|
Cathedral Peak Granodiorite
The Cathedral Peak Granodiorite (CPG) was named after its type locality, Cathedral Peak in Yosemite National Park, California. The granodiorite forms part of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite (Tuolumne Batholith), one of the four major intrusive suites within the Sierra Nevada. It has been assigned radiometric ages between 88 and 87 million years and therefore reached its cooling stage in the Coniacian (Upper Cretaceous). Geographic situation The Cathedral Peak Granodiorite forms part of the central eastern Sierra Nevada in California. It is exposed in glaciated outcrops from the upper Yosemite Valley into the high Sierra Divide. It covers large parts of Mariposa County and Tuolumne County and also touches Madera County and Mono County. At its northern end it includes Tower Peak and Matterhorn Peak, at 12,264 feet (3743 m) its highest elevation. In its southwestern section rises the Cathedral Range with the 10,911 feet Cathedral Peak (3326 m) above Tuolumne Meadows. Califor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mya (unit)
Mya or MYA may refer to: Brands and product names * Mya (TV channel), an Italian Television channel * Mya (program), an intelligent personal assistant created by Motorola * Midwest Young Artists, a comprehensive youth music program Codes * Burmese language (ISO 639-3: ) * Moruya Airport (IATA code: MYA), New South Wales, Australia * The IOC, license plate, and UNDP country code for Myanmar Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ... People * Mya (given name) * Mya (singer) (Mya Marie Harrison, born 1979), American R&B singer-songwriter and actress * Bo Mya (1927–2006), Myanmar rebel leader and chief commander of the Karen National Union Other uses * ''Mýa'' (album), a 1998 album by Mýa * ''Mya'' (bivalve), a genus of soft-shell clams * Million years a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tower Peak (California)
Tower Peak is a mountain in the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada of Mono County, California, Mono and Tuolumne County, California, Tuolumne County, California. To the south of the summit is Yosemite National Park and to the north is the Hoover Wilderness. Mary Lake (Tuolumne County, California), Mary Lake is to the west, Ehrnbeck Peak and Hawksbeak Peak to the east. To the south are Wells Peak and Craig Peak. The next higher mountain is Eagle Peak (Mono County, California), Eagle Peak, about 8 mi east-northeast. Climate Tower Peak is located in an alpine climate zone. Most weather fronts originate in the Pacific Ocean, and travel east toward the Sierra Nevada mountains. As fronts approach, they are forced upward by the peaks (orographic lift), causing them to drop their moisture in the form of rain or snowfall onto the range. References {{California highest Mountains of the Sierra Nevada (United States) Mountains of Mono County, California Mountains of Tuolumne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Map Of Cathedral Peak Granodiorite
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metasediment
In geology, metasedimentary rock is a type of metamorphic rock. Such a rock was first formed through the deposition and solidification of sediment Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of .... Then, the rock was buried underneath subsequent rock and was subjected to high pressures and temperatures, causing the rock to recrystallize. The overall composition of a metasedimentary rock can be used to identify the original sedimentary rock, even where they have been subject to high-grade metamorphism and intense deformation. Types of metasedimentary rocks See also * References Metamorphic petrology {{Rock-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metavolcanic
Metavolcanic rock is volcanic rock that shows signs of having experienced metamorphism. In other words, the rock was originally produced by a volcano, either as lava or tephra. The rock was then subjected to high pressure, high temperature or both, for example by burial under younger rocks, causing the original volcanic rock to recrystallize. Metavolcanic rocks are sometimes described informally as ''metavolcanics''. When it is possible to determine the original volcanic rock type from the properties of the metavolcanic rock (particularly if the degree of metamorphism is slight), the rock is more precisely named by appylying the prefix ''meta-'' to the original rock type. For example, a weakly metamorphosed basalt would be described as a '' metabasalt'', or a weakly metamorphosed tuff as a ''metatuff''. Metavolcanic rock is commonly found in greenstone belt Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the second and middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era as well as the eighth period of the Phanerozoic, Phanerozoic Eon and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP). The beginning of the Toarcian Age started around 183 million years ago and is marked by the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event, a global episode of Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated global temperatures associated with extinctions, likely caused by the eruption of the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six period (geology), geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (geologist), John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''palaiós'' (π� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
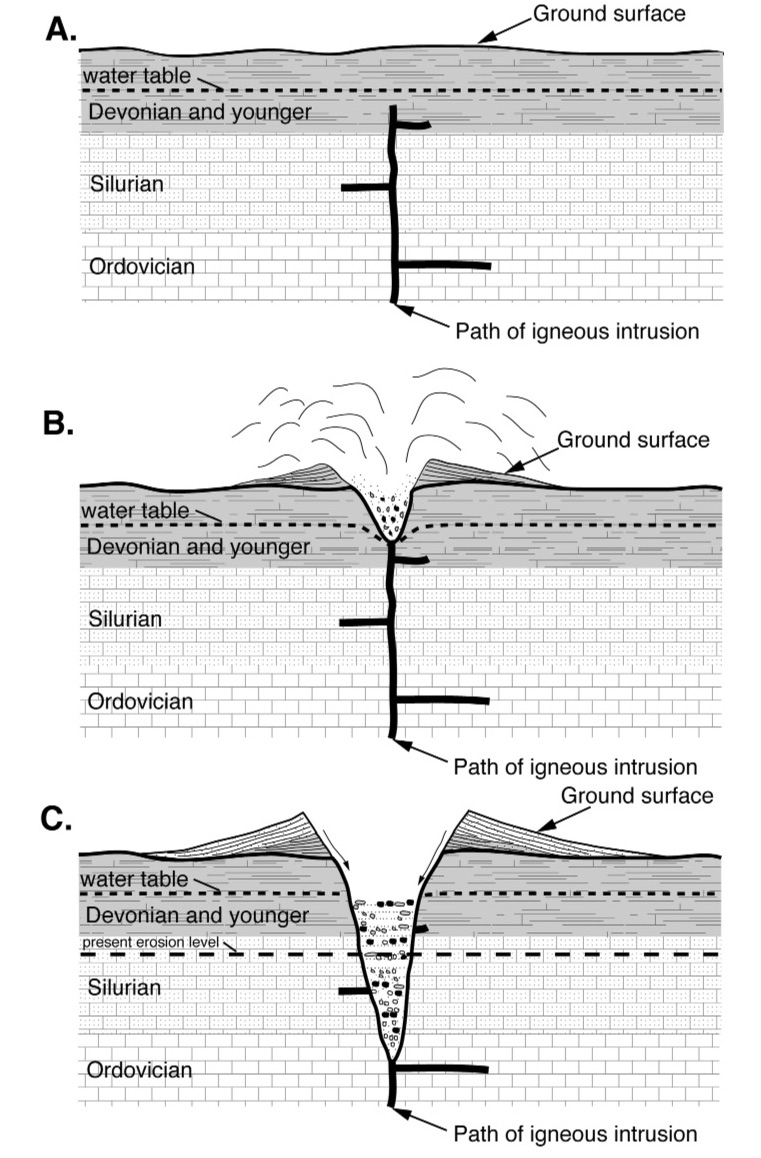
Country Rock (geology)
In geology, country rock is the rock native to an area, in contrast to any intrusion of viscous geologic material, commonly magma, or perhaps rock salt (in salt domes) or unconsolidated sediments. Magma is typically less dense than the rock it intrudes, widening and filling existing cracks, sometimes melting the already-existing country rock. The term "country rock" is similar to, and in many cases interchangeable with, the terms basement and wall rocks. Country rock can denote the widespread lithology of a region in relation to the rock which is being discussed or observed. Geologic settings Settings in geology when the term ''country rock'' is used include: Igneous intrusions When describing a pluton or dike, the igneous rock can be described as intruding the surrounding ''country rock'', the rock into which the pluton has intruded.Newfoundland and LabradorGlossary of Geological Terms Accessed June 2018. When country rock is intruded by a dike, perpendicular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including Regional metamorphism, regional, Contact metamorphism, contact, Hydrothermal metamorphism, hydrothermal, Shock metamorphism, shock, and Dynamic metamorphism, dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kuna Crest Granodiorite
Kuna Crest Granodiorite (also called ''Granodiorite of Glen Aulin''), is found, in Yosemite National Park, United States. The granodiorite forms part of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite (aka Tuolumne Batholith), one of the four major intrusive suites within the Sierra Nevada. Of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite, it is the oldest and darkest rock.The Geologic Story of Yosemite National Park (1987), "Rocks, the building materials," by N. King Huberthe oldest and darkest rock in the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite accessdate: 7 March 2017 Kuna Crest granodiorite forms most of the outer part of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite, on the edges. Name The word ''Kuna'' probably derives from a Shoshonean word, with a meaning "fire," appearing in the Mono dialect of the area, with meaning of ''firewood''. The rocks on Kuna Peak can be a red colorAttractions in Kuna PeakAttractions in Kuna Peak accessdate: 10 March 2017 and Kuna Peak is the highest point on Kuna Crest. Kuna Crest granodiorite was first i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Half Dome Granodiorite
Half Dome Granodiorite is granodiorite (see also granite) found in a region on and near Half Dome, in Yosemite National Park, California, United States. The granodiorite forms part of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite (aka Tuolumne Batholith), one of the four major intrusive suites within the Sierra Nevada. Mineralogy The granodiorite has large crystals of biotite, hornblende, and both feldspars — orthoclase and plagioclase. The space between crystals tends to be filled with quartz. The hornblende tends to have large, over rectangular crystals. The biotite forms hexagonal "blocks," up to across. A knife blade can peel the edges. Sphene is found in Half Dome Granodiorite. The grains are honey-colored, and large at across. Uranium is also present. From petrographic observation, the average mineral proportion of non-layered rocks of Half Dome Granodiorite is 45% plagioclase feldspar, 25% quartz, 8% biotite, 15% K-feldspar, 5% hornblende, 1% titanite, and 1% magnetite. Age H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Johnson Granite Porphyry
Johnson Granite Porphyry is found in Tuolumne Meadows, Yosemite National Park. Johnson Granite Porphyry was named for Johnson Peak, the highest mountain in Tuolumne Meadows, Yosemite National Park. Its area is estimated at , the exposed area covering roughly .Glazner, Allen F, Stock, Greg M. (2010). ''Geology Underfoot in Yosemite''. Mountain Press, p. 53. . Johnson Granite Porphyry is part of the Tuolumne Batholith. Its boundaries are difficult to trace, and are irregular. It is both the youngest, and the most siliceous rock of Tuolumne Intrusive Suite. Geology The innermost, most felsic part of the Tuolumne Batholith is the Johnson Granite Porphyry. It is a highly irregular, elongated body. Completely surrounding it is the much larger body of Cathedral Peak granite. Field observations and magnetic fabrics suggest an extrusive event, that is, Johnson Granite Porphyry may record possible volcanism. This may relate to deformation along active shear zones. Johnson Granite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |