American Civil War
During the American Civil War, sexual behavior, gender roles, and attitudes were affected by the conflict, especially by the absence of menfolk at home and the emergence of new roles for women such as nursing. The advent of photography and easier media distribution, for example, allowed for greater access to sexual material for the common soldier. Nursing Union During the Civil War (1861–65), the United States Sanitary Commission, a federal civilian agency, handled most of the medical and nursing care of the Union armies, together with necessary acquisition and transportation of medical supplies. Dorothea Dix, serving as the Commission's Superintendent, was able to convince the medical corps of the value of women working in 350 Commission or Army hospitals. North and South, over 20,000 women volunteered to work in hospitals, usually in nursing care. They assisted surgeons during procedures, gave medicines, supervised the feedings and cleaned the bedding and clothes. They gave go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |